Copyright
©2005 Baishideng Publishing Group Inc.
World J Gastroenterol. Dec 7, 2005; 11(45): 7136-7141
Published online Dec 7, 2005. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v11.i45.7136
Published online Dec 7, 2005. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v11.i45.7136
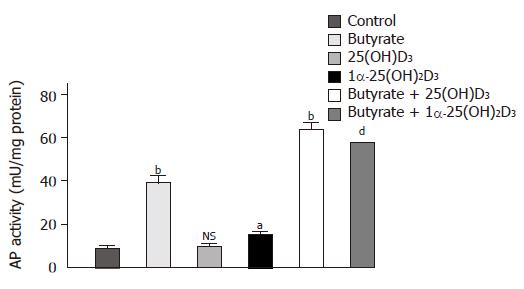
Figure 1 Effects of 1α-25(OH)2D3, 25(OH)2D3 and butyrate on differentiation of Caco-2 cells as assessed by AP activity.
Cells were treated for 48 h with a medium supplemented with 10-6 mol/L 1α-25(OH)2D3, 10-6 mol/L 25(OH)2D3, 3 mmol/L butyrate, or with one of the combinations of butyrate (3 mmol/L) and 1α-25(OH)2D3 (10–6 mol/L) or butyrate (3 mmol/L) and 25(OH)2D3, (10–6 mol/L). Values are expressed as milliunits of AP activity per milligram cellular protein. aP<0.05; bP<0.01; dP<0.001; NS: non significant.
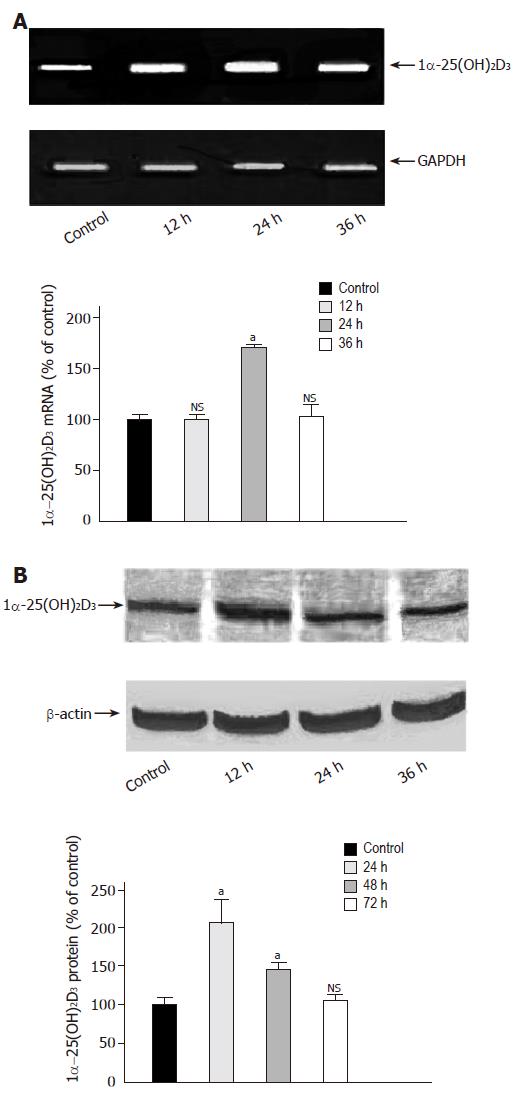
Figure 2 Time-dependent effect of butyrate on 1α-25(OH)2D3 expression.
A: Caco-2 cells were grown for 36 h in serum-free medium in the absence (lane 1) or presence of butyrate (3 mmol/L) (lanes 2-4). 1α-25(OH)2D3 mRNA was analyzed by semiquantitative RT-PCR with the fluorescent dye PicoGreen. B: Caco-2 cells were treated for 72 h in the absence (lane 1) or presence of butyrate (3 mmol/L) (lanes 2-4) and then harvested for immunoblot analysis. The band at approximately 55 ku corresponds to 1α-25(OH)2D3 protein. Quantitation of protein was performed using a luminescent image scanner. aP<0,05 vs control; NS: non significant.
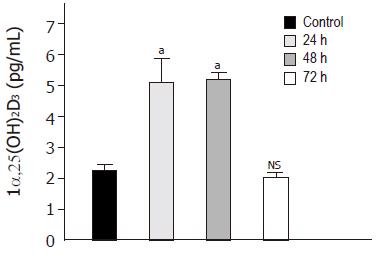
Figure 3 Time-dependent effect of butyrate on 1α-25(OH)2D3 activity.
Caco-2 cells were treated for 72 h in the absence (lane 1) or presence of butyrate (3 mmol/L) (lanes 2-4) and then harvested for ELISA. Values are expressed as pg/mL of 1α-25(OH)2D3. aP<0,05 vs control; NS, non significant.
- Citation: Schröder O, Turak S, Daniel C, Gaschott T, Stein J. Upregulation of 25-hydroxyvitamin D3-1α-hydroxylase by butyrate in Caco-2 cells. World J Gastroenterol 2005; 11(45): 7136-7141
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v11/i45/7136.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v11.i45.7136