Copyright
©2008 The WJG Press and Baishideng.
World J Gastroenterol. Aug 14, 2008; 14(30): 4779-4783
Published online Aug 14, 2008. doi: 10.3748/wjg.14.4779
Published online Aug 14, 2008. doi: 10.3748/wjg.14.4779
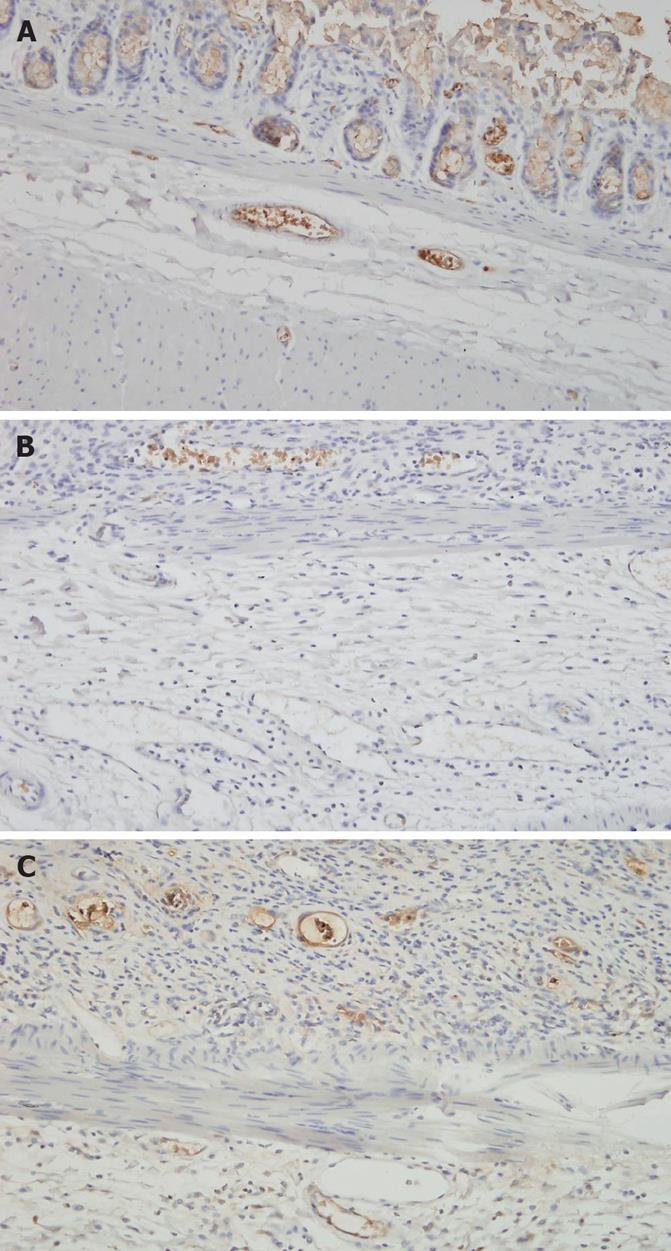
Figure 1 Immunohistochemical staining of TM (thrombomodulin) expression in the endothelial cells of the mucosa and submucosa.
The intensity of TM expression in capillaries is significantly higher in the control group (A) and thalidomide group (C) than in the radiation group (B) (× 200).
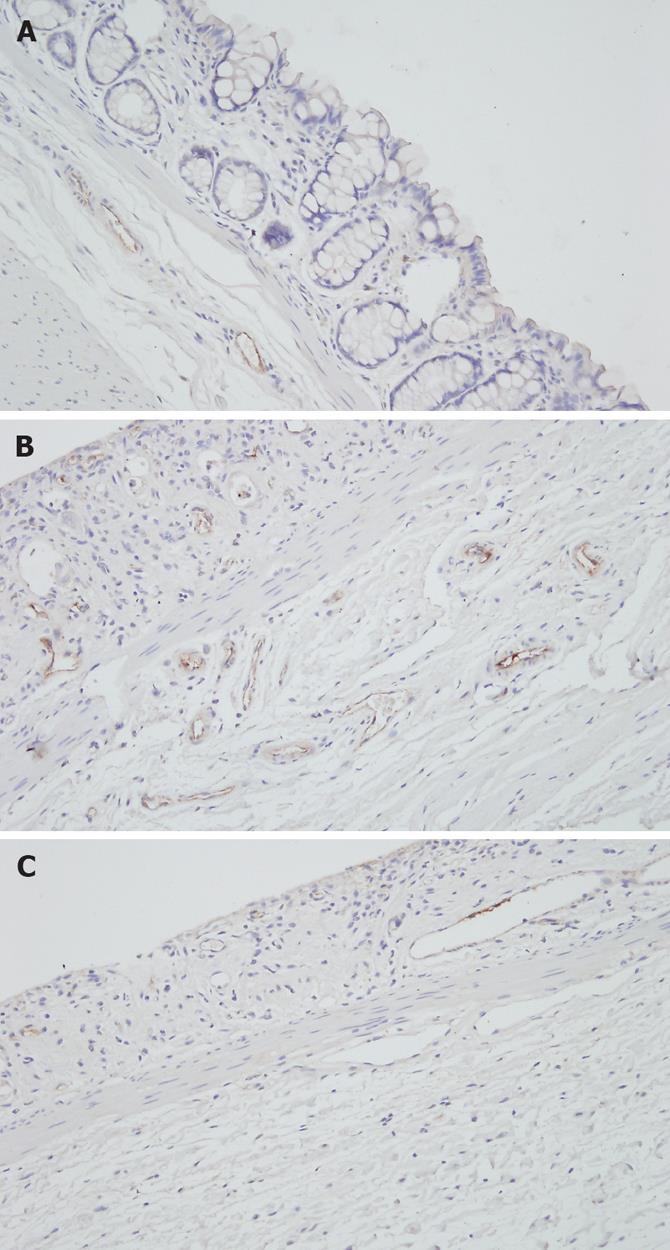
Figure 2 Immunohistochemical staining of vWF expression in the endothelial cells of the mucosa and submucosa.
