Copyright
©2010 Baishideng.
World J Gastroenterol. Apr 21, 2010; 16(15): 1859-1866
Published online Apr 21, 2010. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v16.i15.1859
Published online Apr 21, 2010. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v16.i15.1859
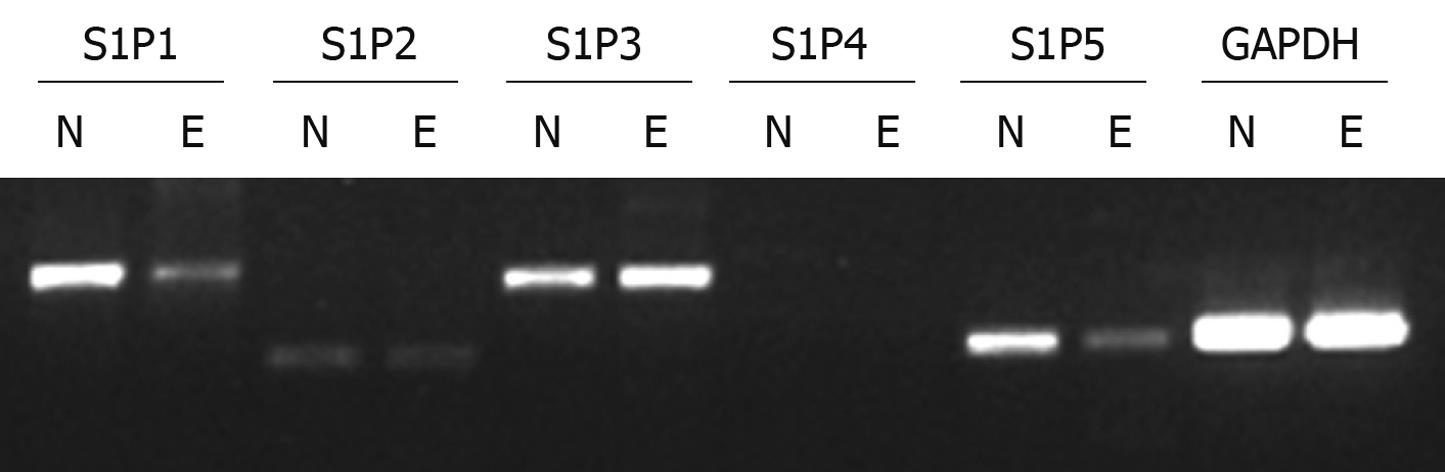
Figure 1 Expression of sphingosine 1-phosphate (S1P) receptors in normal human esophageal mucosal epithelium and Eca109 cell line.
