Copyright
©2007 Baishideng Publishing Group Inc.
World J Gastroenterol. Nov 21, 2007; 13(43): 5787-5793
Published online Nov 21, 2007. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v13.i43.5787
Published online Nov 21, 2007. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v13.i43.5787
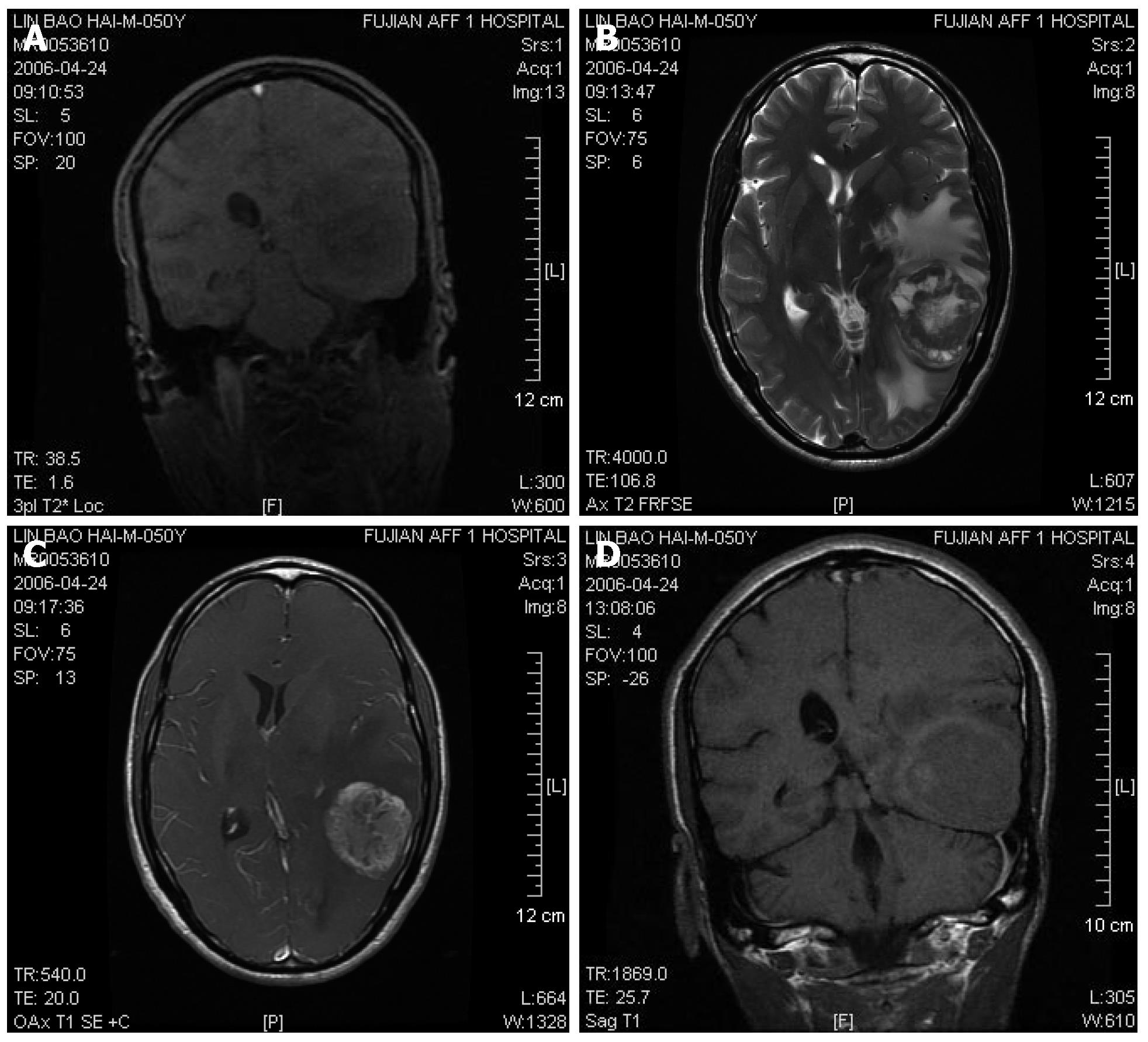
Figure 1 MR imaging revealing a spherical occupying lesion in the left posterior-temple lobe with a high intensity on T2-weighted images and irregular contrast enhancement with a clear boundary and uneven signal in size of about 6.
