Copyright
©2005 Baishideng Publishing Group Inc.
World J Gastroenterol. Nov 7, 2005; 11(41): 6466-6471
Published online Nov 7, 2005. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v11.i41.6466
Published online Nov 7, 2005. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v11.i41.6466
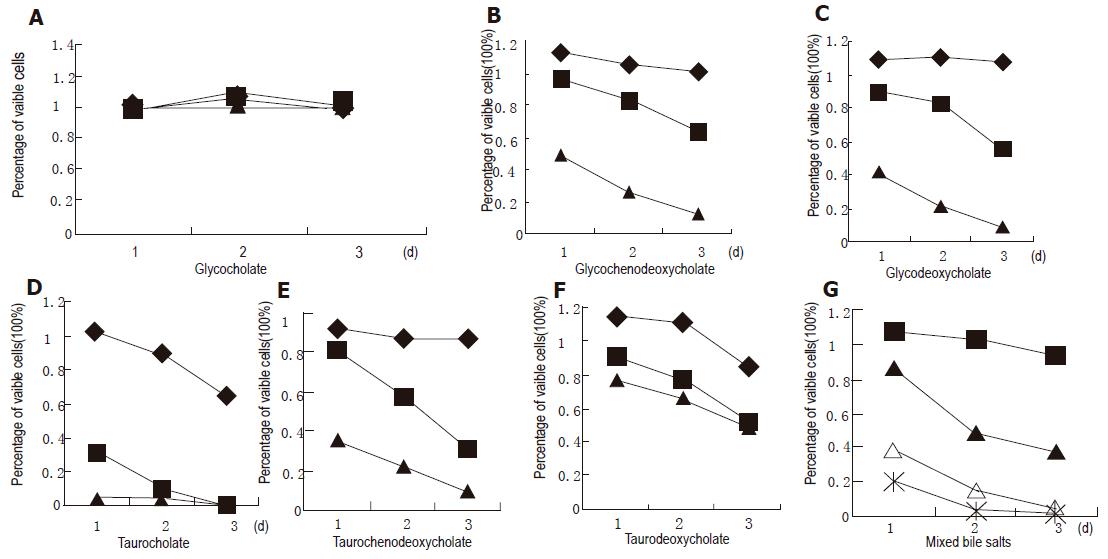
Figure 1 Effect of GC (A), GCDC (B), GDC (C), TC (D), TCDC (E), TDC (F), and mixture (G) on the growth of cultured normal human esophageal epithelial cells.
(at the concentration 50 μmol/L), ■ (250 μmol/L), ▲ (500 μmol/L), △ (1 000 μmol/L), and * (1 500 μmol/L).
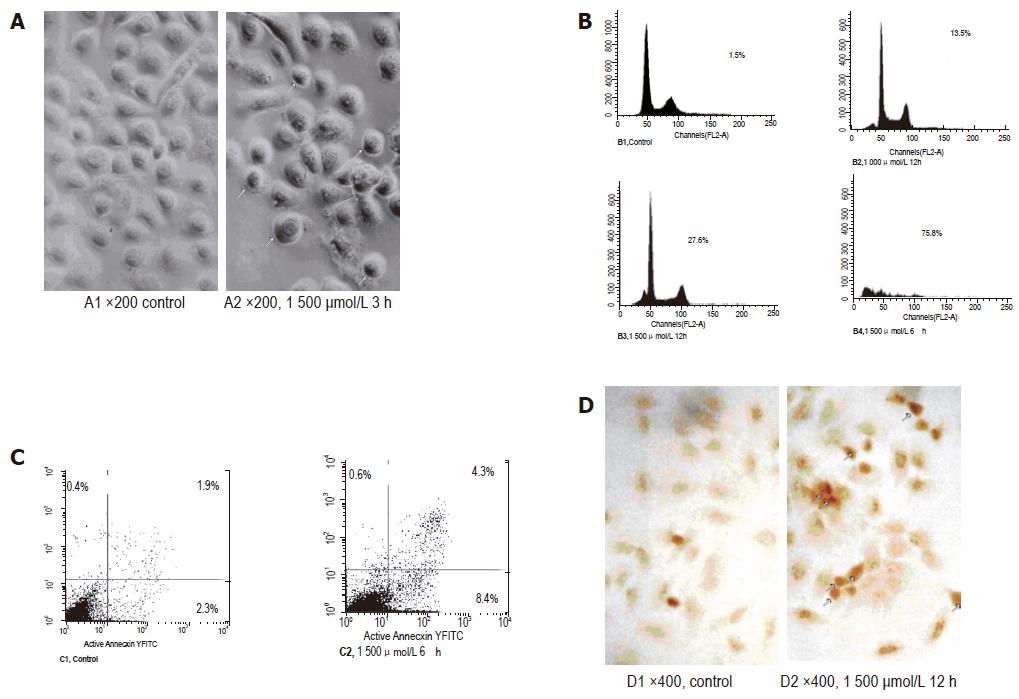
Figure 2 Characterization of bile salt mixture-induced apoptosis of normal esophageal mucosal epithelial cells.
A: Morphological changes of apoptotic membrane blebbing and cell shrinkage; B: apoptotic cells in sub-G1; C: early apoptotic cells; D: positively stained nuclei.
Figure 3 DNA fragments.
N: control; lane 1: cells treated with GC; lane 2: cells treated with TC; lane 3: cells treated with mixture.
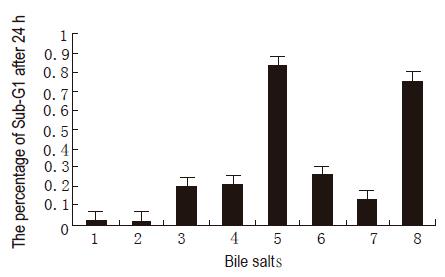
Figure 4 Percentages of apoptotic cells.
1: Control; 2: GC; 3: GCDC; 4: GDC; 5: TC for 2 h; 6: TCDC; 7: TDC; 8: mixture.
- Citation: Zhang R, Gong J, Wang H, Wang L. Bile salts inhibit growth and induce apoptosis of culture human normal esophageal mucosal epithelial cells. World J Gastroenterol 2005; 11(41): 6466-6471
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v11/i41/6466.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v11.i41.6466