Copyright
©The Author(s) 2004.
World J Gastroenterol. Dec 1, 2004; 10(23): 3419-3423
Published online Dec 1, 2004. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v10.i23.3419
Published online Dec 1, 2004. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v10.i23.3419
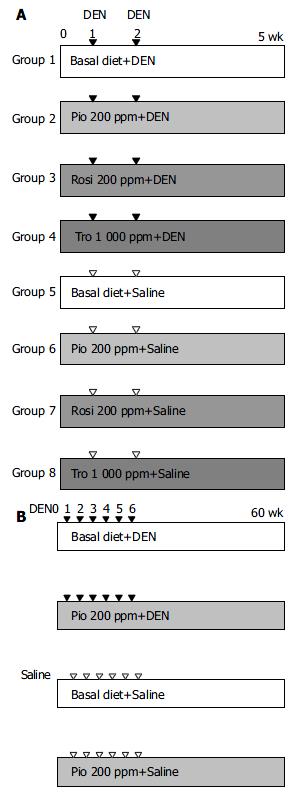
Figure 1 Experimental design for evaluation of chemoprevention efficacy of PPARγ ligands against liver carcinogenesis.
A: In the short-term study of rGST P-positive foci, groups of male Wistar rats were fed experimental diets containing 0 or 200 or 1000 ppm of PPARγ ligands from 1 wk prior to exposure to DEN at 20 mg/kg bm until the termination. B: For liver tumor study, groups of animals were given the basal diet or experi-mental diet containing 200-ppm Pio continuously from 1 wk prior to exposure of animals to DEN, IP, at 1to 6 experimental weeks at 20 mg/kg bm until the termination.
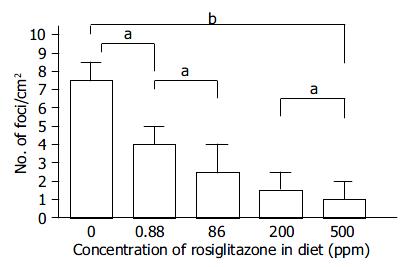
Figure 2 Dose-dependent suppression of the formation of rGST P-positive foci by rosiglitazone.
As clearly demonstrated, Rosi suppressed the formation of rGST P-positive foci in a dose-dependent manner within the range of 0.88-500 ppm in diet (aP < 0.05, bP < 0.01).
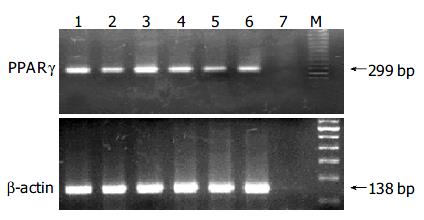
Figure 3 Expression of PPARγ mRNA in liver tumors.
Lanes 1 and 4: normal liver tissues; lanes 2, 3, 5, and 6: liver tumor tissues; lane 7: water.
- Citation: Guo YT, Leng XS, Li T, Zhao JM, Lin XH. Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor γ ligands suppress liver carcinogenesis induced by diethylnitrosamine in rats. World J Gastroenterol 2004; 10(23): 3419-3423
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v10/i23/3419.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v10.i23.3419