Both the total number of microvessels and the number of vWF expressing microvessels are markedly higher in the radiation group (B) than in the control group (A), which are attenuated in the thalidomide group (C) (× 200).
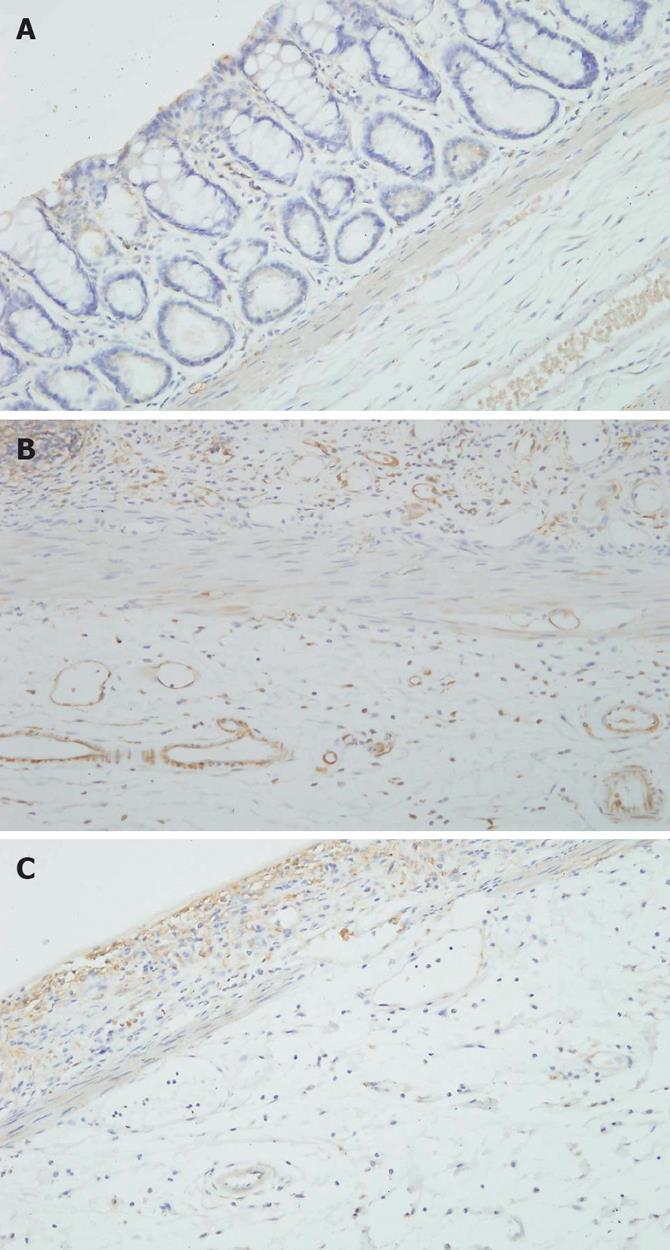
Figure 3 Immunohistochemical staining of VEGF expression in the endothelial cells of the mucosa and submucosa.
The number of VEGF-positive microvessels and the intensity of VEGF expression were significantly higher in the radiation group (B) than in the control (A) and thalidomide (C) groups (× 200).
- Citation: Kim KT, Chae HS, Kim JS, Kim HK, Cho YS, Choi W, Choi KY, Rho SY, Kang SJ. Thalidomide effect in endothelial cell of acute radiation proctitis. World J Gastroenterol 2008; 14(30): 4779-4783
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v14/i30/4779.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.14.4779