0 cm × 4.8 cm × 4.0 cm after administration of gadolinium-diethylene triamino pentaacetic acid (Gd-DTPA). A: Coronal gradient-recalled echo; B: Cross-sectional T2WI; C: Cross-sectional contrast enhancement T1WI; D: Coronal T1WI-delayed scan 4 h after contrast media injected via veins.
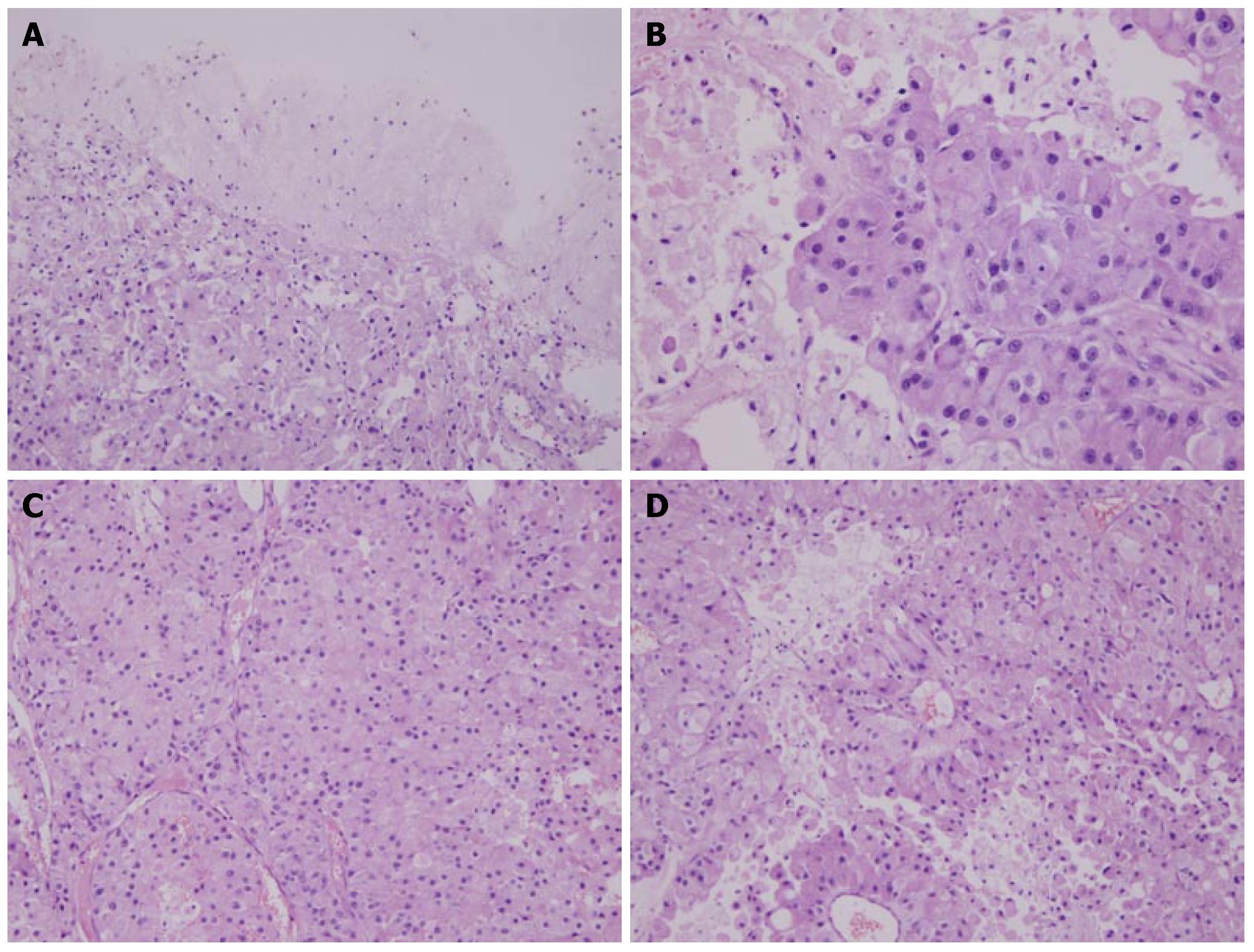
Figure 2 Brain metastatic tumor showing the growth pattern of solid cell nests (HE stain).
