Copyright
©2005 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Jan 21, 2005; 11(3): 377-381
Published online Jan 21, 2005. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v11.i3.377
Published online Jan 21, 2005. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v11.i3.377
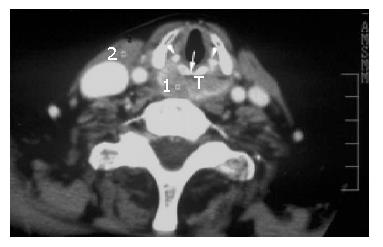
Figure 1 Axial contract-enhanced CT scan at the subglottic level of a 56-year-old man with postcricoid carcinoma (T) invading the esophageal inlet.
Arrowheads point to the arytenoid cartilage and the arrow points to the cricoid cartilage.
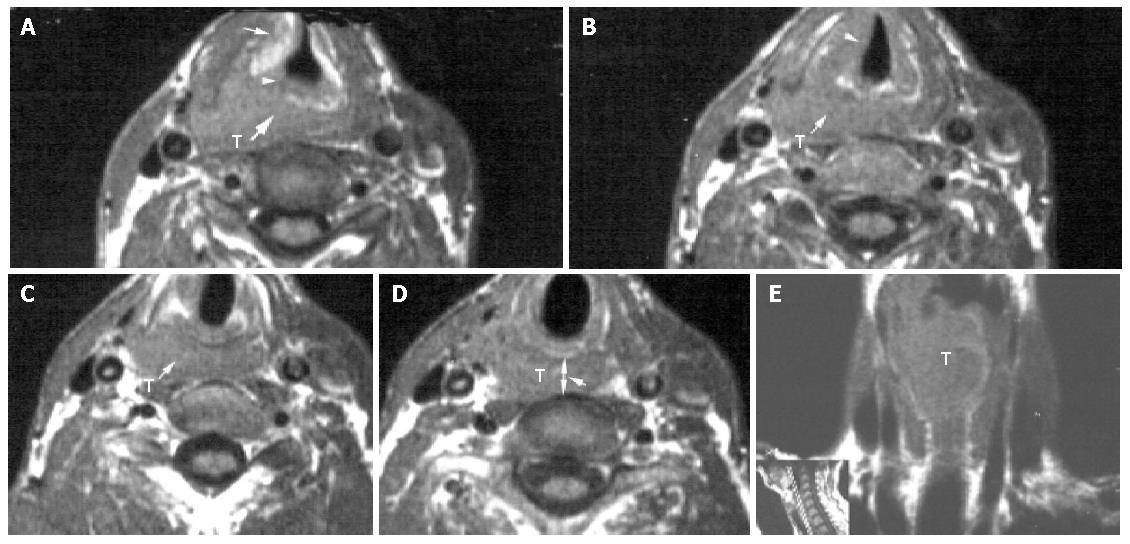
Figure 2 T1-weighted image of a 72 year-old man with pyriform sinus carcinoma invading the esophageal inlet.
A: Axial T1-weighted image of a right-sided pyriform sinus tumor mass (T) invading the right false cord, the laryngeal ventricle, the right paraglottic space (arrow), the right aryepiglottic fold (arrowhead) and the postcricoid region (heavy arrow); B: Axial T1-weighted image of the tumor mass (T) involving the right true vocal cord (arrowhead) and extending to the postcricoid region (arrow); C: Axial T1-weighted image 5 mm above the esophageal inlet level of a pyriform sinus tumor mass (T) invading the postcricoid region (arrow); D: Axial T1-weighted image of the neoplastic esophageal inlet involvement (arrow). T = tumor mass, arrowhead points to the distance between the posterior aspect of the cricoid cartilage and the anterior aspect of the vertebra (d-CV=1.32); E: Conoral T1-weighted image of a tumor mass (T) arising from the right piriform sinus with extension to the postcricoid region and the anteriorlateral wall of the esophagus, including esophageal inlet and cervical esophagus.
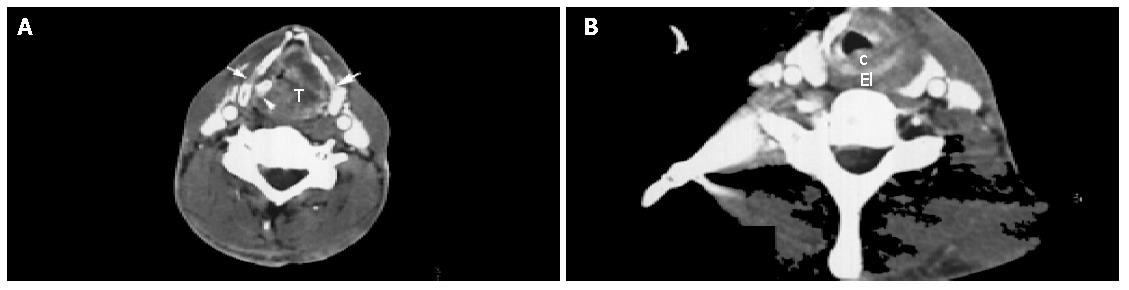
Figure 3 Axial contrast-enhanced CT of a 67-year-old man with direct esophageal inlet involvement by laryngeal carcinoma.
A: Axial contrast-enhanced CT at the supraglottic level of a left-sided laryngeal tumor mass (T) invading both aryepiglottic folds, both false cords, laryngeal ventricles and paraglottic spaces. Arrows point to the destruction of thyroid cartilages. Arrowhead points to the intact arytenoid cartilage; B: Axial contrast-enhanced CT at the esophageal inlet level of a tumor mass extending to the subglottic region, eroding the cricoid cartilage (C) and invading the esophageal inlet (EI).
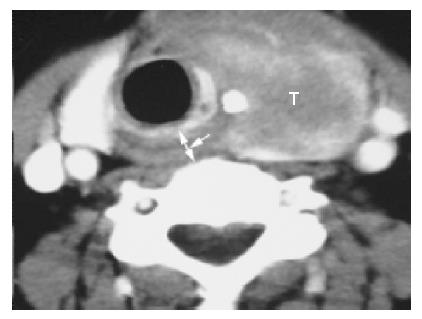
Figure 4 Axial contrast-enhanced CT of a 49-year-old woman with thyroid carcinoma invading the esophageal inlet.
Arrowhead points to the distance between the posterior aspect of the cricoid cartilage and the anterior aspect of the vertebra (d-CV = 1.12).
- Citation: Chen B, Yin SK, Zhuang QX, Cheng YS. CT and MR imaging for detecting neoplastic invasion of esophageal inlet. World J Gastroenterol 2005; 11(3): 377-381
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v11/i3/377.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v11.i3.377