Copyright
©The Author(s) 2004.
World J Gastroenterol. Mar 1, 2004; 10(5): 694-698
Published online Mar 1, 2004. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v10.i5.694
Published online Mar 1, 2004. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v10.i5.694
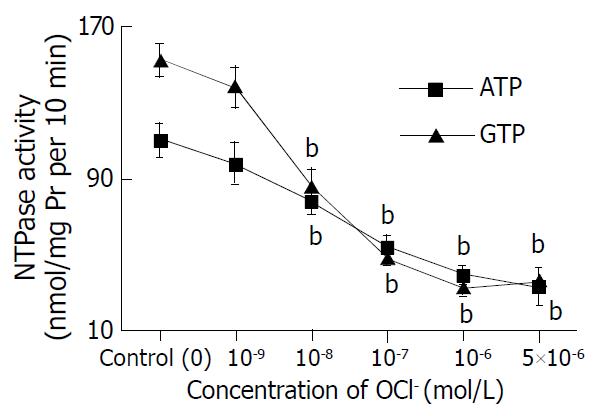
Figure 1 Inhibitory effect of hypochlorous acid on hepatic nuclear NTPase activity.
ATP and GTP were used as reaction substrates, respectively. Mean ± SD, n = 6. aP < 0.05, bP < 0.01 com-pared with control.
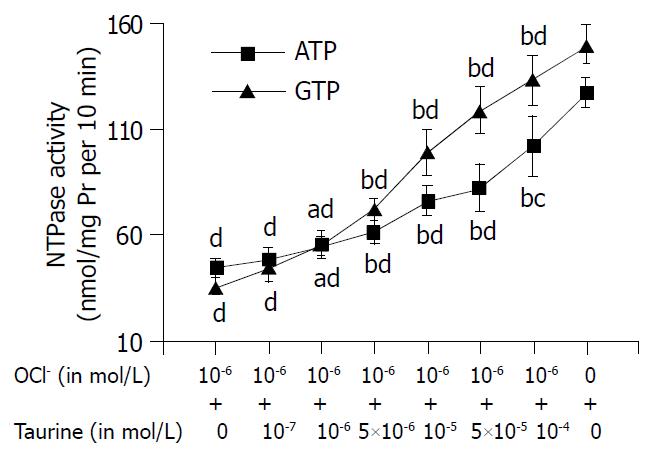
Figure 2 Effect of taurine on OCl--induced inhibition of NTPase activity in hepatic nuclei.
ATP and GTP were used as reaction substrates, respectively. Mean ± SD, n = 6. aP < 0.05, bP < 0.01 com-pared with OCl (10-6 mol/L) group. cP < 0.05, dP < 0.01 compared with control.
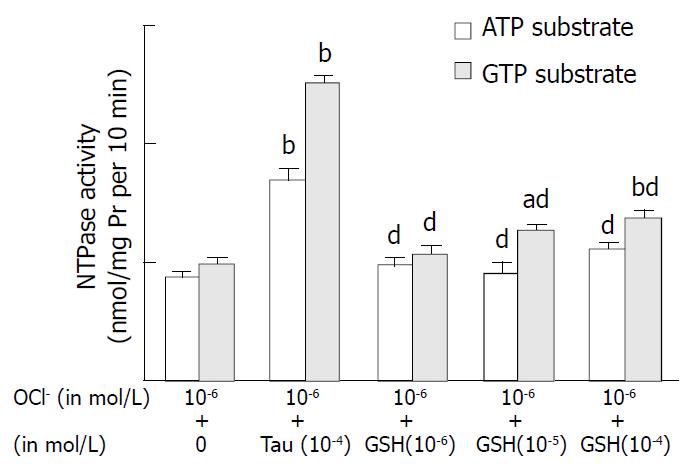
Figure 3 Effects of glutathione on OCl--induced inhibition of NTPase activity in hepatic nuclei.
ATP and GTP were used as reaction substrates, respectively. Mean ± SD, n = 6. bP < 0.01 com-pared with control group (OCl-1 10-6 mol/L). aP < 0.05, cP < 0.01 compared with (10-6 mol/L OCl-1 + 10-4 mol/L taurine).
- Citation: Li JX, Pang YZ, Tang CS, Li ZQ. Protective effect of taurine on hypochlorous acid toxicity to nuclear nucleoside triphosphatase in isolated nuclei from rat liver. World J Gastroenterol 2004; 10(5): 694-698
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v10/i5/694.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v10.i5.694