N: Normal human esophageal mucosal epithelium; E: Eca109 cell line.
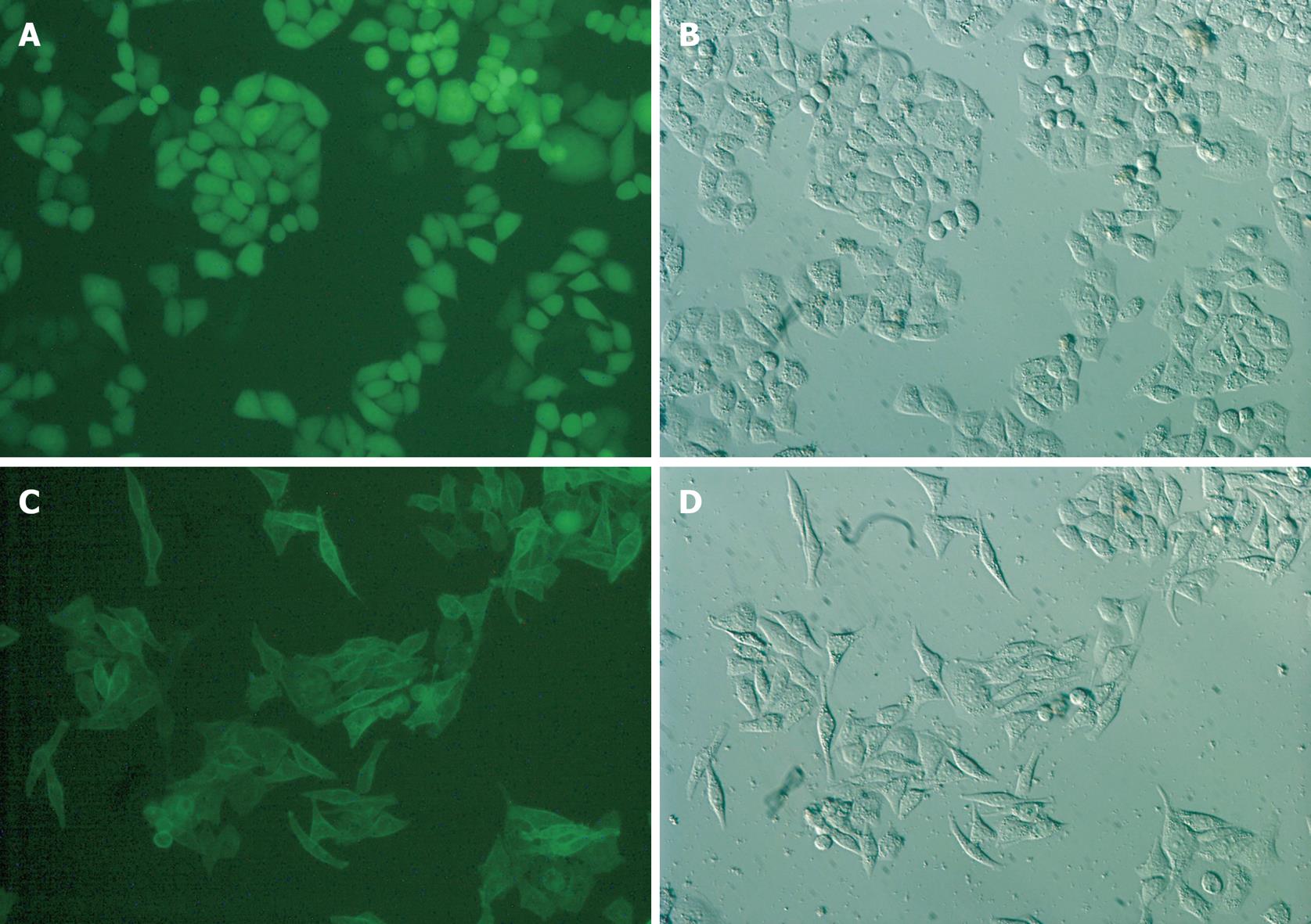
Figure 2 S1P5 receptor overexpression in Eca109 cells causes cell spindle change with elongated and extended filopodia-like projections in a medium containing 10% FBS or 0.
1% fatty acid-free BSA (× 200). A, B: Eca109/control-EGFP; C, D: Eca109/S1P5-EGFP.
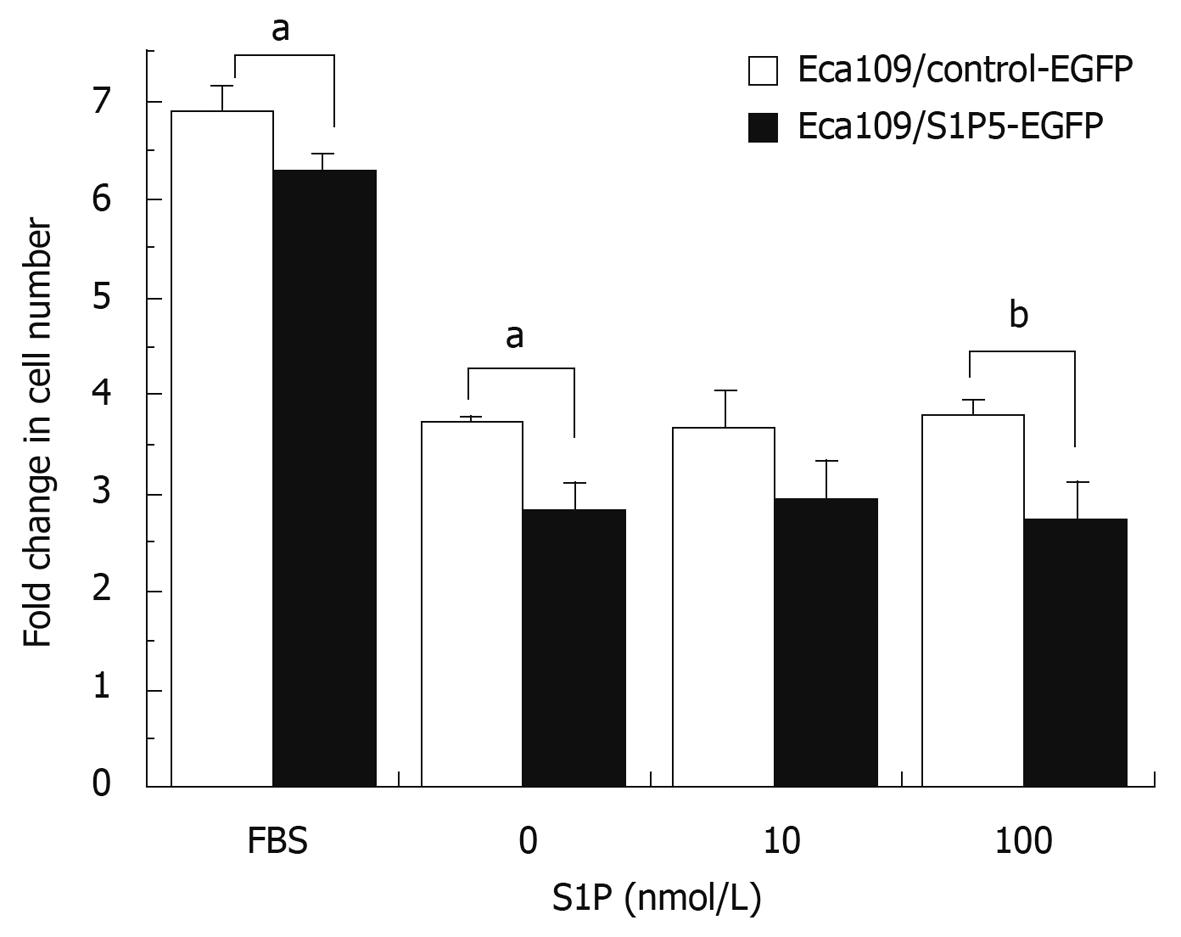
Figure 3 MTT assay showing proliferation of control-EGFP or S1P5-EGFP-transfected Eca109 cells.
