Copyright
©The Author(s) 2004.
World J Gastroenterol. May 15, 2004; 10(10): 1452-1456
Published online May 15, 2004. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v10.i10.1452
Published online May 15, 2004. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v10.i10.1452
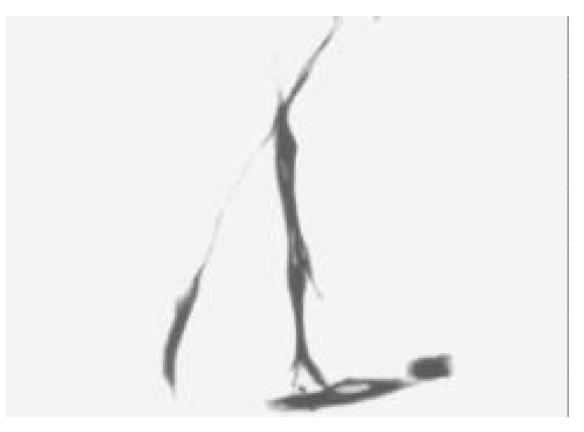
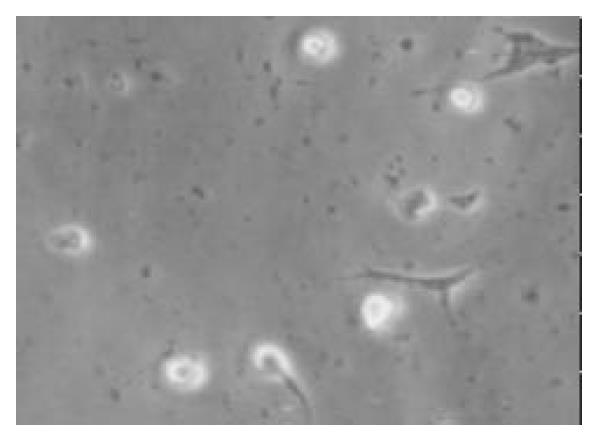
Figure 1 After being cultured for 24 h, a few cells were adherented on the bottom of non-sticky flasks, some of the cells processed protrusions (× 100).
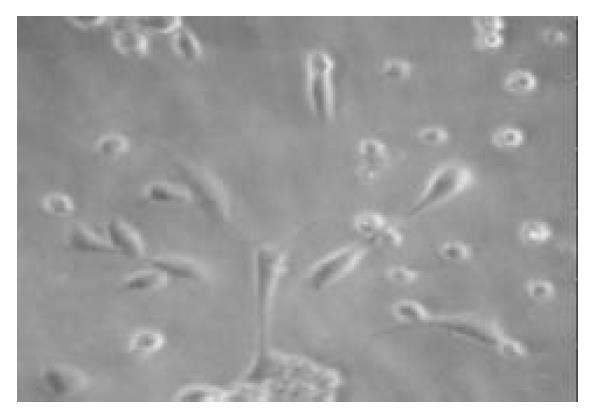
Figure 2 After being cultured for 2 wk in the media added the keratinocyte growth factor, the number of cells increased, the cells became fusiform with a few processes (× 100).
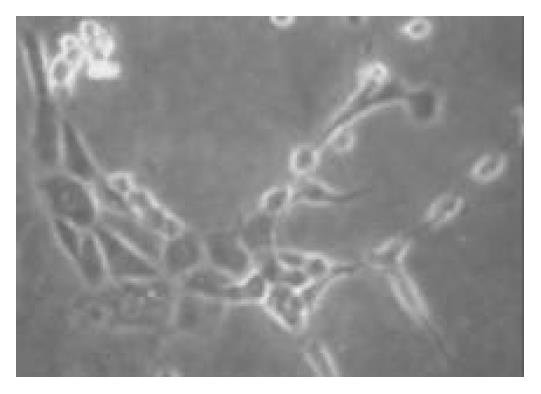
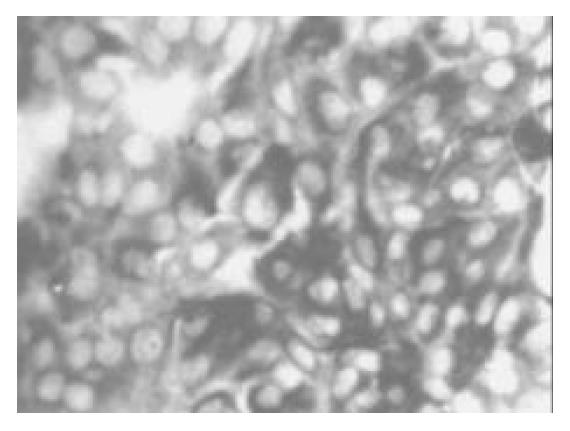
Figure 3 Most cells of culture were positive for CK-19 immu-noreactivity after being cultured for 2 wk (× 100).
