Copyright
©2008 The WJG Press and Baishideng.
World J Gastroenterol. Oct 21, 2008; 14(39): 5990-5995
Published online Oct 21, 2008. doi: 10.3748/wjg.14.5990
Published online Oct 21, 2008. doi: 10.3748/wjg.14.5990
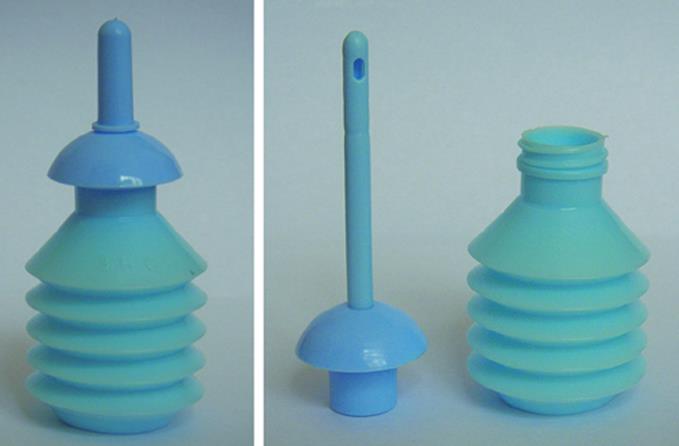
Figure 1 Specific instrument for enema (Enema irrigator disposable).
Fifteen mL of the liquid vitamin E was rectally administered in our patients using this disposable enema irrigator.
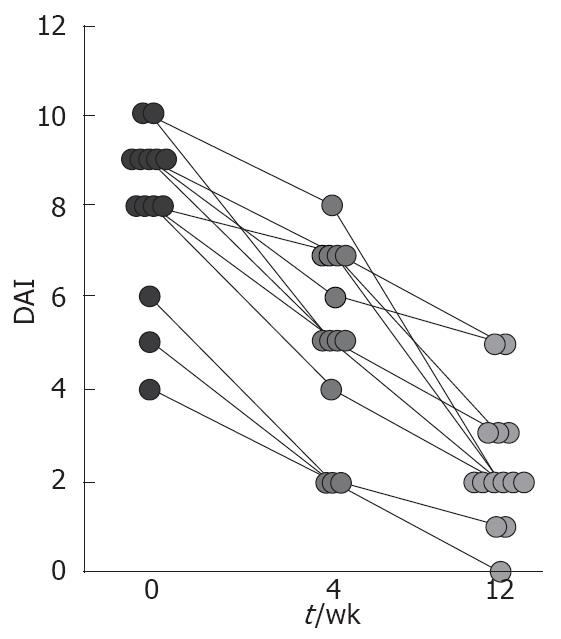
Figure 2 Individual changes in disease activity from week 0 to 12, assessed by the Mayo Disease Activity Index, in subjects who received d-α Tocopherol enema.
One patient who was withdrawn early from the study is not included. There was a significant decrease in the mean DAI score for patients after 4th and 12th weeks of therapy (P < 0.0001).
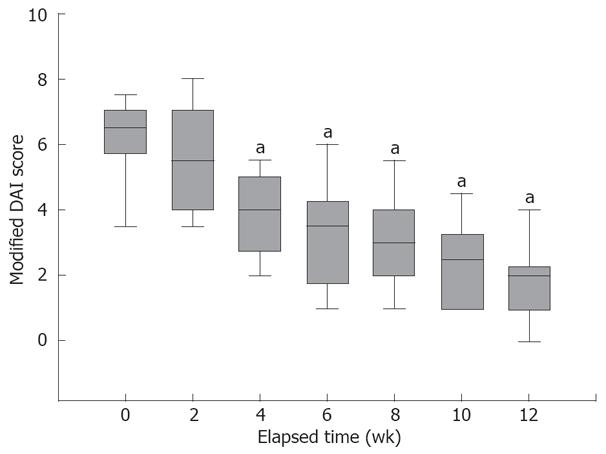
Figure 3 Change in the modified DAI.
A modified DAI score, including all components of the complete DAI other than the endoscopic appearance is calculated at each observation point. By week 4 the mean modified DAI score significantly decreased compared to baseline (week 0) scores. aP < 0.0001 vs baseline.
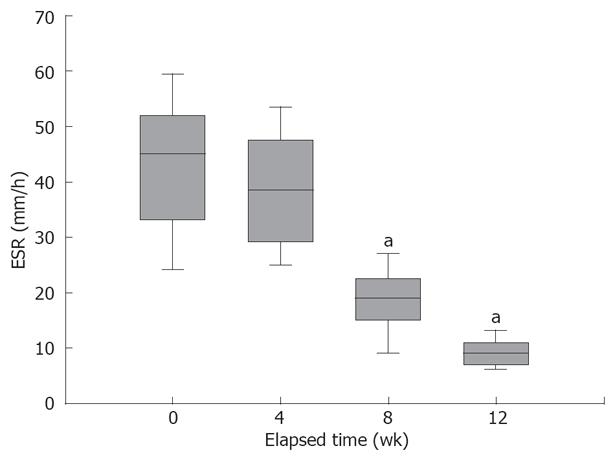
Figure 4 Individual changes in ESR from week 0 to 12, in our patients.
There was a significant decrease in the mean ESR on the 8th and the 12th week of therapy compared to the beginning of the study. aP < 0.0001 vs baseline (0 wk).
- Citation: Mirbagheri SA, Nezami BG, Assa S, Hajimahmoodi M. Rectal administration of d-alpha tocopherol for active ulcerative colitis: A preliminary report. World J Gastroenterol 2008; 14(39): 5990-5995
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v14/i39/5990.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.14.5990