Copyright
©2006 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Mar 21, 2006; 12(11): 1813-1815
Published online Mar 21, 2006. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v12.i11.1813
Published online Mar 21, 2006. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v12.i11.1813
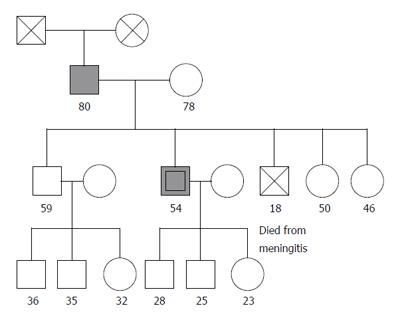
Figure 1 Pedigree of the family with GISTs without cutaneous hyperpigmentation.
Hatched symbols indicate family members with GISTs. Double circles denote multiple GISTs. Squares indicate males and circles indicate females.
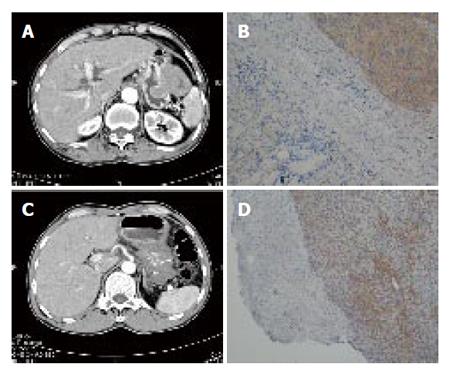
Figure 2 A: Abdominal CT revealed gastric GIST at the anterior wall and greater curvature side of high body of the stomach; B: Microscopic findings of the tumor resected.
Tumor cells were composed of resicular spindle cells with mild nuclear pleomorphism but no necrosis, expressing strong positive c-kit staining immunohistochemically. (IHC staining, 200X); C: Abdominal CT revealed a gastric GIST measuring 13 cm x 10 cm in size occupying the whole stomach. D: Microscopic findings of the tumor resected. Tumor comprised proliferation of spindle cells with mild nuclear atypia in the mxyoid stroma but no necrosis, expressing positive c-kit staining. (IHC staining, 200X).
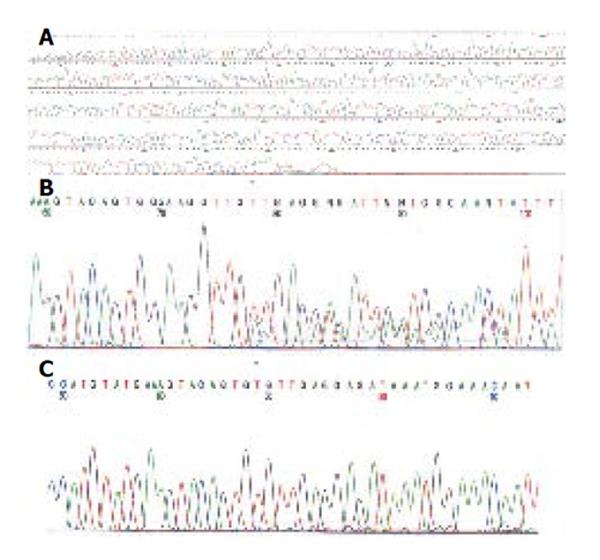
Figure 3 A.
Direct sequencing analysis of DNA from peripheral leukocyte obtained from patients 1 and 2 revealed no mutation in exon 11 of c-kit gene; B. Direct sequencing analysis of DNA from patient 1 showed deletion mutation at codon 560 in exon 11, causing a deletion mutant 560 del V; C. Direct sequencing analysis of DNA from patient 2 revealed deletion at codons 557-559 in exon 11, resulting in replacement of WKV by C.
- Citation: Yeh CN, Chen TW, Jan YY. Sporadic somatic mutation of c-kit gene in a family with gastrointestinal stromal tumors without cutaneous hyperpigmentation. World J Gastroenterol 2006; 12(11): 1813-1815
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v12/i11/1813.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v12.i11.1813