Copyright
©2009 The WJG Press and Baishideng.
World J Gastroenterol. May 7, 2009; 15(17): 2145-2150
Published online May 7, 2009. doi: 10.3748/wjg.15.2145
Published online May 7, 2009. doi: 10.3748/wjg.15.2145
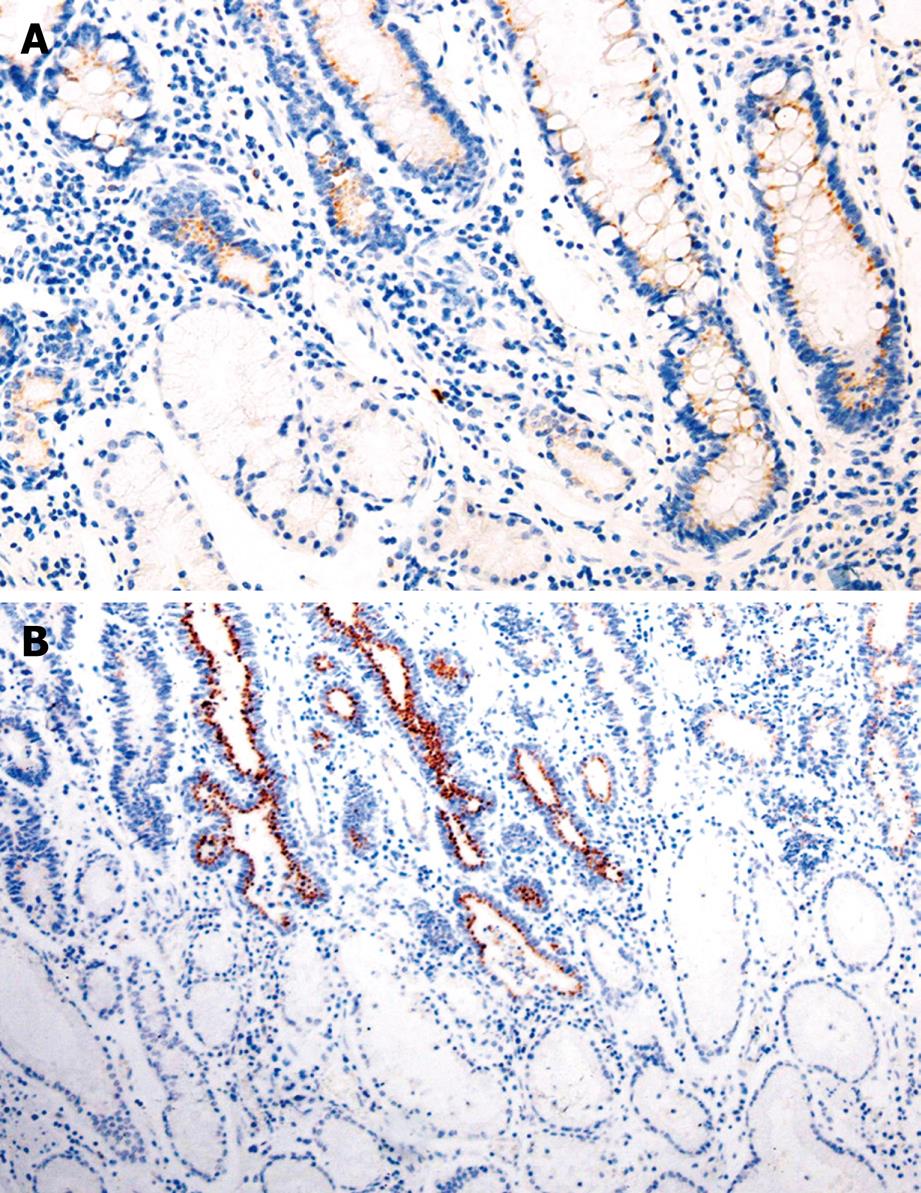
Figure 1 Expression of Bmi-1 in IM (A, × 200) and GC (B, × 100) (PV-9000).
