Copyright
©2010 Baishideng.
World J Gastroenterol. Apr 28, 2010; 16(16): 1979-1985
Published online Apr 28, 2010. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v16.i16.1979
Published online Apr 28, 2010. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v16.i16.1979
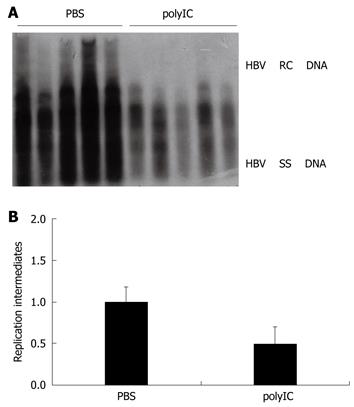
Figure 1 Evaluation of the effect of polyIC on hepatitis B virus (HBV) replication using the HBV replication mouse model.
A: The effect of polyIC on HBV DNA replication intermediates in mouse model. After hydrodynamic transfection, mice were treated with phosphate-buffered saline (PBS) (control) or polyIC; B: The relative intensity of HBV DNA replication intermediates of the mouse model for PBS group and polyIC group which inhibited the HBV replication by about one fold. The levels of HBV DNA replication intermediates in PBS-treated group were set to 1, and the relative levels of polyIC-treated group were calculated accordingly.
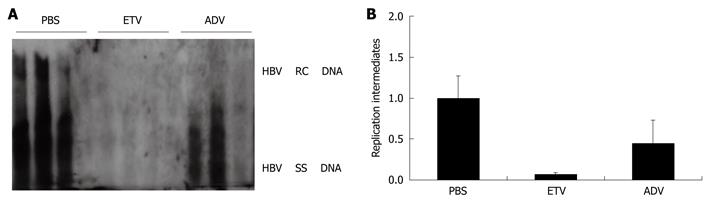
Figure 2 Evaluation of the effect of nucleoside analogues entecavir (ETV) and adefovir (ADV) on HBV replication using the HBV replication mouse model.
After hydrodynamic transfection, mice were administered by oral gavage with two different nucleoside analogues: entecavir at a dose of 0.075 mg/kg per day and adefovir at a dose of 1.5 mg/kg per day for 3 d. A: HBV DNA replication intermediates in the mouse model treated with PBS (control), entecavir and adefovir, respectively; B: The relative levels of HBV DNA replication intermediates in the mouse model among different groups treated with PBS (control), entecavir and adefovir, respectively. The levels of HBV DNA replication intermediates in PBS treated group were set to 1, and the relative levels of treated groups were calculated accordingly.
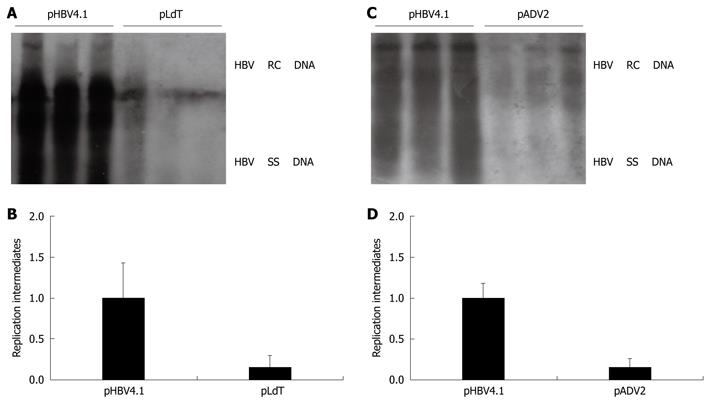
Figure 3 Assessment of HBV replication ability of drug-resistant HBV mutants using the HBV replication mouse model.
The levels of HBV DNA replication intermediates in wild type group were set to 1, and the relative levels of mutant groups were calculated accordingly. A, B: The HBV DNA replication intermediates and relative intensity between wild type injected with pHBV4.1 and telbivudine resistance mutant injected with pLdT (rtM204I); C, D: The HBV DNA replication intermediates and relative intensity between wild type injected with pHBV4.1 and adefovir resistance mutant injected with pADV2 (rtA181V + N236T).