aP < 0.05, bP < 0.01 vs control group.
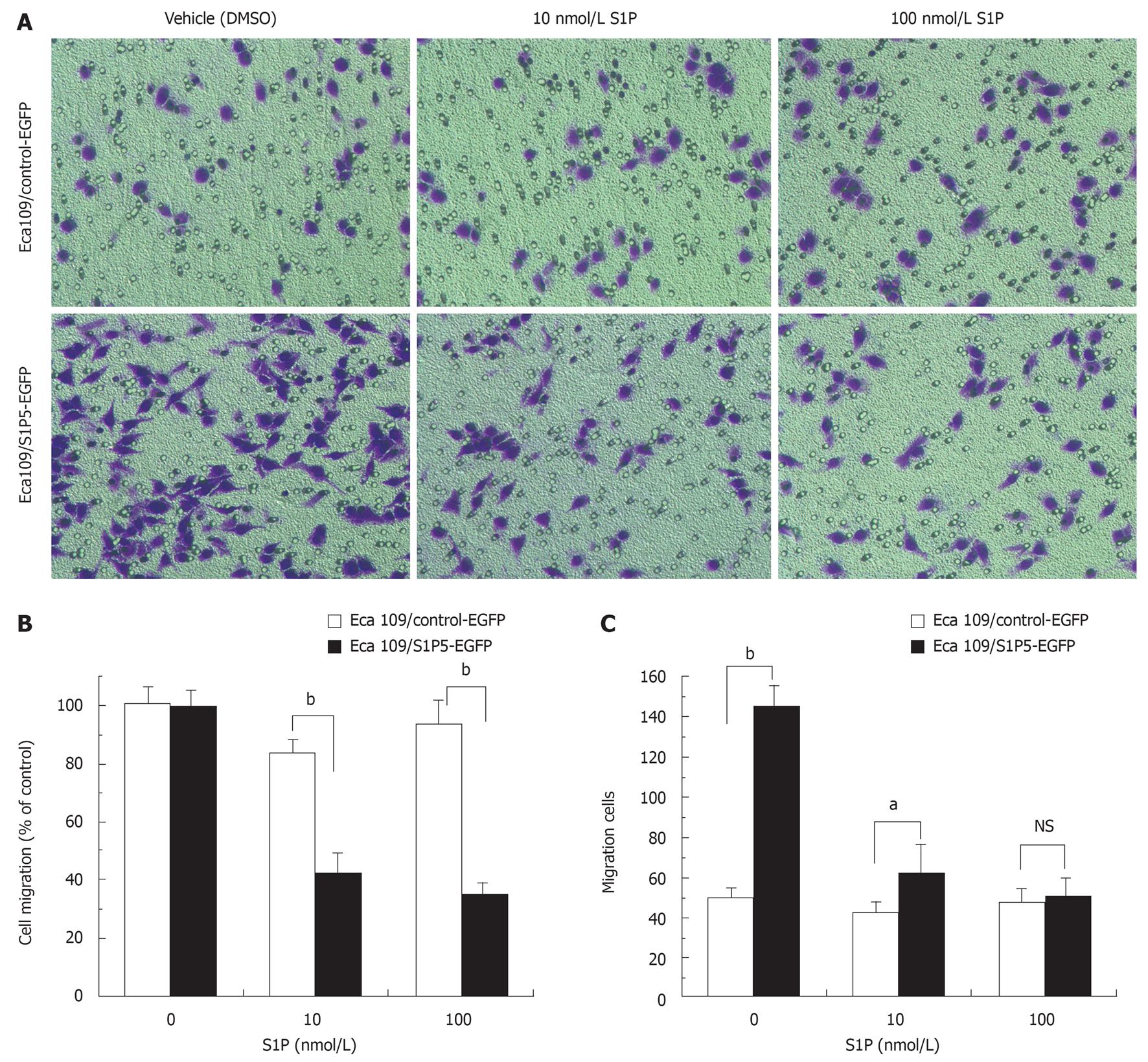
Figure 4 Effect of S1P on migration of S1P5-EGFP-transfected Eca109 cells and control-EGFP Eca109 cells.
