Copyright
©2007 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Aug 21, 2007; 13(31): 4224-4229
Published online Aug 21, 2007. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v13.i31.4224
Published online Aug 21, 2007. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v13.i31.4224
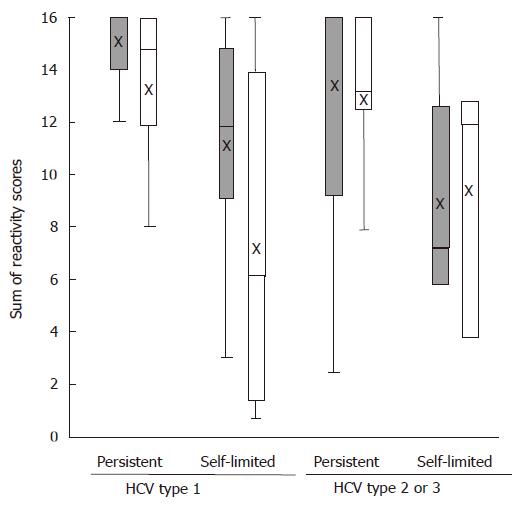
Figure 1 Serological reactivity to HCV encoded proteins with respect to virus type, the putative source and the outcome of infection.
Grey indicates iv drug use and white indicates iv non-use. Mean values are indicated by x, medians by -, boxes show the interquartil range (central 50% of observations) and whiskers show the largest and lowest observed value (if not identified as outlier). By applying a regression model, an overall lower reactivity in patients with self-limited infection could be confirmed (P = 0.0012). Quantitative reactivity appears not to be affected by the outcome or the source of infection in patients with HCV types 2 or 3 (P = 0.9512).
- Citation: Wietzke-Braun P, Mänhardt LB, Rosenberger A, Uy A, Ramadori G, Mihm S. Spontaneous elimination of hepatitis C virus infection: A retrospective study on demographic, clinical, and serological correlates. World J Gastroenterol 2007; 13(31): 4224-4229
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v13/i31/4224.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v13.i31.4224