Copyright
©2010 Baishideng.
World J Gastroenterol. Mar 28, 2010; 16(12): 1541-1544
Published online Mar 28, 2010. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v16.i12.1541
Published online Mar 28, 2010. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v16.i12.1541
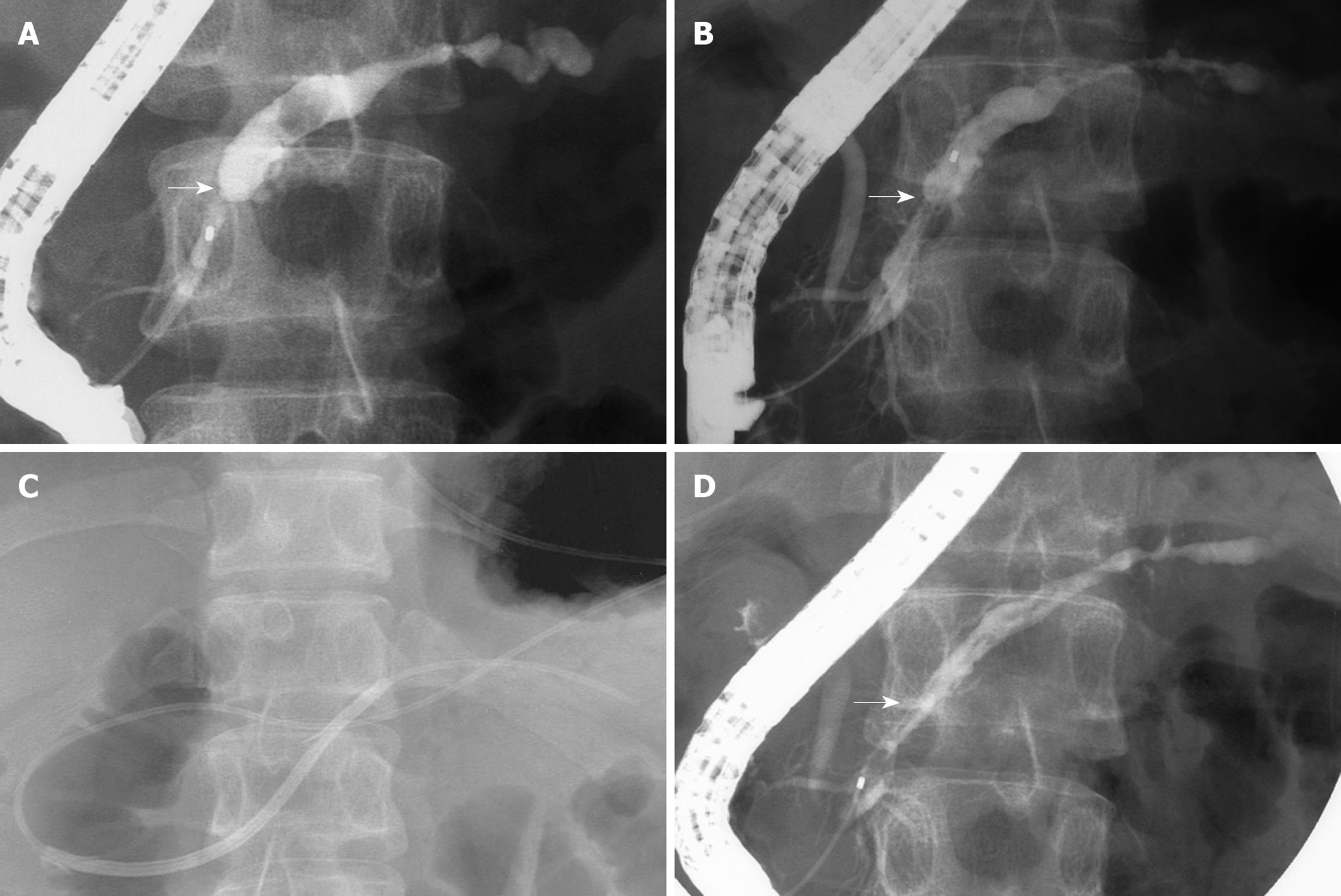
Figure 1 Pancreatic duct incision of a refractory pancreatic duct stricture.