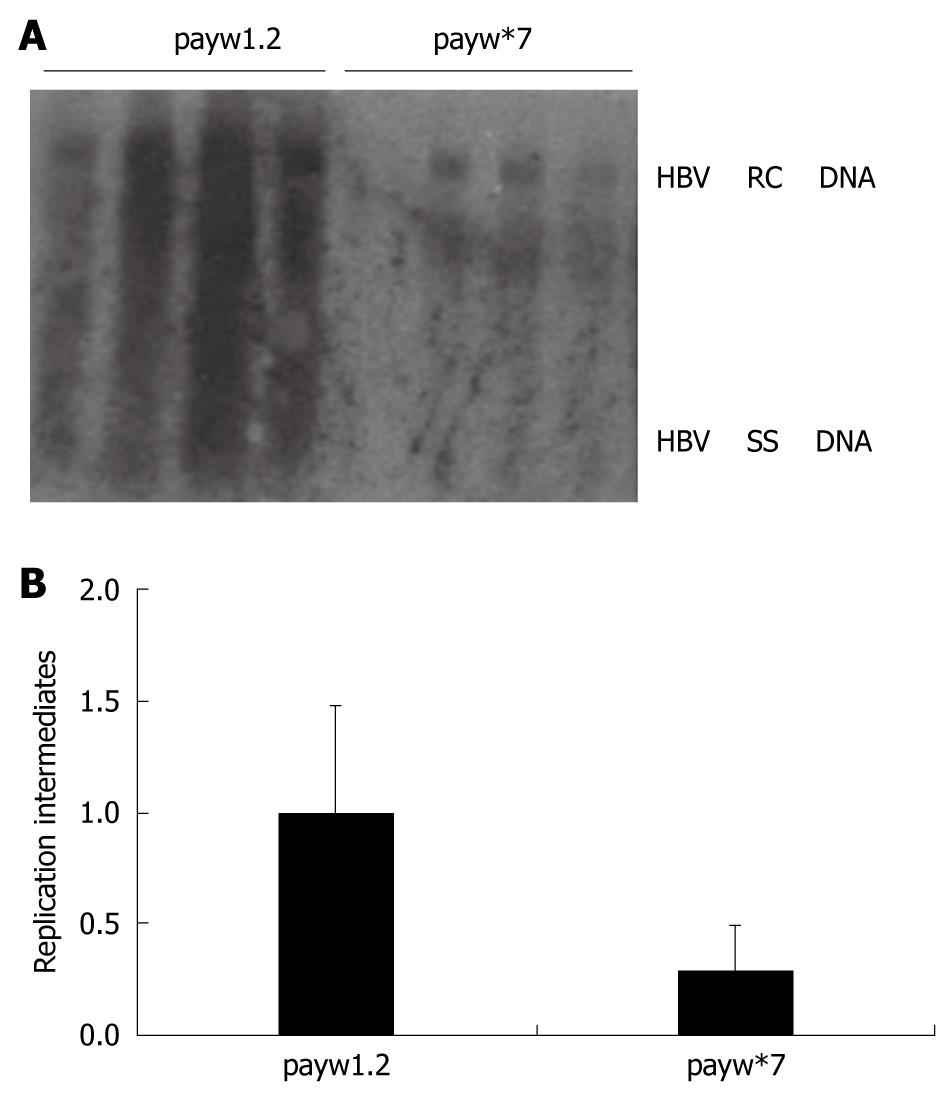
Figure 4 Assessment of HBV replication ability of HBx-minus mutant using the HBV replication mouse model.
A: The levels of HBV DNA replication intermediates between wild group injected with payw1.2 and HBx-minus mutant group injected with payw*7; B: The relative intensity of HBV DNA replication intermediates between wild group injected with payw1.2 and HBx-minus mutant group injected with payw*7. The levels of HBV DNA replication intermediates were reported to the levels of the mice injected with payw1.2, which were set at 1.
- Citation: Gao Z, Liu FJ, Liu L, Zhou TY, Lei J, Xu L, Liu C, Dai J, Chen EQ, Tang H. Application of hepatitis B virus replication mouse model. World J Gastroenterol 2010; 16(16): 1979-1985
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v16/i16/1979.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v16.i16.1979