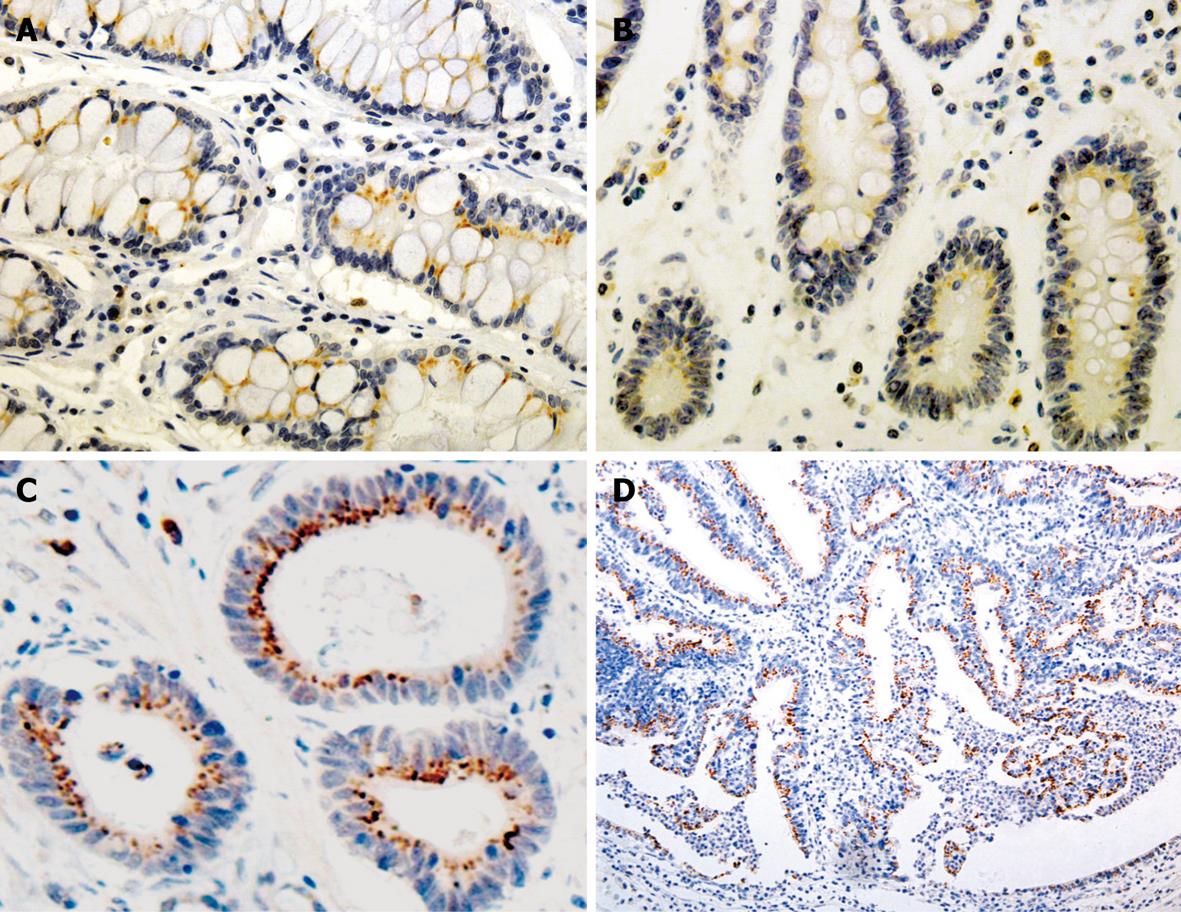
Figure 2 Expression of Bmi-1 in IM (A), mild DYS (B), gastric tubular adenocarcinoma (C) and papillary adenocarcinoma (D) (PV-9000 A-C × 400, D × 200).