A: Eca109 cells are allowed to migrate for 8 h, and stained with crystal violet (× 200); B: Results are expressed as percentage in cell migration of S1P-treated cells compared to vehicle (DMSO)-treated cells; C: Results are expressed as migration cell number. aP < 0.05, bP < 0.001 indicate a statistically significant effect between S1P5-EGFP and control-EGFP transfected Eca109 cells treated by indicated concentrations of S1P or vehicle. NS: Not significant.
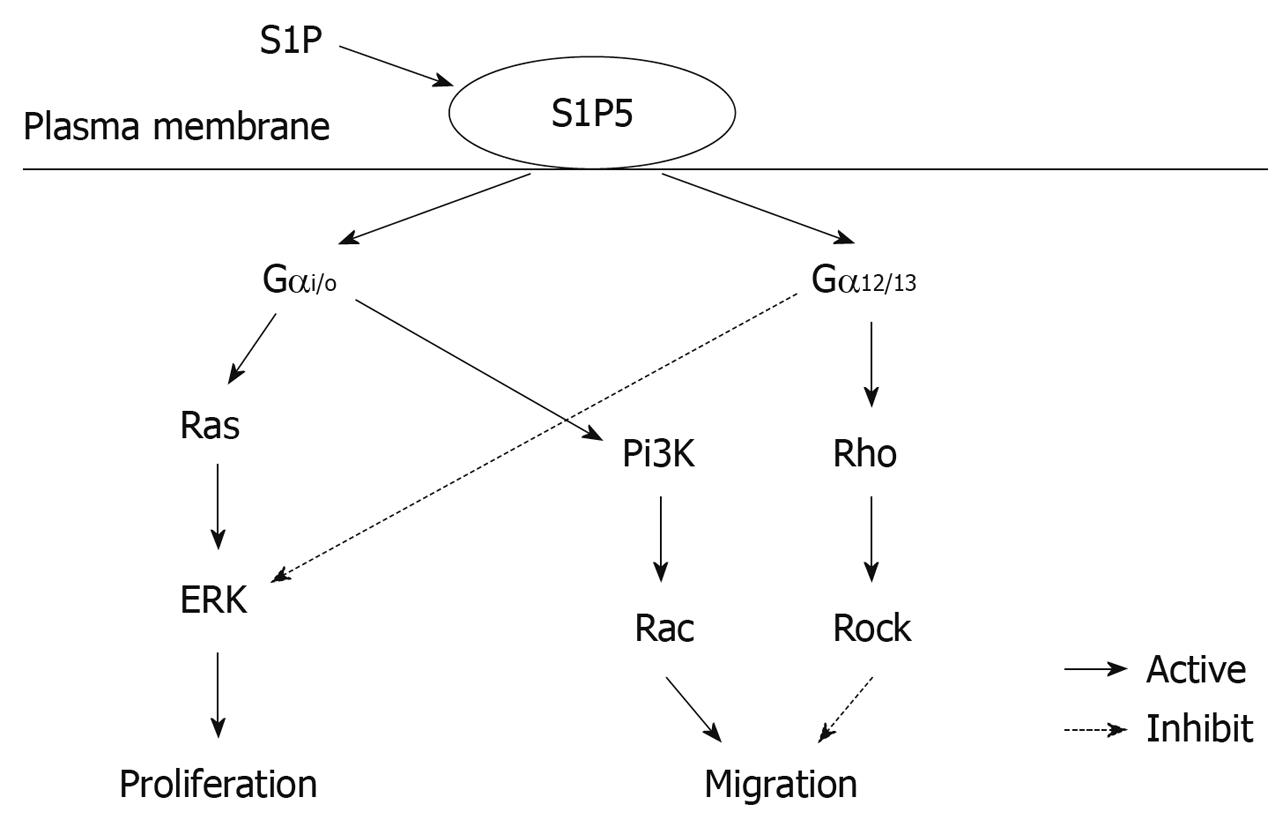
Figure 5 Putative signaling pathway of S1P5.
- Citation: Hu WM, Li L, Jing BQ, Zhao YS, Wang CL, Feng L, Xie YE. Effect of S1P5 on proliferation and migration of human esophageal cancer cells. World J Gastroenterol 2010; 16(15): 1859-1866
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v16/i15/1859.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v16.i15.1859