A: Polygonal tumor cells with abundant eosinophilic cytoplasm, rich blood vessels and clear boundary of tumor and brain parenchyma (× 100); B: Polygonal tumor cells showing epitheliod and abundant eosinophilic cytoplasm, rich chromatin nuclei with obvious nucleoli (× 200); C: Round nuclei with obvious nucleoli, rich blood vessels resembling sinusoid-like blood spaces in hepatocellular carcinoma (× 200); D: Tumor cells exhibiting radial pattern surrounding thin- walled vessels (× 200).
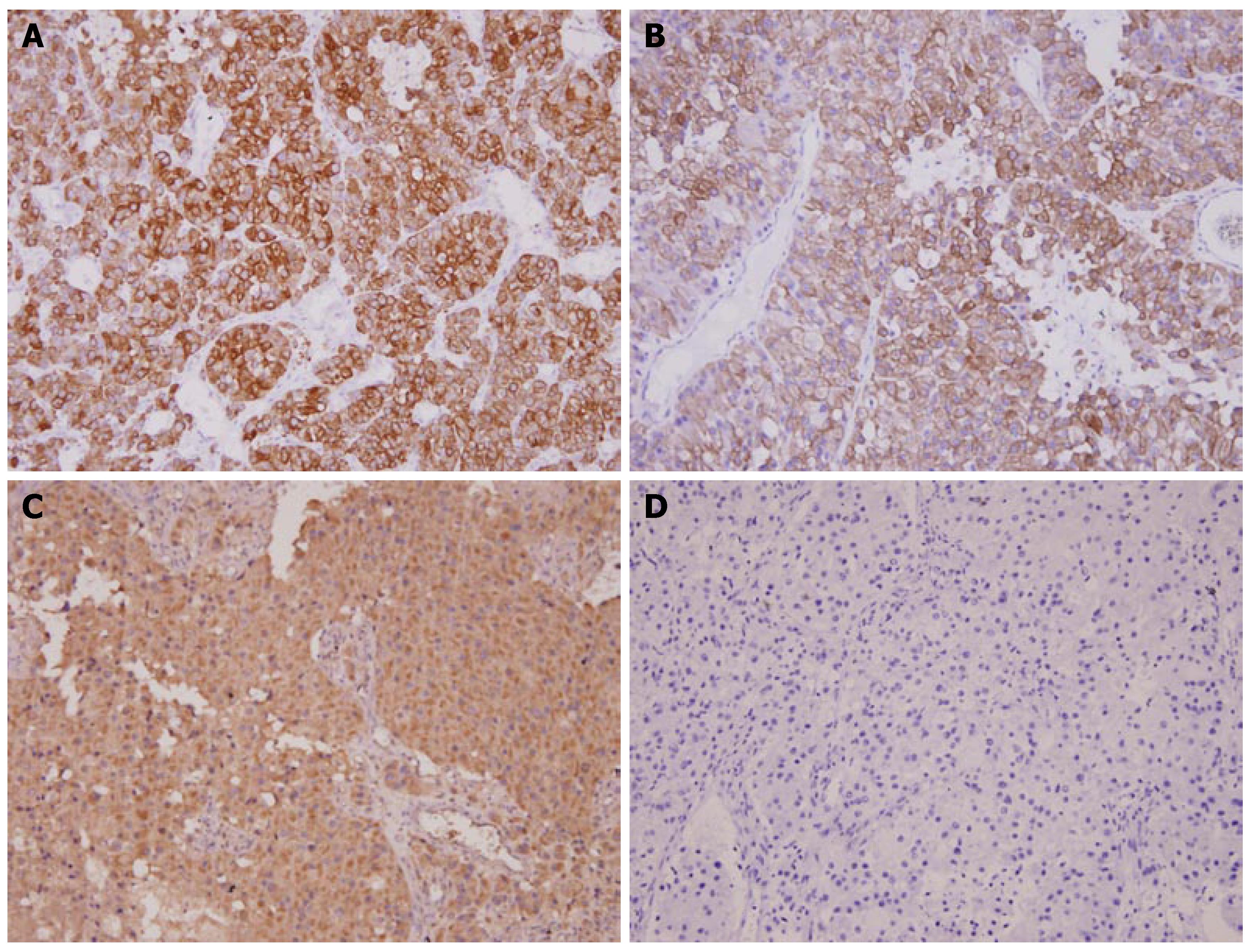
Figure 3 Immunoreactive characte-ristics of brain metastatic tumor (EnVision).
