Copyright
©2008 The WJG Press and Baishideng.
World J Gastroenterol. Apr 21, 2008; 14(15): 2388-2393
Published online Apr 21, 2008. doi: 10.3748/wjg.14.2388
Published online Apr 21, 2008. doi: 10.3748/wjg.14.2388
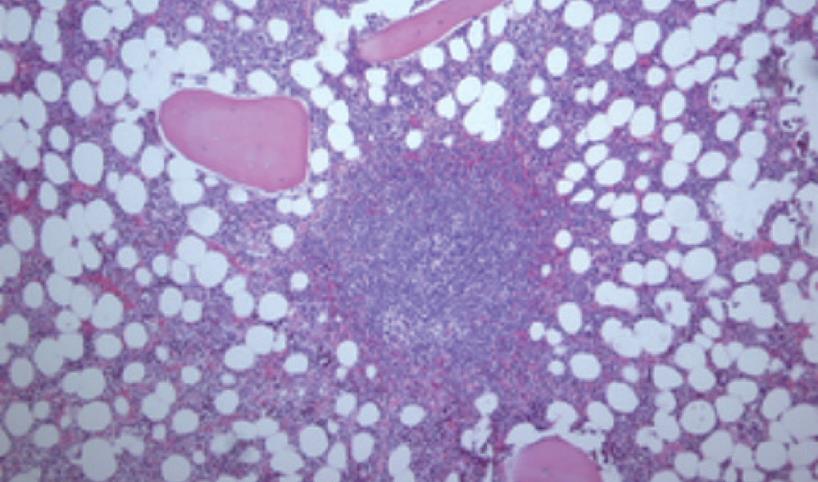
Figure 1 Bone marrow pathohistology in gastric MALT lymphoma patients (HE, × 100).
Paratrabecular nodal lymphoid BM infiltration with neoplastic cells.
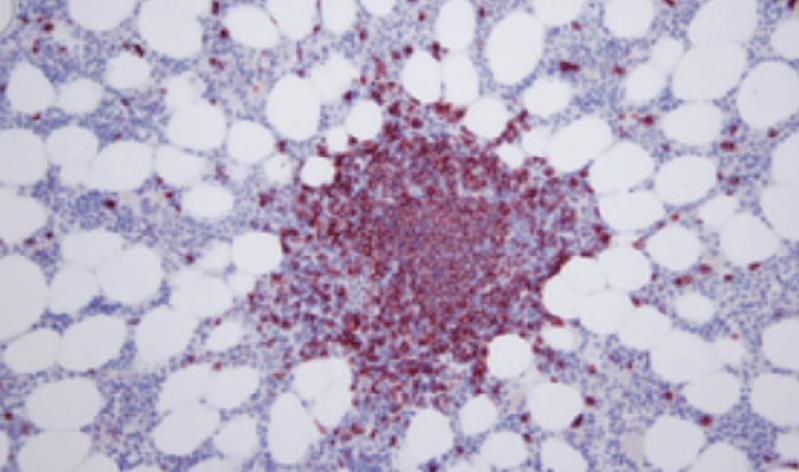
Figure 2 Immunohistochemistry of CD20 antigen expression in bone marrow biopsy (× 200).
Nodal lymphoid BM infiltration with CD20+ in lymphoma cells.
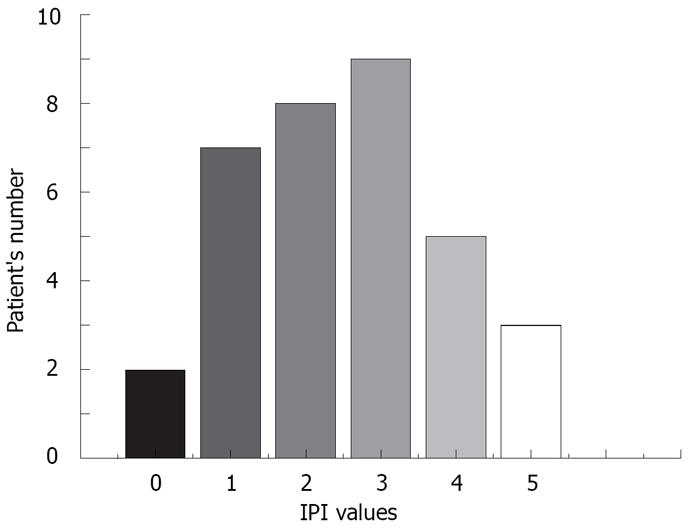
Figure 3 Distribution of IPI values in gastric MALT lymphoma patients.
IPI score was a highly significant (P < 0.01) prognostic factor for overall survival of patients.
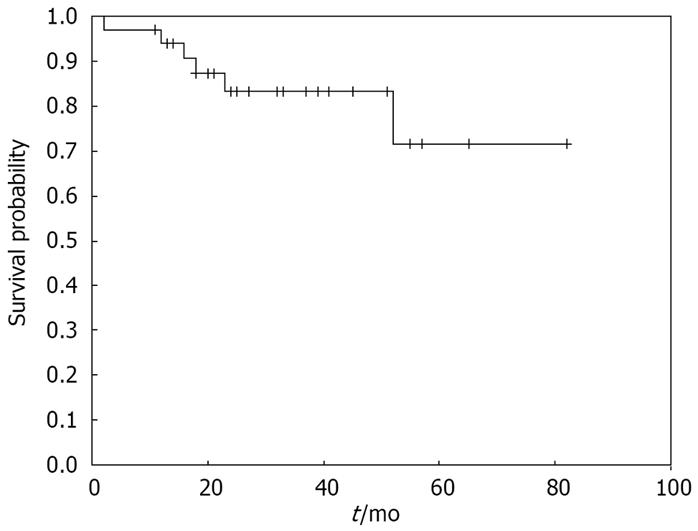
Figure 4 Kaplan-Meir curve of cumulative survival probability in gastric MALT lymphoma patients.
Cumulative survival probability was high in the following period with low rate of death.
- Citation: Todorovic M, Balint B, Jevtic M, Suvajdzic N, Ceric A, Stamatovic D, Markovic O, Perunicic M, Marjanovic S, Krstic M. Primary gastric mucosa associated lymphoid tissue lymphoma: Clinical data predicted treatment outcome. World J Gastroenterol 2008; 14(15): 2388-2393
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v14/i15/2388.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.14.2388