Copyright
©2010 Baishideng.
World J Gastroenterol. Jul 7, 2010; 16(25): 3211-3214
Published online Jul 7, 2010. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v16.i25.3211
Published online Jul 7, 2010. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v16.i25.3211
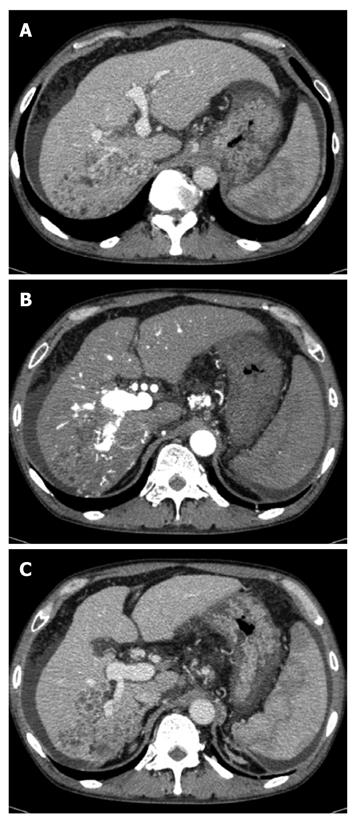
Figure 1 Computed tomography examination.
A: Low-density lesion in the posterior segment of the liver, which pressed the vena cava and right hepatic vein and opposed the right anterior superior portal vein; B: Hyper-enhanced portal vein during the arterial phase; C: Tumor thrombus in the posterior branch of the portal vein. A tumor opposed the right anterior inferior portal vein.
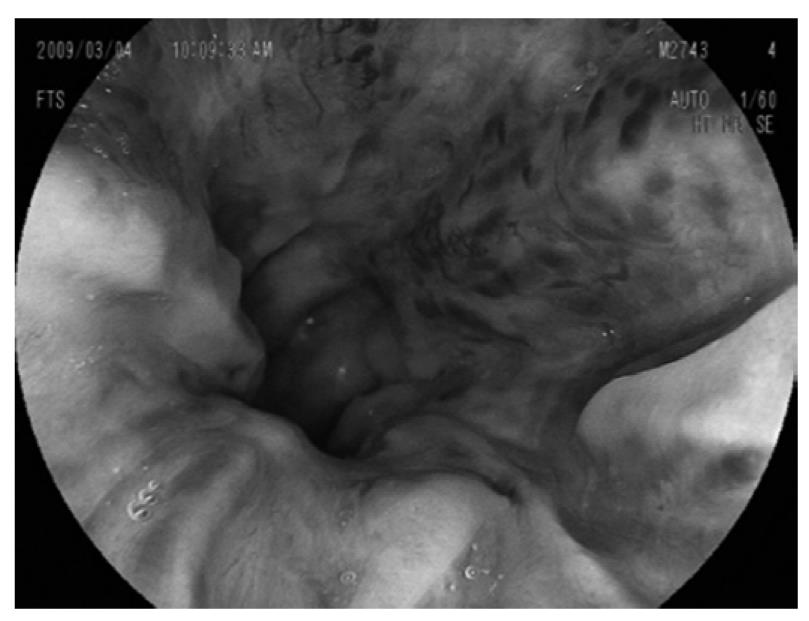
Figure 2 Upper gastrointestinal endoscopy revealing severe esophageal varices.
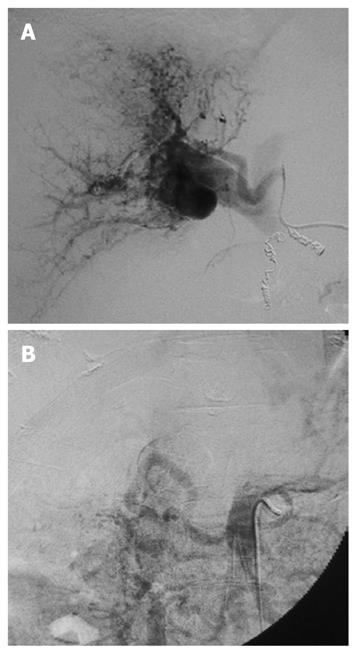
Figure 3 Arteriography.
A: Right hepatic arteriography exhibiting the right portal vein, caused by severe intratumoral arterioportal shunt; B: Transarterial portography revealing non-enhancement of the portal vein because of portal hypertension.
- Citation: Ishii H, Sonoyama T, Nakashima S, Nagata H, Shiozaki A, Kuriu Y, Ikoma H, Nakanishi M, Ichikawa D, Fujiwara H, Okamoto K, Ochiai T, Kokuba Y, Sakakura C, Otsuji E. Surgical treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma with severe intratumoral arterioportal shunt. World J Gastroenterol 2010; 16(25): 3211-3214
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v16/i25/3211.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v16.i25.3211