A: Positively- stained cytokeratin AE1/AE3 (× 200); B: Positively-stained cytokeratin 8 (× 200); C: Positively-stained AFP (× 200); D: Negatively-stained Hep-Par-1 (× 200).
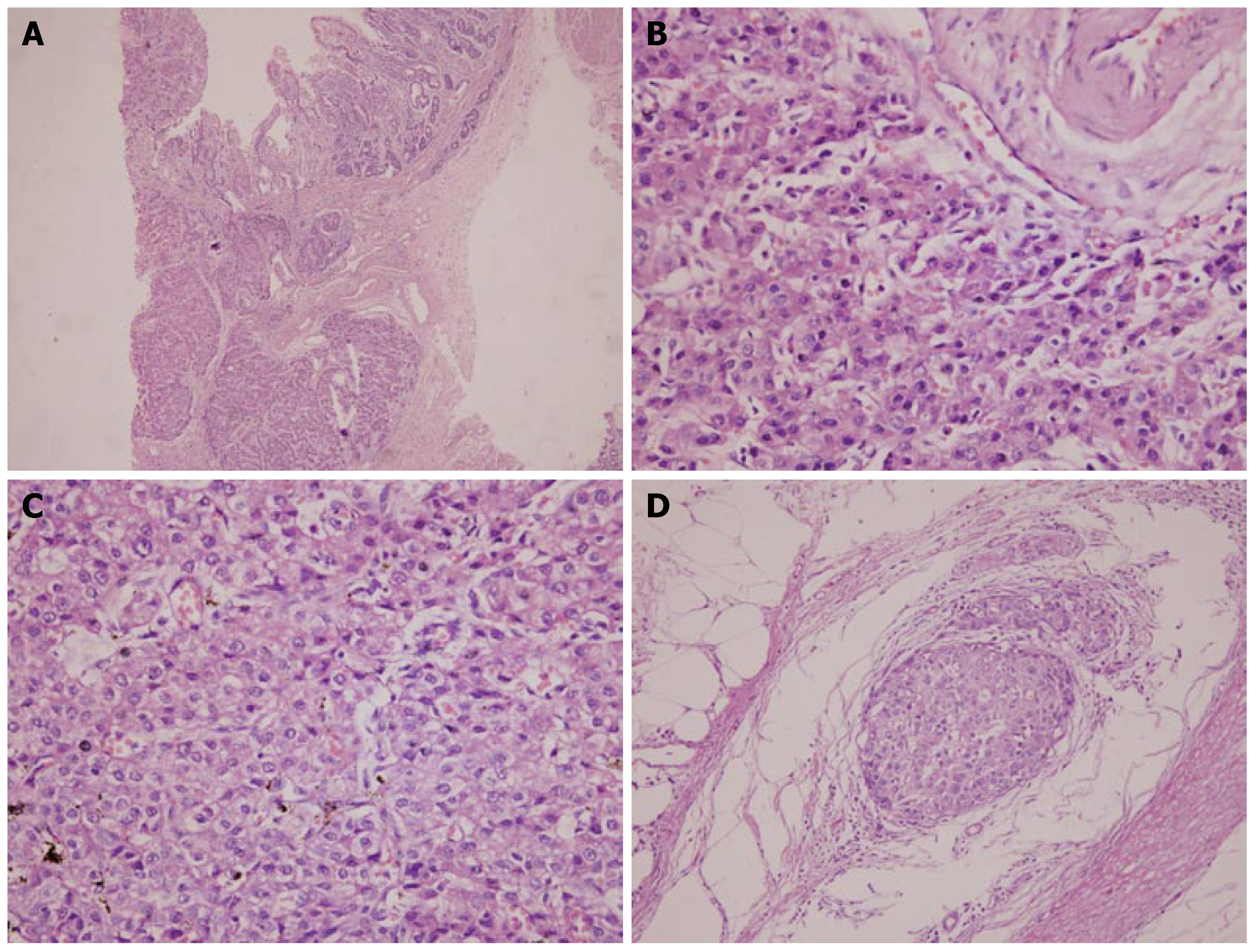
Figure 4 Histopathological features of primary gastric hepatoid adeno-carcinoma.
