Copyright
©2007 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Mar 14, 2007; 13(10): 1534-1540
Published online Mar 14, 2007. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v13.i10.1534
Published online Mar 14, 2007. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v13.i10.1534
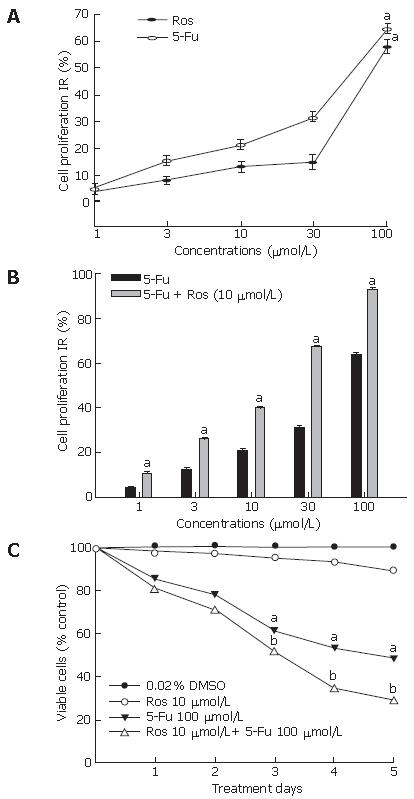
Figure 1 Effect of rosiglitazone and/or 5-Fu on proliferation and growth of HT-29 cells exposed to rosiglitazone or 5-Fu (A), 5-Fu with or without 10 μmol/L rosiglitazone (B), and treated with rosiglitazone and 5-Fu (C) at the indicated concentration for 72 h.
aP < 0.05 vs control group, bP < 0.01 vs rosiglitazone group.
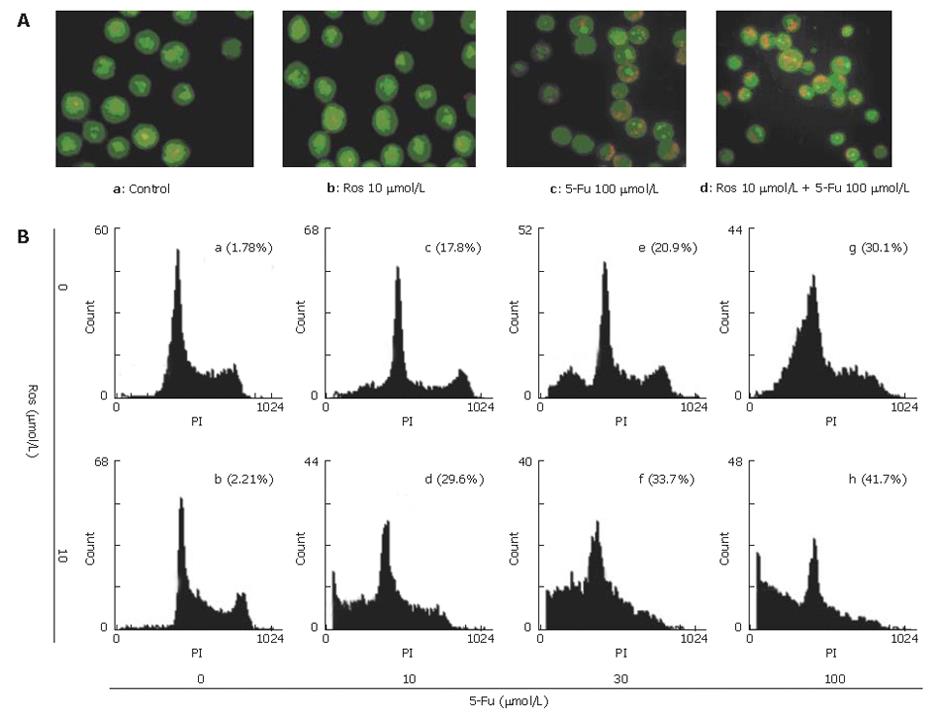
Figure 2 Apoptosis of HT-29 cells induced by AO/EB staining (A) and flow cytometrical analysis (B).