A: Pancreatography reveals a short pancreatic duct stricture (arrow) and upstream ductal dilation; B: Pancreatography after removal of a 10-Fr stent shows a stricture (arrow) still remaining; C: Wire-guided snare forceps are advanced into the pancreatic duct through the major papilla; D: Pancreatography reveals resolution of pancreatic duct stricture (arrow).
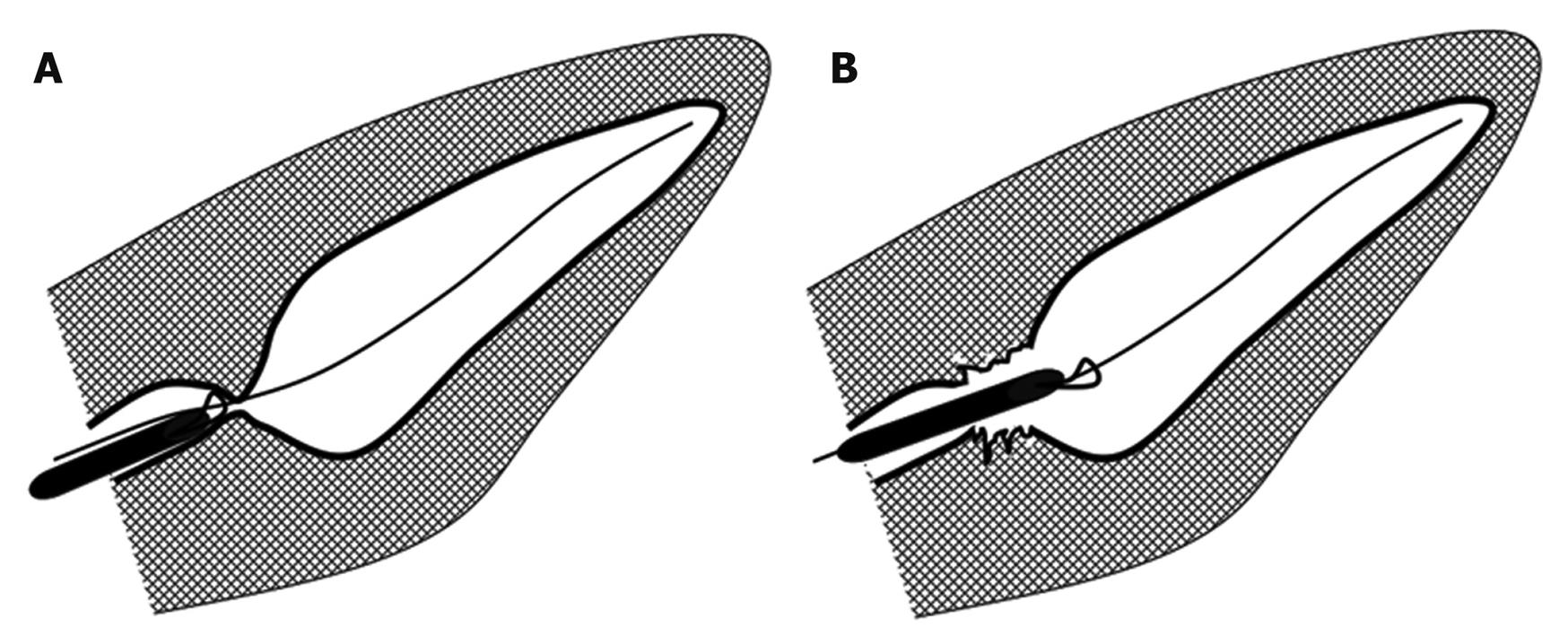
Figure 2 Diagram of pancreatic duct incision using snare forceps.
A: Snare forceps are advanced into the pancreatic duct stricture; B: Pancreatic duct incision is performed with an electrocautery snare.
