Copyright
©2005 Baishideng Publishing Group Inc.
World J Gastroenterol. May 21, 2005; 11(19): 2864-2868
Published online May 21, 2005. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v11.i19.2864
Published online May 21, 2005. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v11.i19.2864
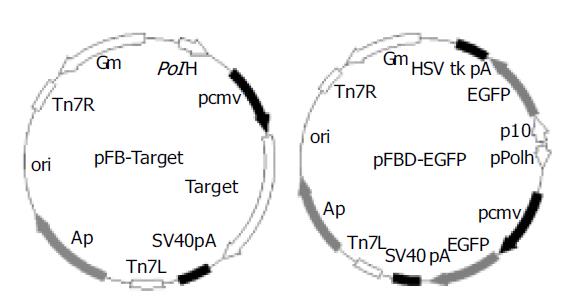
Figure 1 Map of pFB-targets (target is A1, A2 or BP respectively) and pFBD-EGFP.
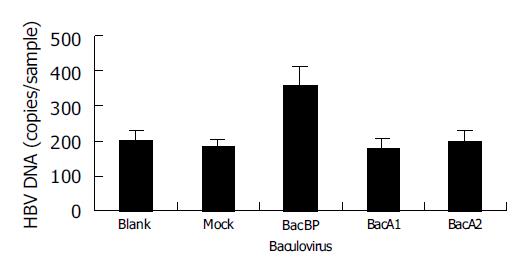
Figure 2 HBV binding to WI-38 cells infected with different recombinant balculoviruses; blank: uninfected cells; mock: BacEGFP infected cells.
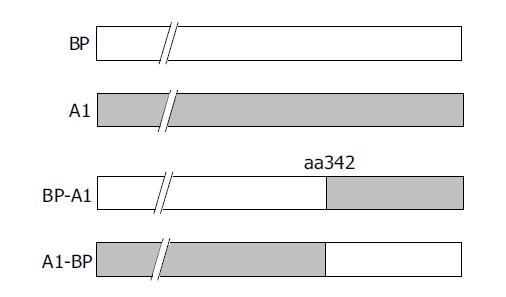
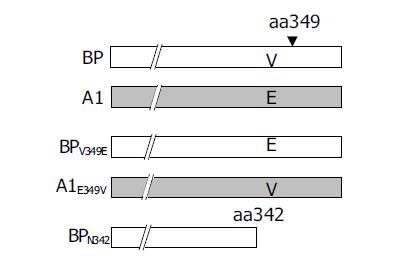
Figure 3 Construction of chimeric mutants of BP and A1.
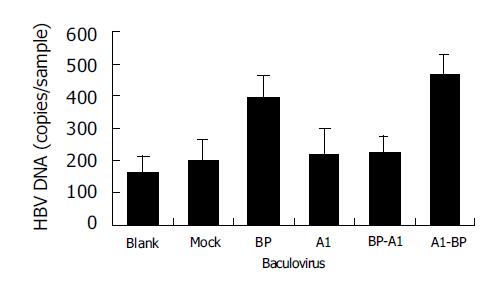
Figure 4 HBV binding to WI-38 cells expressing chimeric mutants of BP and A1.
Blank: uninfected cells; mock: BacEGFP infected cells.
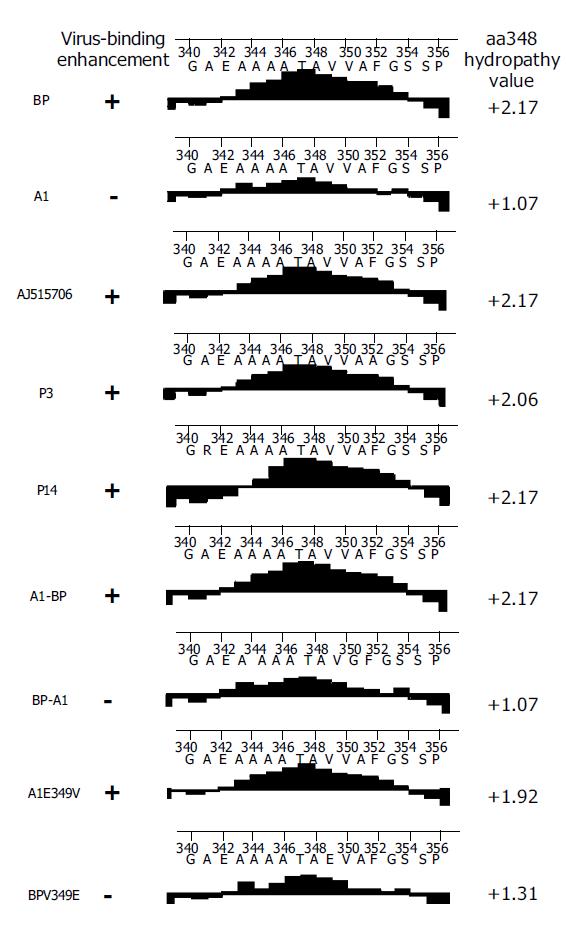
Figure 5 Hydrophobicity analysis of several SCCA1 proteins.
Figure 6 Construction of different SCCA1 mutants.
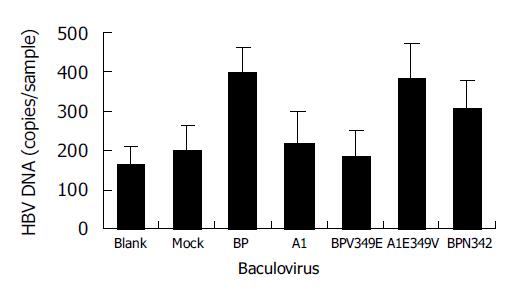
Figure 7 HBV binding to WI-38 cells expressing site-mutants of BP and A1.
Blank: uninfected cells; mock: BacEGFP infected cells.
- Citation: Chen M, Cheng T, Xu CY, Wu T, Ou SH, Zhang T, Zhang J, Xia NS. Hydrophobicity of reactive site loop of SCCA1 affects its binding to hepatitis B virus. World J Gastroenterol 2005; 11(19): 2864-2868
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v11/i19/2864.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v11.i19.2864