Copyright
©2005 Baishideng Publishing Group Inc.
World J Gastroenterol. Jan 28, 2005; 11(4): 577-579
Published online Jan 28, 2005. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v11.i4.577
Published online Jan 28, 2005. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v11.i4.577
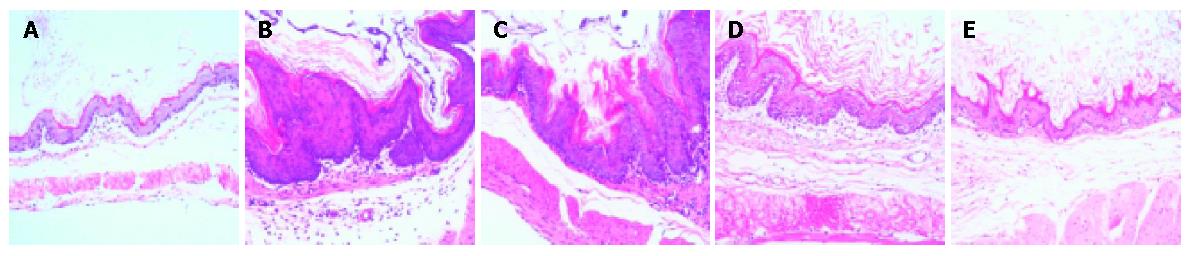
Figure 1 Histopathologic changes of forestomachs according to each treatment in BaP-induced forestomach carcinogenesis (n = 5/each group).
Note the significantly reduced hyperplasia of the gastric mucosa in PGW8 group, compared with SW groups. A: CO group (normal mucosa of forestomach); B: SW4 group; C: SW8 group; D: PGW4 group; E: PGW8 group (×200).
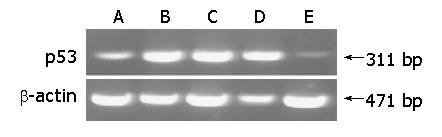
Figure 2 p53 mRNA expression in BaP-induced forestomach carcinogenesis by RT-PCR analysis (n = 5/each group).
The p53 gene expression was greatly down-regulated in PGW8 group, compared to the SW groups. The b-actin transcript levels among all groups were the same. A: CO group, B: SW4 group, C: SW8 group, D: PGW4 group, E: PGW8 group.
-
Citation: Bae JS, Jang KH, Yim H, Park SC, Jin HK. Inhibitory effects of polysaccharides isolated from
Phellinus gilvus on benzo(a)pyrene-induced forestomach carcinogenesis in mice. World J Gastroenterol 2005; 11(4): 577-579 - URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v11/i4/577.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v11.i4.577