Copyright
©2005 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Jan 14, 2005; 11(2): 237-241
Published online Jan 14, 2005. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v11.i2.237
Published online Jan 14, 2005. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v11.i2.237
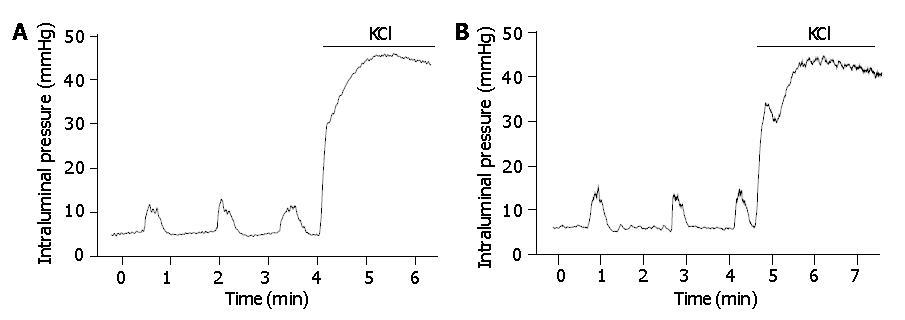
Figure 1 Motor activities of circular muscle in isolated colonic segments.
Motor activities of circular muscle were measured as changes in intraluminal pressure in (A) normal rat colon and (B) IBS rat colon. No difference was observed between groups in the spontaneous rhythmic phasic contraction and in the KCl (60 mmol/L)-induced tonic contraction.
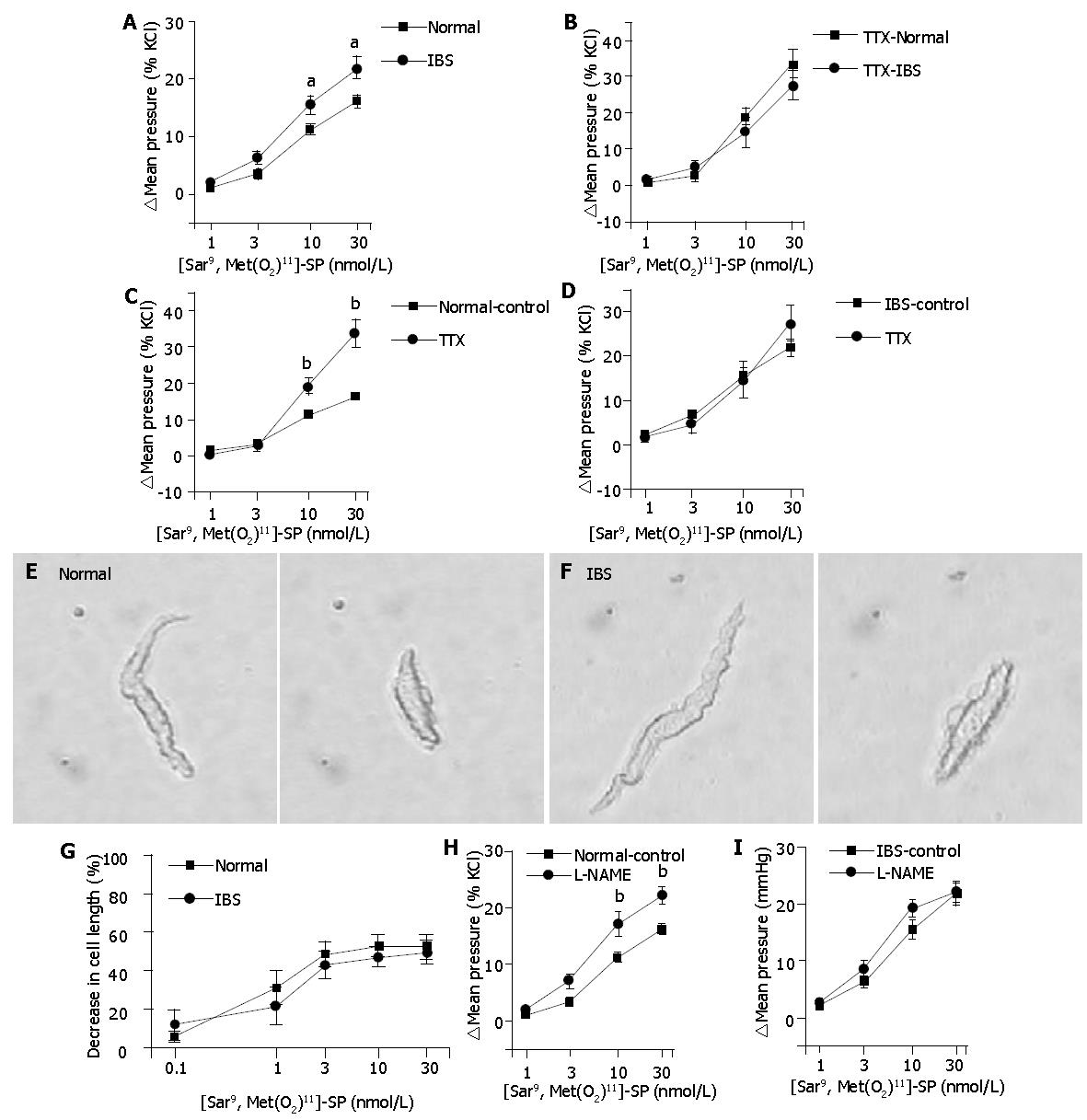
Figure 2 Contractile effect of NK1R agonist on isolated distal colonic segments, isolated colonic myocytes, and NOS inhibitor-pretreated isolated colonic segments.
A: The contractile sensitivity of IBS rat colon to [Sar9,Met(O2)11]-SP was higher than that of normal rat colon. aP<0.05 vs normal by Student’s t-test with Bonferroni correction; B: Under the presence of TTX (1 μmol/L), no statistical difference was detected between groups in the [Sar9,Met(O2)11]-SP-induced contraction; C and D: TTX increased the [Sar9,Met(O2)11]-SP-induced contraction in normal rat colon but not in IBS rat colon. bP<0.01 vs control by Student’s t-test with Bonferroni correction (n = 12 in normal control, 9 in IBS control, 8 in TTX-normal, 7 in TTX-IBS); E and F: Photographs of myocytes in normal and IBS groups under control condition (left), and under the presence of 30 nmol/L [Sar9,Met(O2)11]-SP (right). Bar = 30 μm. G: Dose-response plot showing the contractile effect of [Sar9,Met(O2)11]-SP on the isolated colonic myocytes. The [Sar9,Met(O2)11]-SP-induced contraction was measured as a percent decrease in cell length (n = 7 in normal, 8 in IBS); H and I: Normal and IBS rat colonic segments were incubated with a NOS inhibitor L-NAME (0.1 mmol/L) for 10 min before the cumulative administration of [Sar9,Met(O2)11]-SP. bP<0.01 vs control by Student’s t-test (H: n = 12 in control, 7 in L-NAME. I: n = 9 in control, 6 in L-NAME).
- Citation: La JH, Kim TW, Sung TS, Kim HJ, Kim JY, Yang IS. Increase in neurokinin-1 receptor-mediated colonic motor response in a rat model of irritable bowel syndrome. World J Gastroenterol 2005; 11(2): 237-241
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v11/i2/237.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v11.i2.237