Copyright
©2005 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Jan 14, 2005; 11(2): 232-236
Published online Jan 14, 2005. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v11.i2.232
Published online Jan 14, 2005. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v11.i2.232
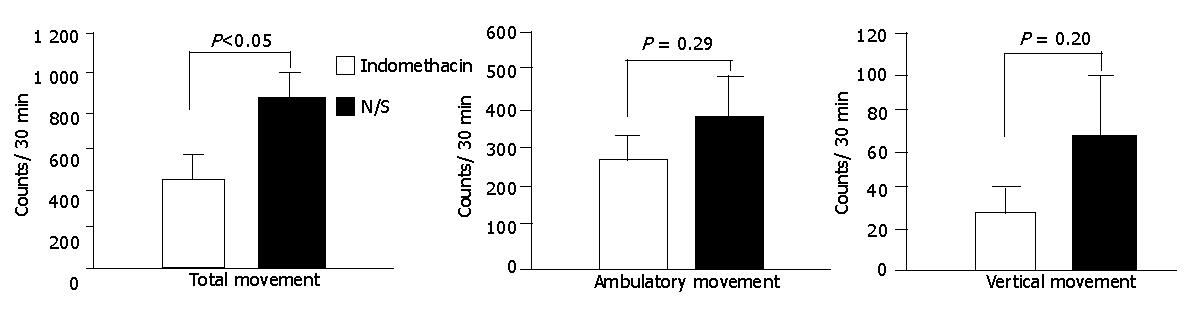
Figure 1 Comparison of the degree of hepatic encephalopathy by total, ambulatory and vertical movement counts between rats with fulminant hepatic failure treated with indomethacin (n = 19) or N/S (n = 16).
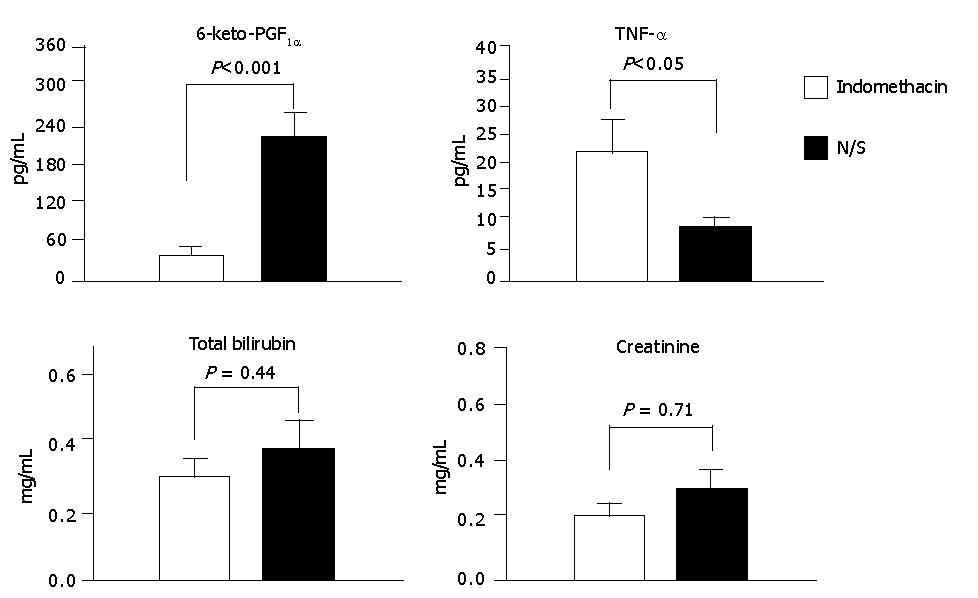
Figure 2 Comparison of the plasma levels of 6-keto-PGF1α, TNF-α, total bilirubin, and creatinine between rats with fulminant hepatic failure treated with indomethacin (n = 19) or N/S (n = 16).
- Citation: Chu CJ, Hsiao CC, Wang TF, Chan CY, Lee FY, Chang FY, Chen YC, Huang HC, Wang SS, Lee SD. Prostacyclin inhibition by indomethacin aggravates hepatic damage and encephalopathy in rats with thioacetamide-induced fulminant hepatic failure. World J Gastroenterol 2005; 11(2): 232-236
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v11/i2/232.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v11.i2.232