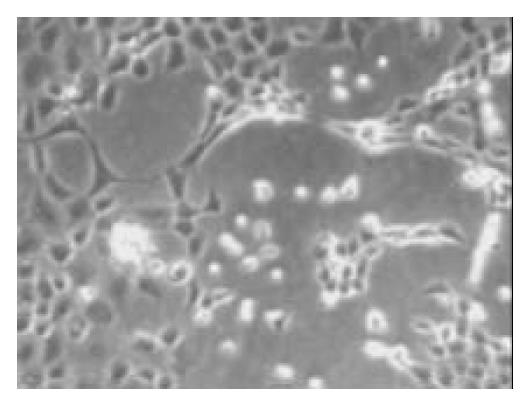
Figure 4 The cells were cobblestone pattern after being cul-tured for 4 wk (× 150).
Figure 5 The cells were cobblestone pattern and formed mono-layer after being cultured for 6 wk (× 100).
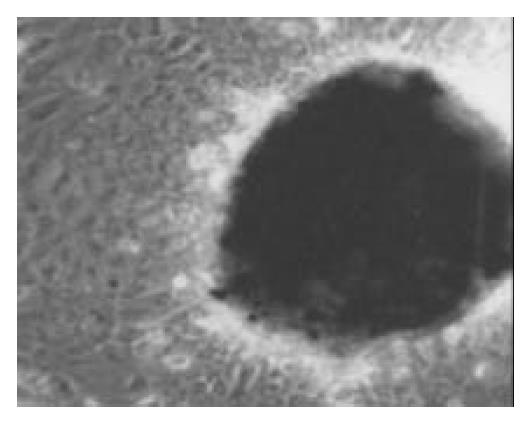
Figure 6 The cells were induced to form pancreatic islet-like struc-tures after being cultured in the media containing 17.
8 mmol/L glucose for 1 wk (× 100).
Figure 7 After being cultured in the medium containing 17.
8 mmol/L glucose for 1 wk, many cells in islet-like struc-tures were positve for insulin immunoreactivity (× 150).
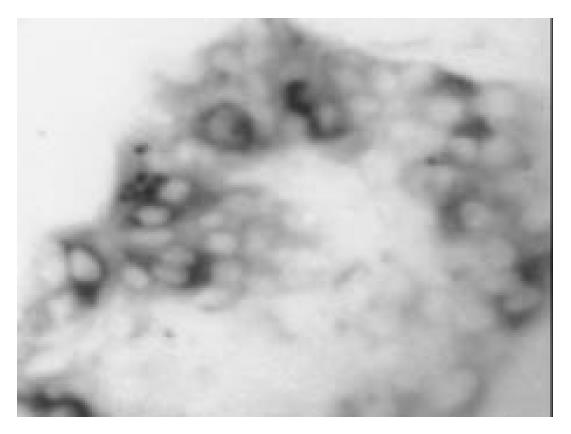
Figure 8 After being cultured in the medium containing 17 mmol/L glucose for 1 wk, a few cells in islet-like structures were posi-tive for glucagon immunoreactivity (× 150).
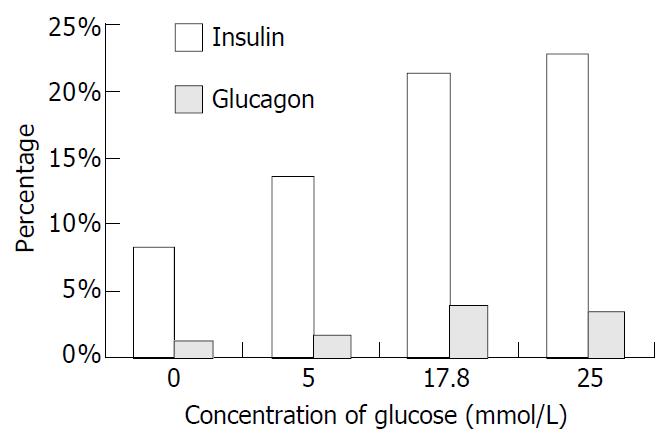
Figure 9 Percentage of immunopositive cells induced by glucose.
-
Citation: Yao ZX, Qin ML, Liu JJ, Chen XS, Zhou DS.
In vitro cultivation of human fetal pancreatic ductal stem cells and their differentiation into insulin-producing cells. World J Gastroenterol 2004; 10(10): 1452-1456 - URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v10/i10/1452.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v10.i10.1452