Copyright
©2007 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Aug 28, 2007; 13(32): 4372-4378
Published online Aug 28, 2007. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v13.i32.4372
Published online Aug 28, 2007. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v13.i32.4372
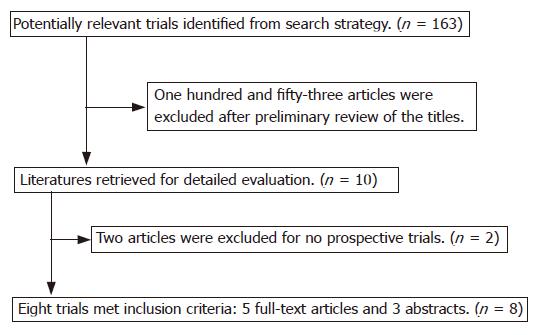
Figure 1 Trial search flow for meta-analysis.
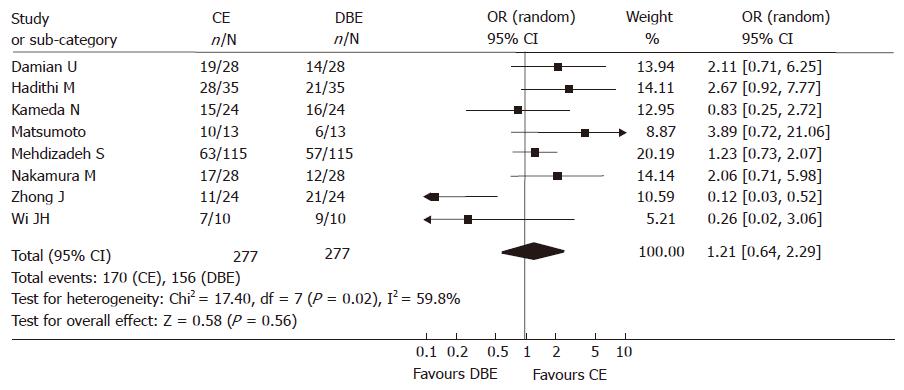
Figure 2 Comparison of the yield of CE and DBE (All studies).
The existence of heterogeneity was confirmed (chi2 test, P = 0.02), random model was used. The summary OR was 1.21 (95% CI = 0.64-2.29). There was no significant difference between the yield of CE and DBE (P = 0.56).
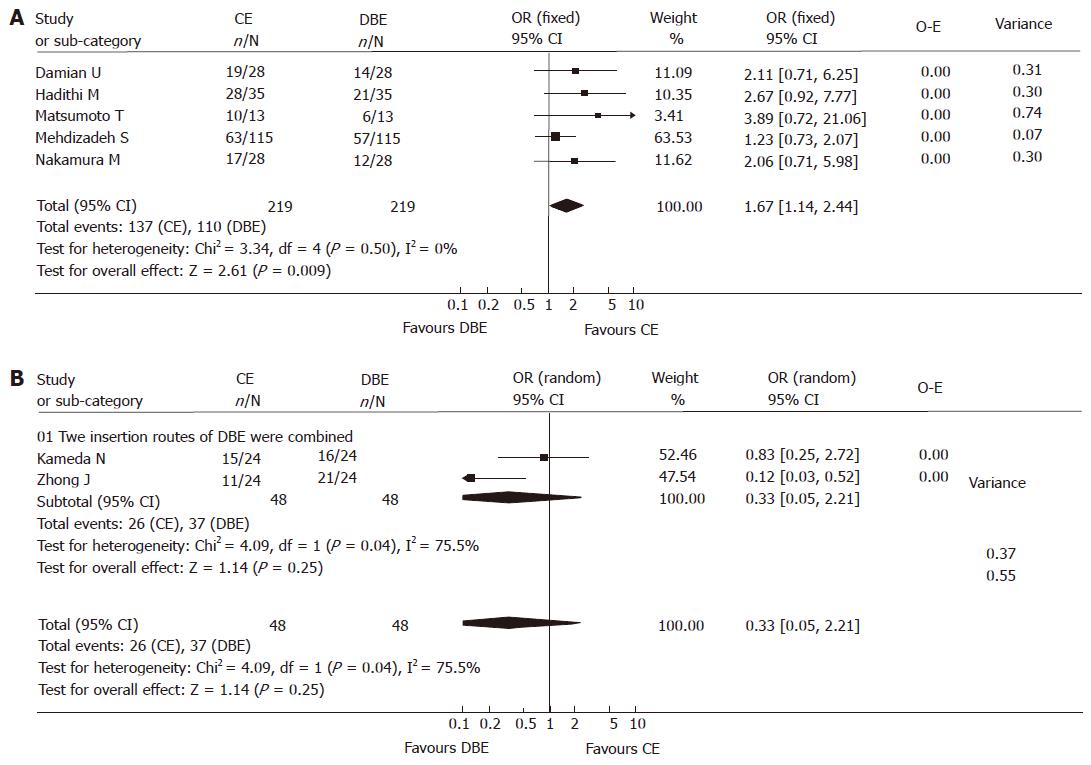
Figure 3 A: Comparison of the yields of CE and DBE without combination of the two insertion approaches.
