Copyright
©2006 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Mar 21, 2006; 12(11): 1718-1722
Published online Mar 21, 2006. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v12.i11.1718
Published online Mar 21, 2006. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v12.i11.1718
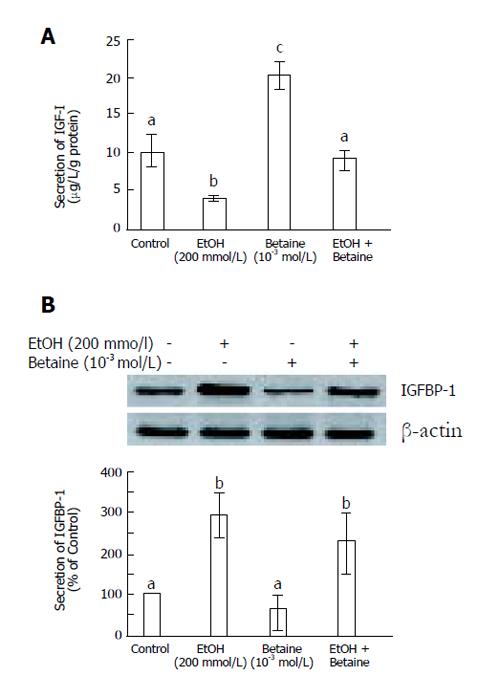
Figure 1 Betaine inhibits the ethanol-stimulated reduction in IGF-I and increases in IGFBP-1 secretion in primary rat hepatocytes (mean ± SD).
A: IGF-I, B: IGFBP-1.
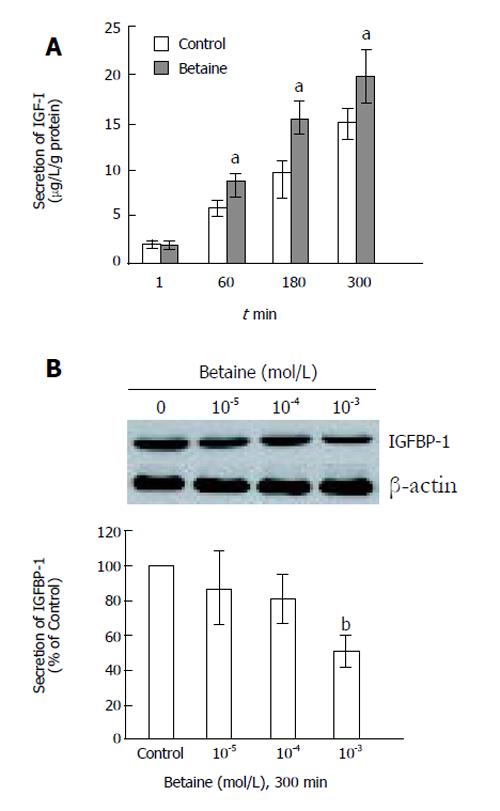
Figure 2 Betaine stimulates IGF-I secretion and decreases IGFBP-1 secretion in primary rat hepatocytes (mean ± SD).
A: IGF-I, B: IGFBP-1. aP < 0.05; bP < 0.01 vs control.
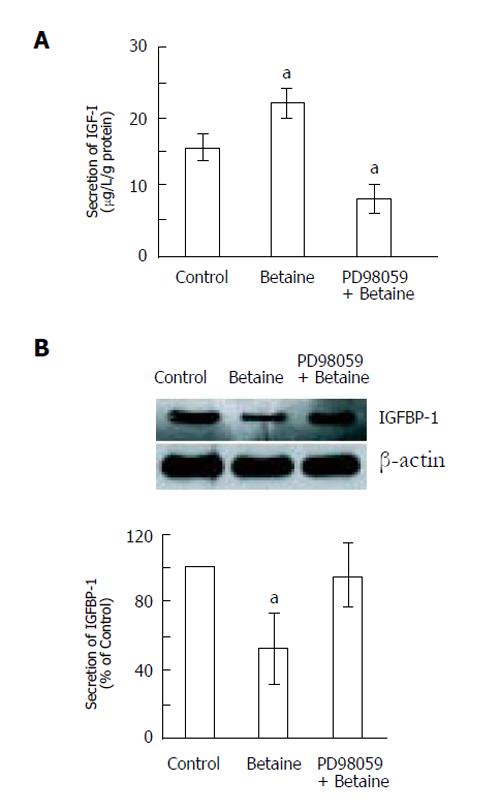
Figure 3 PD98059 attenuates the stimulation of IGF-I and attenuation of IGFBP-1 secretion effected by betaine (mean ± SD).
A: IGF-I, B: IGFBP-1. aP < 0.05, vs control.
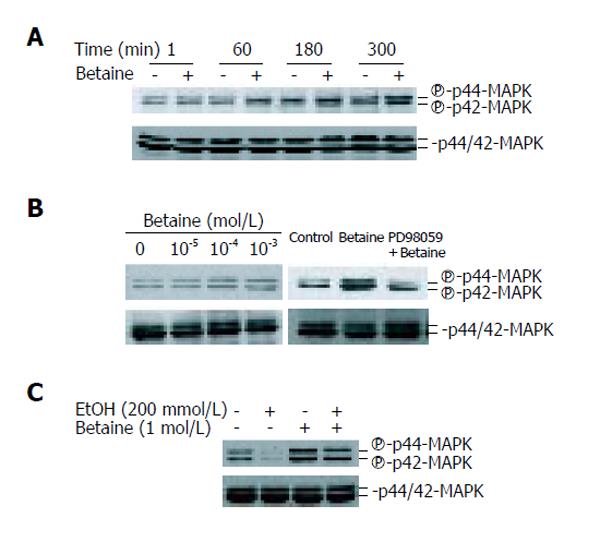
Figure 4 Betaine stimulates the phosphorylation of p42/44 MAPK in primary rat hepatocytes.
A: Time-dependent activation of p42/44 MAPK by 10-3 mol/L betaine, B: Dose-dependent activation of p42/44 MAPK by betaine for 300 min (left panel). Treatment with betaine following pretreatment with PD98059 for 10 min (right panel), C: Betaine-stimulated recovery of p42/44 MAPK activation in ethanol-treated cells.
- Citation: Lee MS, Kim MS, Park SY, Kang CW. Effects of betaine on ethanol-stimulated secretion of IGF-I and IGFBP-1 in rat primary hepatocytes: Involvement of p42/44 MAPK activation. World J Gastroenterol 2006; 12(11): 1718-1722
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v12/i11/1718.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v12.i11.1718