Copyright
©2008 The WJG Press and Baishideng.
World J Gastroenterol. Aug 21, 2008; 14(31): 4897-4902
Published online Aug 21, 2008. doi: 10.3748/wjg.14.4897
Published online Aug 21, 2008. doi: 10.3748/wjg.14.4897
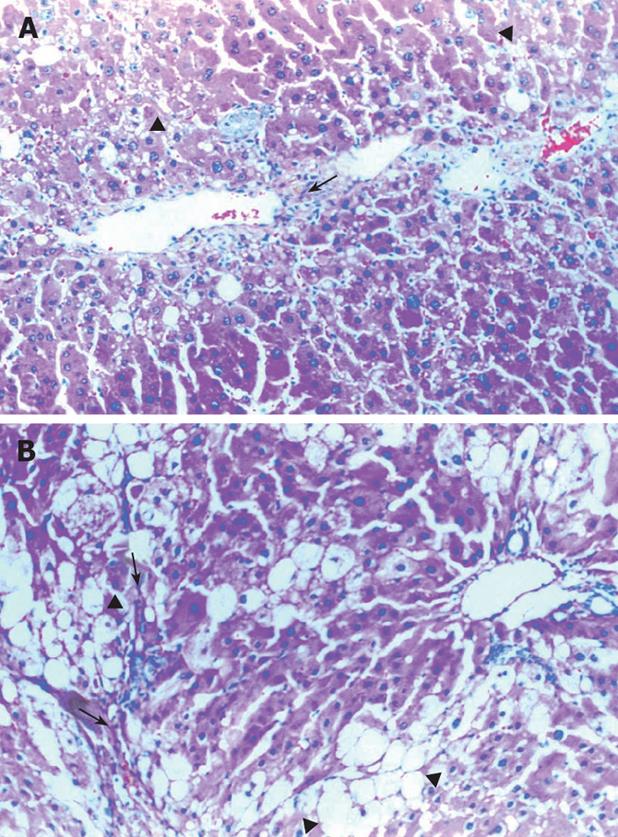
Figure 1 A: Mild bile duct proliferation (arrow) and microvesicular changes (arrowheads) in Taurine treated animals (HE, × 200); B: Severe macro and microvesicular fatty accumulation (arrowheads) and fibrosis (arrows) in Taurine untreated group (HE, × 50).
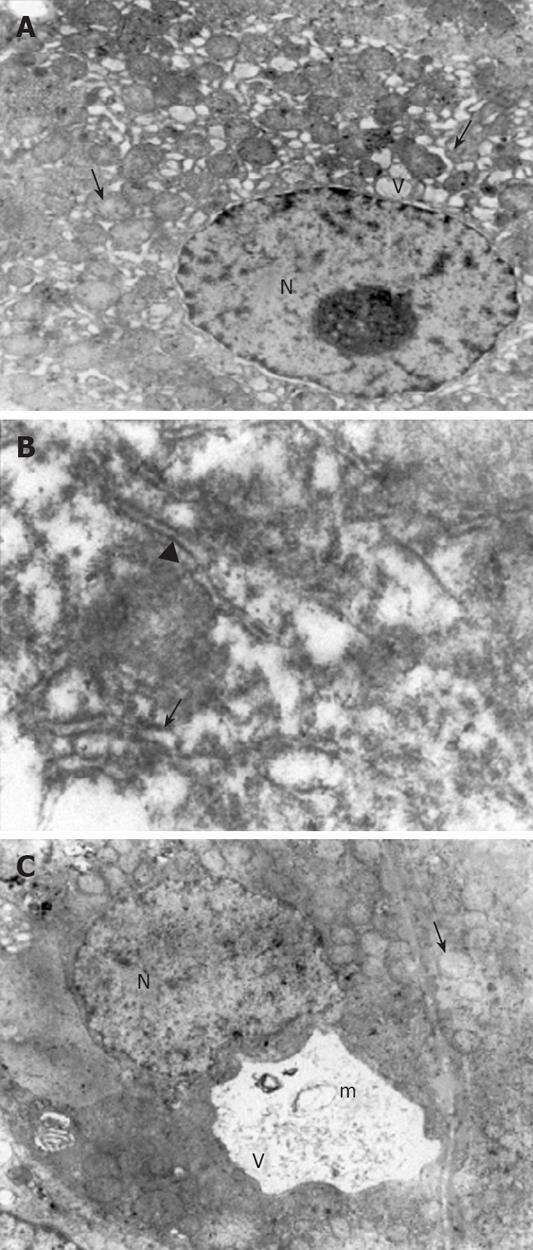
Figure 2 Electron micrographs.
A: The dilatations in the rER (arrow) and sER (arrowhead), large vacuoles in the hepatocytes (V), a normal nucleus (N) and mitochondria with a prominent edema (small arrow) in CCl4 plus taurine treated group (× 4000); B: Large dilatations (arrow) and focal breaks (arrowhead) in the rER in CCl4 plus saline treated group (× 30 000); C: The vacuolizations (V) and myelin figures (m) in the sER, nucleus (N) and mitochondria with prominent edema (arrow) in CCl4 plus saline treated group (× 4000).
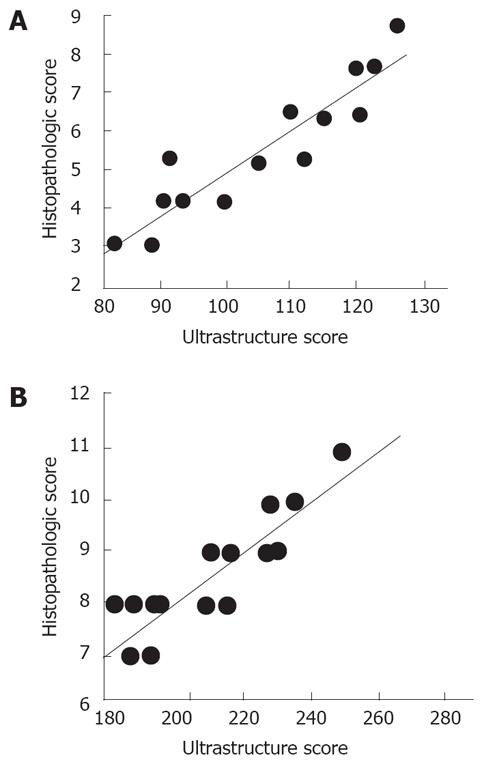
Figure 3 Correlation of histopathologic and ultrastructure scores in CCl4.
A: Plus Taurine treated group (r = 0.931); B: Plus Saline treated group (r = 0.899).
- Citation: Tasci I, Mas N, Mas MR, Tuncer M, Comert B. Ultrastructural changes in hepatocytes after taurine treatment in CCl4 induced liver injury. World J Gastroenterol 2008; 14(31): 4897-4902
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v14/i31/4897.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.14.4897