Copyright
©The Author(s) 2004.
World J Gastroenterol. May 15, 2004; 10(10): 1521-1525
Published online May 15, 2004. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v10.i10.1521
Published online May 15, 2004. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v10.i10.1521
Figure 1 Expressions of NF-κBp65 and IκB in nuclei and cytoplasm.
A: Expression of NF-κBp65 in nuclei, B: Expres-sion of IκB in cytoplasm, Lanes1-2: expression before treatment, Lanes3: expression after probiotics treatment, Lanes4: expression in control.
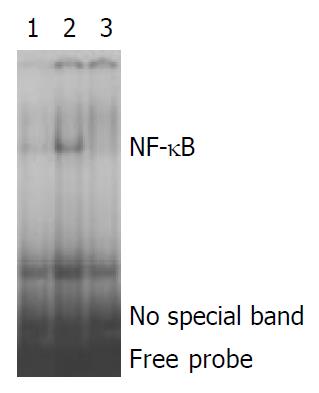
Figure 2 Inhibition of NF-κB binding DNA by BIFICO.
1, Cool probe; 2, Activation NF-κB before treatment; 3: Probiotic significantly inhibited activation of NF-κB.
Figure 3 Activation of NF-κB in.
Placebo group 1, Cool probe; 2, Activation of NF-κB before treatment; 3, Placebo did not obviously inhibit the activation of NF-κB.
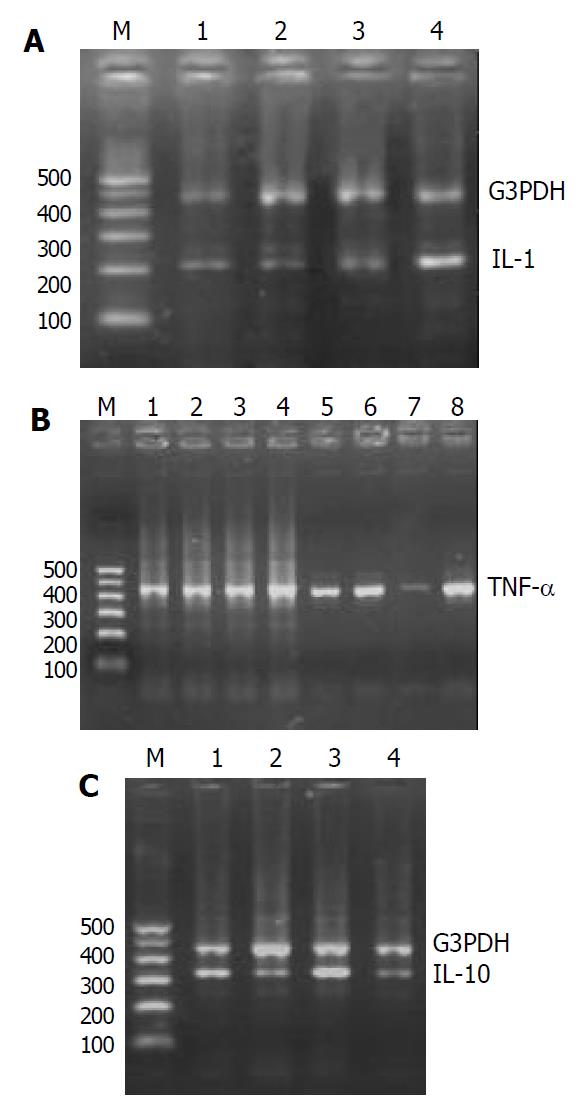
Figure 4 Expressions of IL-1mRNA, TNF-α mRNA and IL-10 mRNA.
A: Expression of IL-1 mRNA, Lanes 1,2: IL-1 mRNA expression before treatment; lane 3: BIFICO inhibited IL-1 mRNA expression; lane 4: IL-1 mRNA expression in placebo group. B: Expression of TNF-α mRNA, Lanes 1, 2, 3, 4 G3PDH; lanes 5, 6: TNF-α mRNA expression before treatment; Lane 7: BIFICO inhibited significantly mRNA expression of TNF-α; lane 8: TNF-α mRNA expression in placebo group. C: Expres-sion of IL-10 mRNA, Lanes 1, 2: IL-10 mRNA before treatment; lane 3: BIFICO enhanced IL-10 mRNA expression; lane 4: IL-10 mRNA in placebo group.
- Citation: Cui HH, Chen CL, Wang JD, Yang YJ, Cun Y, Wu JB, Liu YH, Dan HL, Jian YT, Chen XQ. Effects of probiotic on intestinal mucosa of patients with ulcerative colitis. World J Gastroenterol 2004; 10(10): 1521-1525
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v10/i10/1521.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v10.i10.1521