A: Tumor located at submucosa and intramuscle showing the growth pattern of solid cell nests (× 40); B: Part of tumor grown in cords separated by sinusoid-like blood spaces (×200); C: Part of tumor grown in solid appearance showing polygonal epithelioid tumor cells with abundant eosinophilic cytoplasm, round nuclei with obvious nucleoli (× 200); D: Intralymph vascular tumor thrombosis in primary carcinoma (× 200).
Figure 5 Immunohistochemical characteristics of primary gastric hepatoid adenocarcinoma.
A: Positively-stained cytokeratin AE1/AE3 (× 200); B: Positively-stained cytokeratin 8 (× 200); C: Positively-stained AFP (× 200); D: Negatively-stained Hep-Par-1 (× 200).
Figure 6 CT imaging features of liver metastatic tumor.
A: CT scan revealing nodular or lump-like, high-density contrast mass in liver lobes during arterial phase; B: Uneven enhancement during portal venous phase.
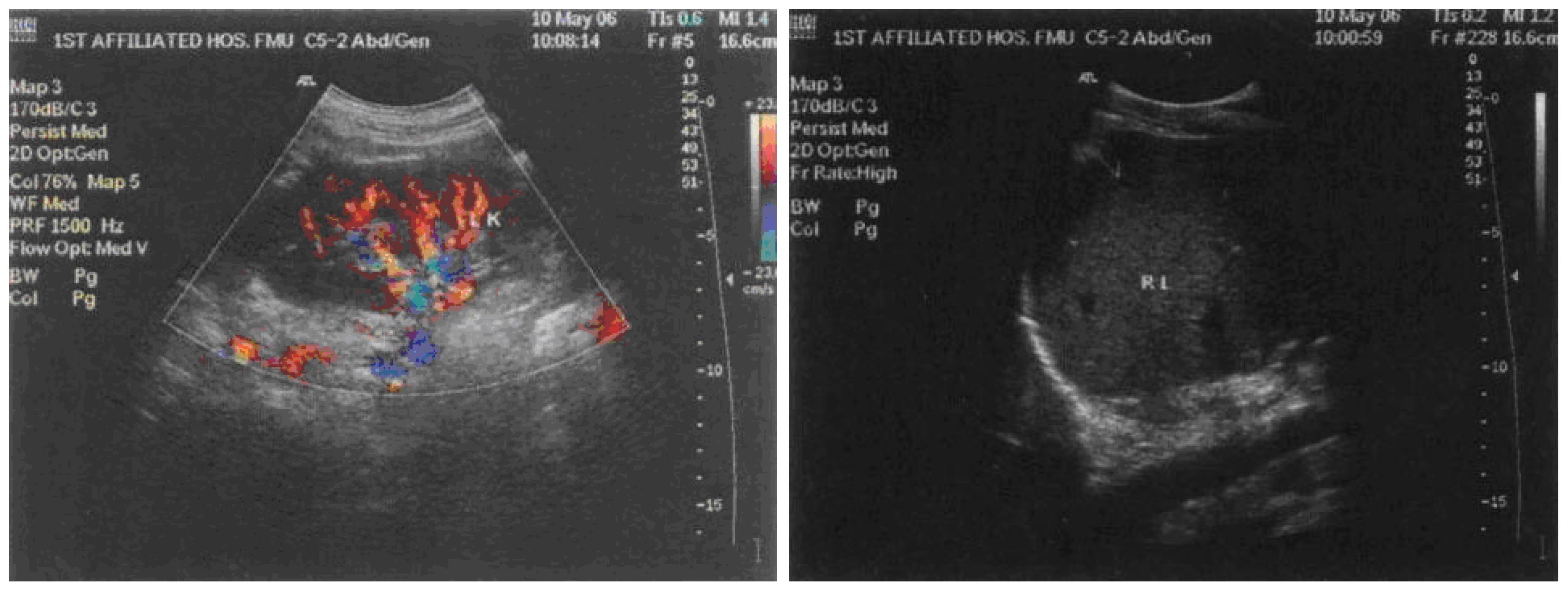
Figure 7 Features of ultrasound examination before operation of the brain metastasis.
- Citation: Zhang S, Wang M, Xue YH, Chen YP. Cerebral metastasis from hepatoid adenocarcinoma of the stomach. World J Gastroenterol 2007; 13(43): 5787-5793
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v13/i43/5787.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v13.i43.5787