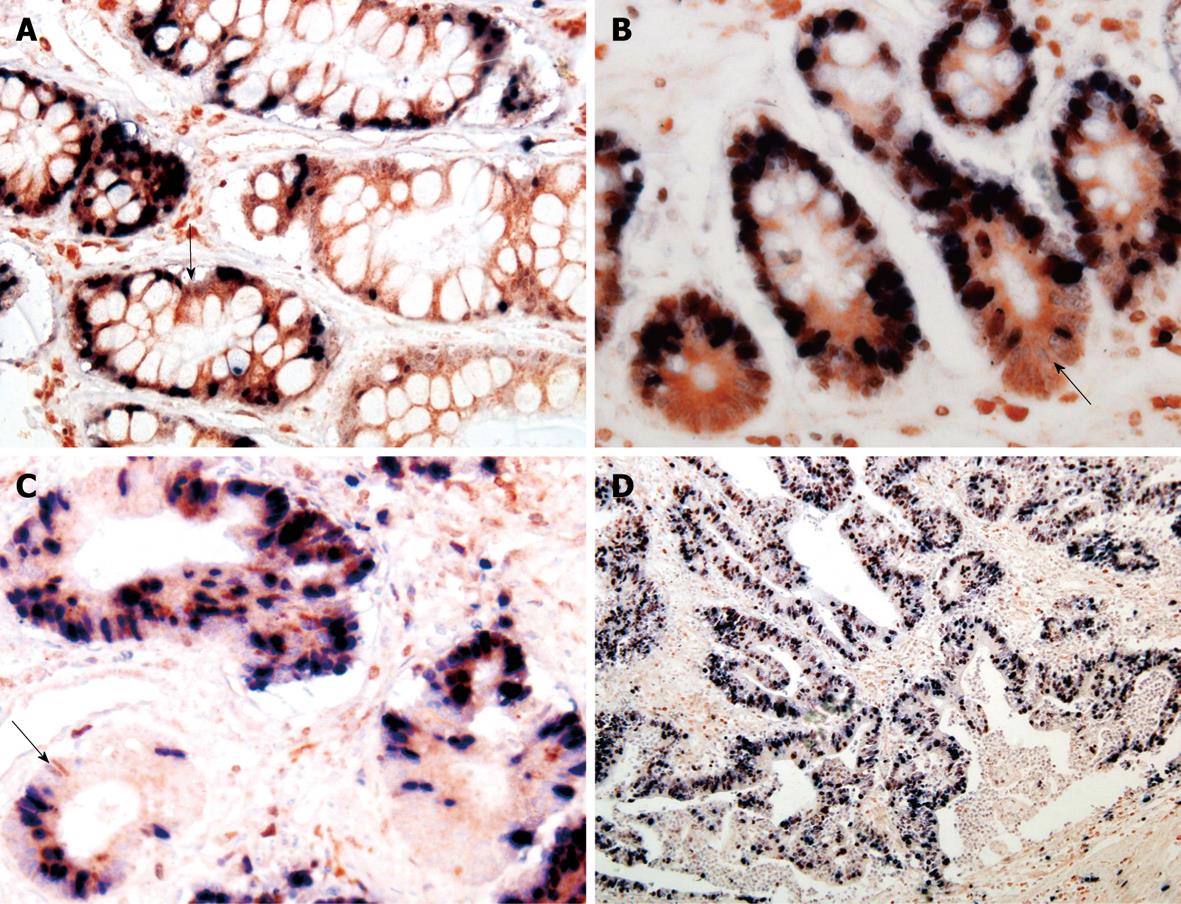
Figure 3 Distribution of Bcl-2+/ki-67- cells in IM (A), mild DYS (B), gastric tubular adenocarcinoma (C) and papillary adenocarcinoma (D).
Red fine granules in cytoplasm and unstained nuclei were defined as Bcl-2+/ki-67- cells as shown by the arrows (Immunohistochemical double staining, A-C × 400, D × 200).
- Citation: Zhao J, Luo XD, Da CL, Xin Y. Clinicopathological significance of B-cell-specific Moloney murine leukemia virus insertion site 1 expression in gastric carcinoma and its precancerous lesion. World J Gastroenterol 2009; 15(17): 2145-2150
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v15/i17/2145.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.15.2145