The yield of CE was significantly higher than that of DBE when the combination of two approaches was not used (fixed model, P = 0.009); B: Comparison of the yields of CE and DBE with the two insertion approaches combined. The yield of DBE with combinatory oral and anal routes was moderately higher than that of CE (random model, P = 0.25).
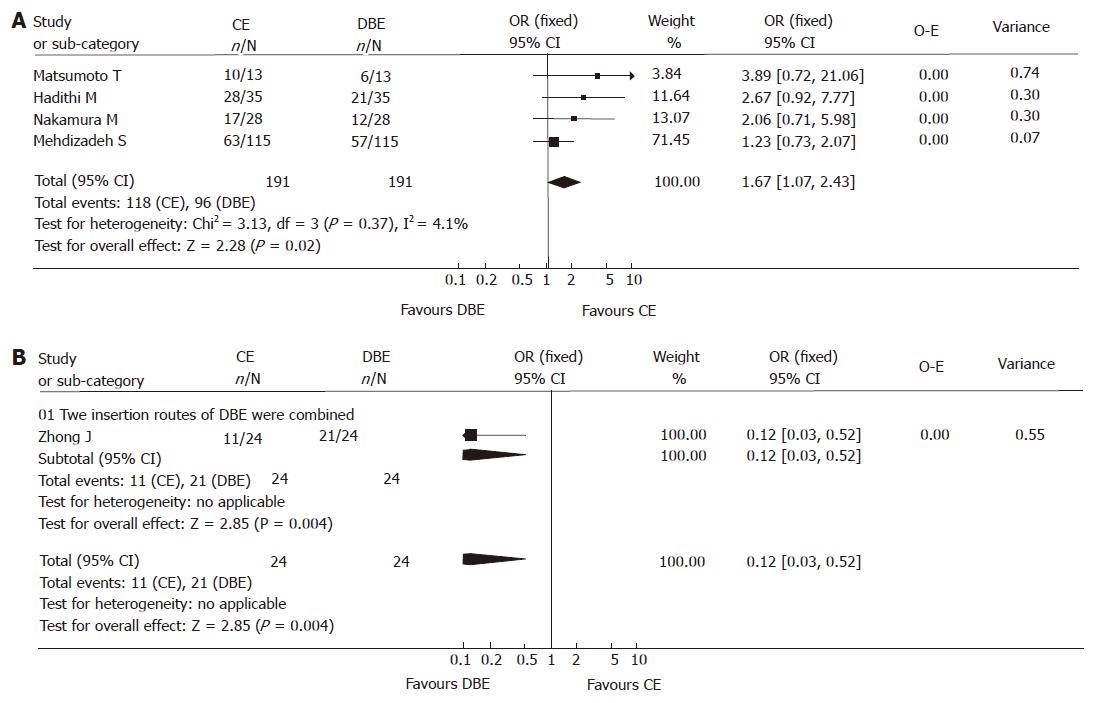
Figure 4 A: Comparison of the yield of CE and DBE without combination of the two insertion approaches (focused on the fully published papers on obscure GI bleeding).
The yield of CE was significantly higher than that of DBE when the combination of two approaches was not used (fixed model, P = 0.02); B: Comparison of the yield of CE and DBE with 2 insertion approaches combined (focused on the fully published papers on obscure GI bleeding). The yield of DBE with combinatory oral and anal routes was significantly higher than that of CE (fixed model, P = 0.004), just one study was included however.
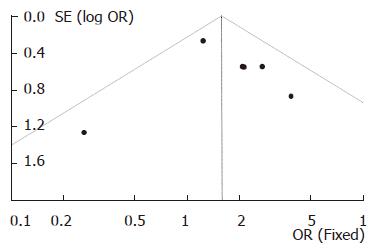
Figure 5 Funnel plot for the analysis of publication bias on the studies in which the DBE was performed without combination of the two approaches.
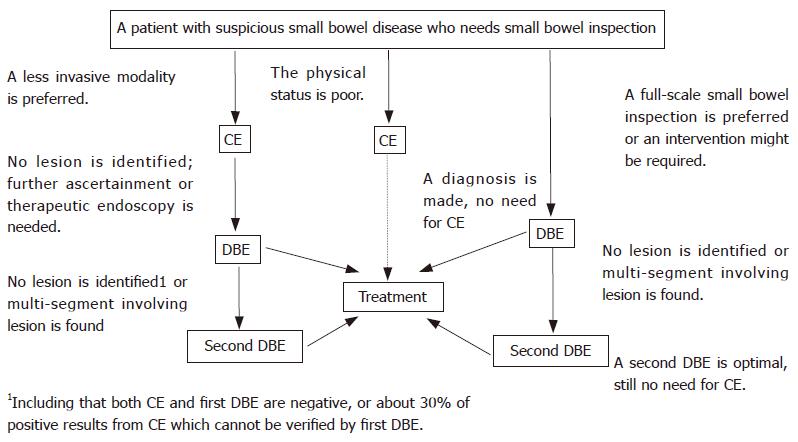
Figure 6 Diagnosing flow according to DBE performed based on a capsule-directed strategy or a combinatory oral and anal routes strategy.
- Citation: Chen X, Ran ZH, Tong JL. A meta-analysis of the yield of capsule endoscopy compared to double-balloon enteroscopy in patients with small bowel diseases. World J Gastroenterol 2007; 13(32): 4372-4378
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v13/i32/4372.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v13.i32.4372