HT-29 cells were treated with rosigliatzone and/or 5-Fu at the indicated concentration for 72 h, then harvested and stained with AO/EB. Results are representative of three experiments.
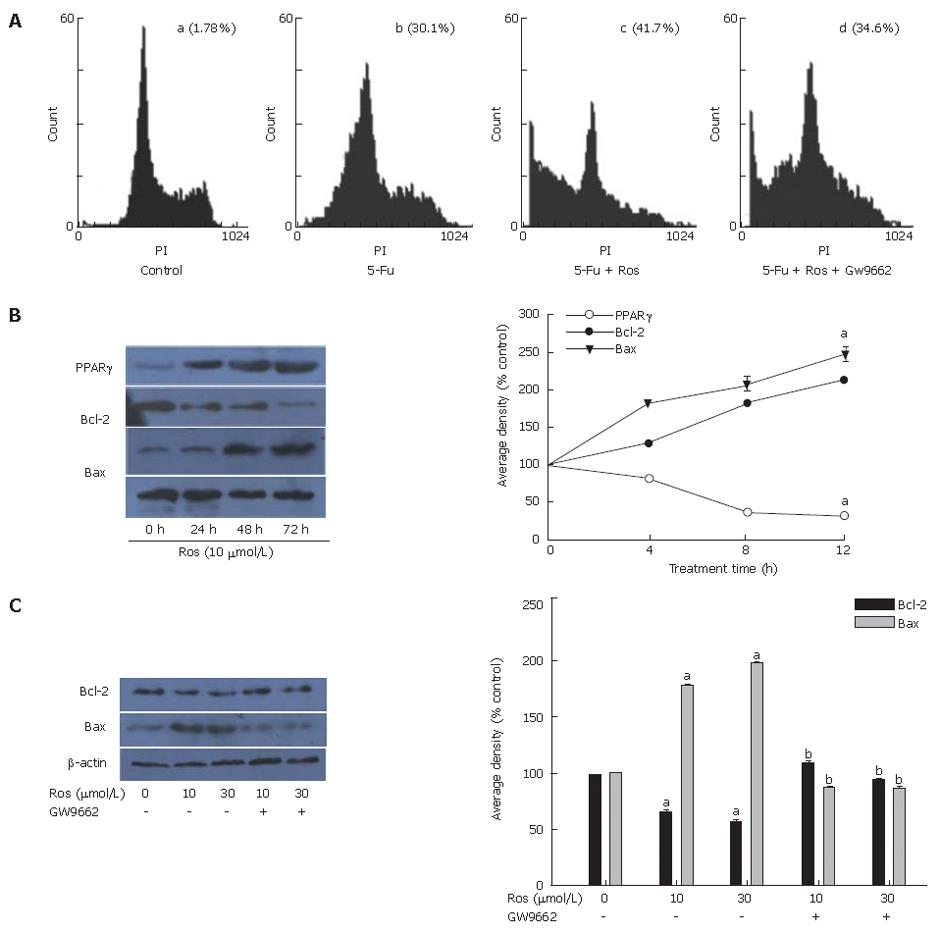
Figure 3 Effect of rosiglitazone on 5-Fu induced apoptosis (A), time-dependent expression of PPARγ, Bax and Bcl-2 (B), and PPARγ-dependent expression of Bax, Bcl-2 and β-actin (C).
aP < 0.05, bP < 0.01.
- Citation: Zhang YQ, Tang XQ, Sun L, Dong L, Qin Y, Liu HQ, Xia H, Cao JG. Rosiglitazone enhances fluorouracil-induced apoptosis of HT-29 cells by activating peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor γ. World J Gastroenterol 2007; 13(10): 1534-1540
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v13/i10/1534.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v13.i10.1534