Copyright
©The Author(s) 2004.
World J Gastroenterol. Aug 1, 2004; 10(15): 2205-2208
Published online Aug 1, 2004. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v10.i15.2205
Published online Aug 1, 2004. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v10.i15.2205
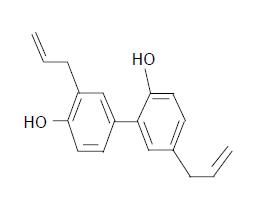
Figure 1 Chemical structure of honokiol (C18H18O2, Mr 266.
33).
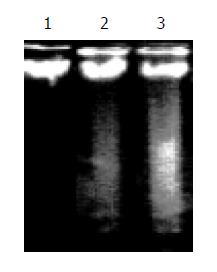
Figure 2 Differences in vehicle and honokiol induced apoptotic DNA laddering of RKO cells.
Lane 1: Vehicle; Lane 2: 5 μg/mL; Lane 3: 10 μg/mL.
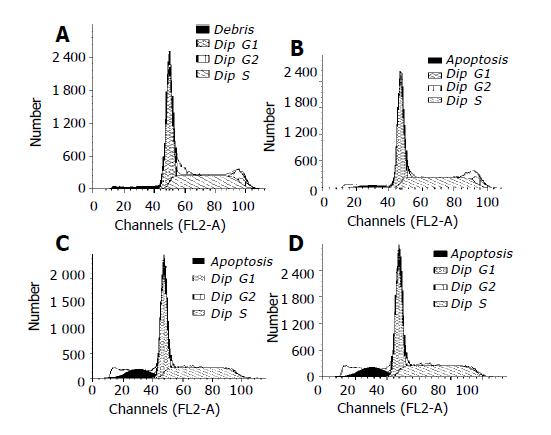
Figure 3 Apoptosis of RKO cells detected by FCM.
A: Vehicle; B: 5 μg/mL honokiol; C: 10 μg/mL honokiol; D: 15 μg/mL honokiol.
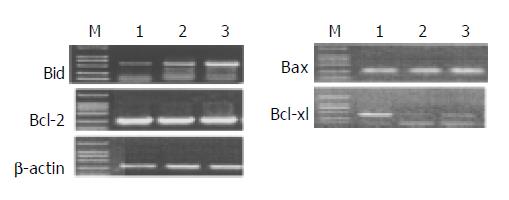
Figure 4 Analysis of Bcl- 2, Bax, Bid and Bcl- xl mRNA by RT-PCR.
M: DNA mark; Lane 1: Vehicle; Lane 2: 5 μg/mL honokiol; Lane 3: 10 μg/mL honokiol.
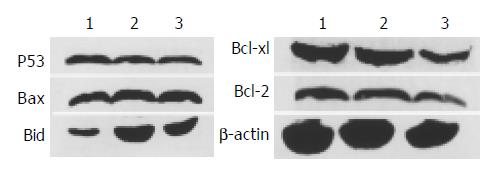
Figure 5 Western blotting of honokiol- and vehicle-induced Bax, Bcl-2, Bcl-xl, Bid and p53 protein levels in RKO cell line.
Lane 1: Vehicle; Lane 2: 5 μg/mL; Lane 3: 10 μg/mL.
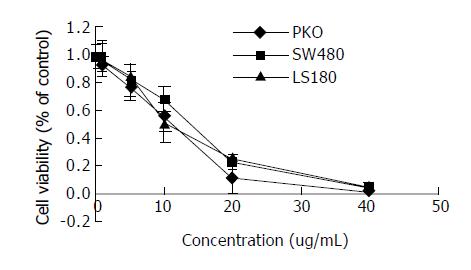
Figure 6 Concentration-dependent inhibition of RKO, SW480 and LS180 cells exposed to the various concentrations of honokiol shown by MTT assay.
- Citation: Wang T, Chen F, Chen Z, Wu YF, Xu XL, Zheng S, Hu X. Honokiol induces apoptosis through p53-independent pathway in human colorectal cell line RKO. World J Gastroenterol 2004; 10(15): 2205-2208
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v10/i15/2205.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v10.i15.2205