Copyright
©2009 The WJG Press and Baishideng.
World J Gastroenterol. Feb 28, 2009; 15(8): 919-926
Published online Feb 28, 2009. doi: 10.3748/wjg.15.919
Published online Feb 28, 2009. doi: 10.3748/wjg.15.919
Figure 1 Sequence comparison on line (http://align.genome.jp) of the rdxA gene between metronidazole resistant strain (R2) and H pylori reference strain 26 695 (S).
Figure 2 Sequence comparison on line (http://align.genome.jp) of the rdxA gene between metronidazole resistant strain (R2) and its corresponding susceptible strain in the presence of aspirin [R2 (A)].
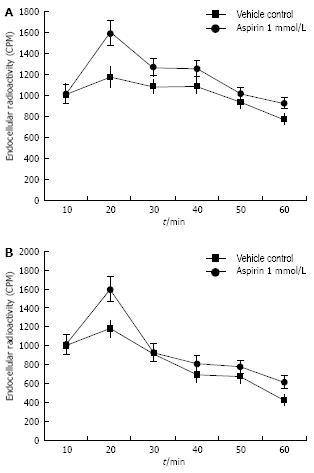
Figure 3 Radioactivity of H pylori cells treated with aspirin (1 mmol/L) or vehicle control (DMSO).
A: CCCP; B: No CCCP.
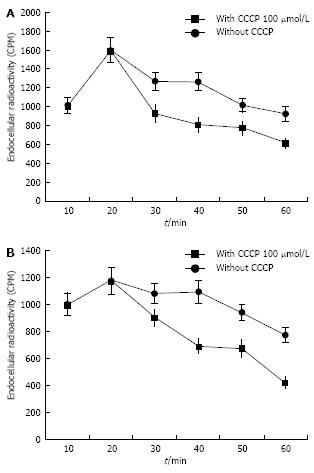
Figure 4 Radioactivity of H pylori cells treated with CCCP (100 µmol/L) or without CCCP.
A: Aspirin; B: Vehicle control.
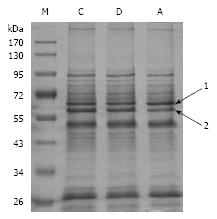
Figure 5 OMP profiles of H pylori 26 695.
M: Size marker; C: Control; D: DMSO; A: Aspirin. Band 1: OMP increased in the presence of aspirin; Band 2: OMP decreased in the presence of aspirin.
- Citation: Zhang XP, Wang WH, Tian Y, Gao W, Li J. Aspirin increases susceptibility of Helicobacter pylori to metronidazole by augmenting endocellular concentrations of antimicrobials. World J Gastroenterol 2009; 15(8): 919-926
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v15/i8/919.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.15.919