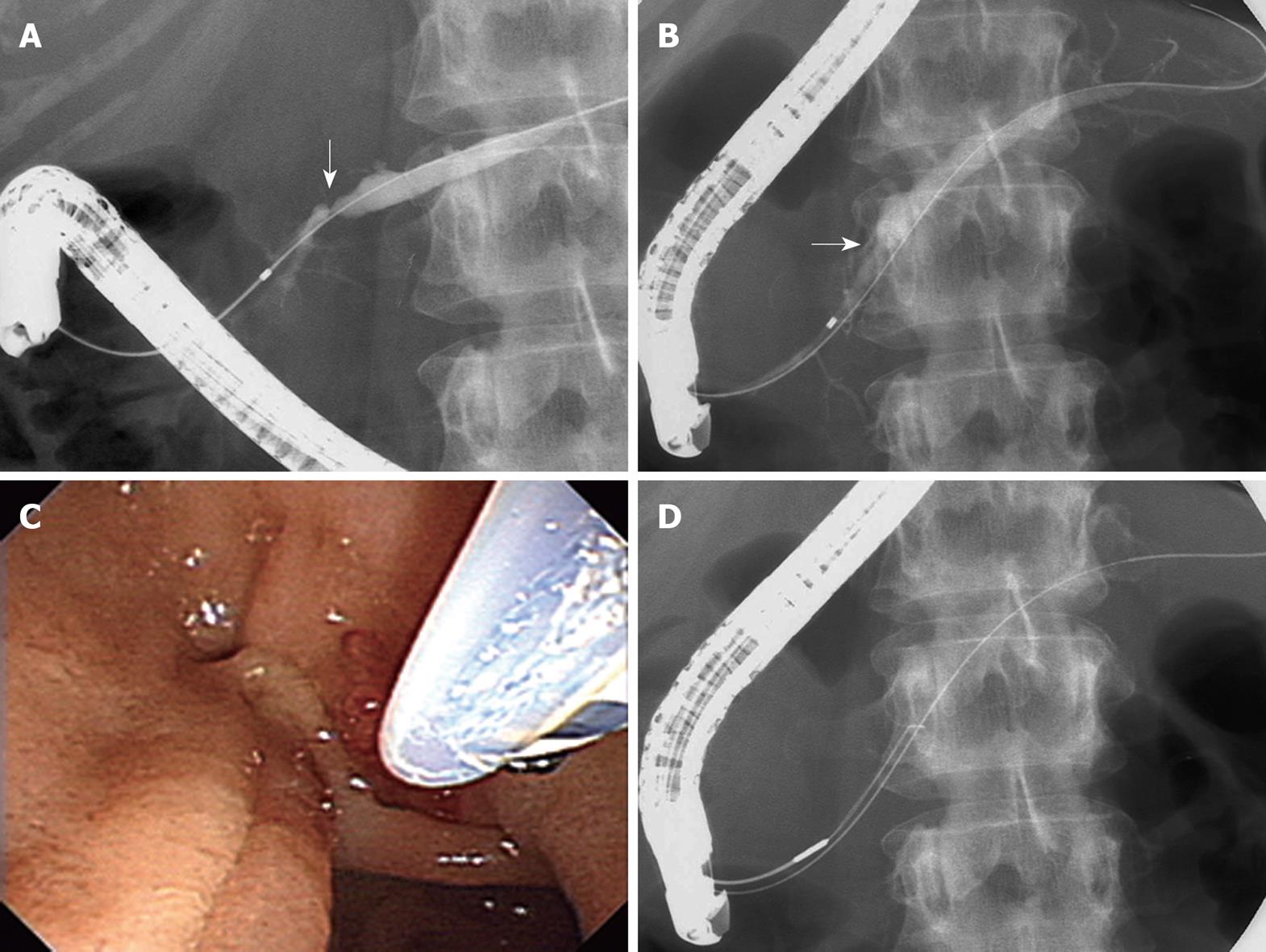
Figure 3 Pancreatic duct incision of a refractory pancreatic duct stricture.
A: Pancreatography reveals a short pancreatic duct stricture (arrow) and upstream ductal dilation; B: Pancreatography after removal of a 10-Fr stent shows a stricture (arrow) still remaining; C: Pancreatic duct incision of the stricture using electrocautery snare; D: Wire-guided snare forceps advanced into the pancreatic duct through the major papilla.
- Citation: Itoi T, Sofuni A, Itokawa F, Kurihara T, Tsuchiya T, Ishii K, Tsuji S, Ikeuchi N, Moriyasu F. Transpapillary incision of refractory circumscript pancreatic duct stricture using wire-guided snare forceps. World J Gastroenterol 2010; 16(12): 1541-1544
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v16/i12/1541.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v16.i12.1541