Copyright
©The Author(s) 2004.
World J Gastroenterol. May 15, 2004; 10(10): 1415-1420
Published online May 15, 2004. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v10.i10.1415
Published online May 15, 2004. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v10.i10.1415
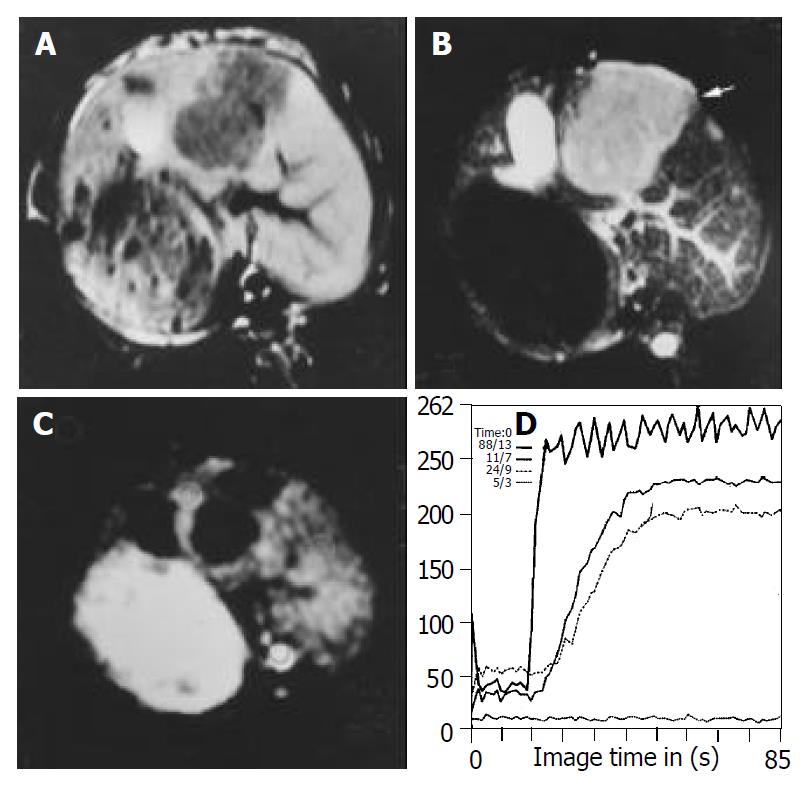
Figure 1 Images obtained before treatment in control group.
A: T1WI shows hypointense lesions in left lobe of the liver. B: T2WI shows homogeneous hyperintense lesions in left lobe of the liver. C: FP T1-weighted image with gadolinium shows rim enhance-ment and no enhancement in the center of lesion. D: Signal intensity time curve derived from FP, SS of the curve in the border of the lesion is steeper than that of the normal liver.
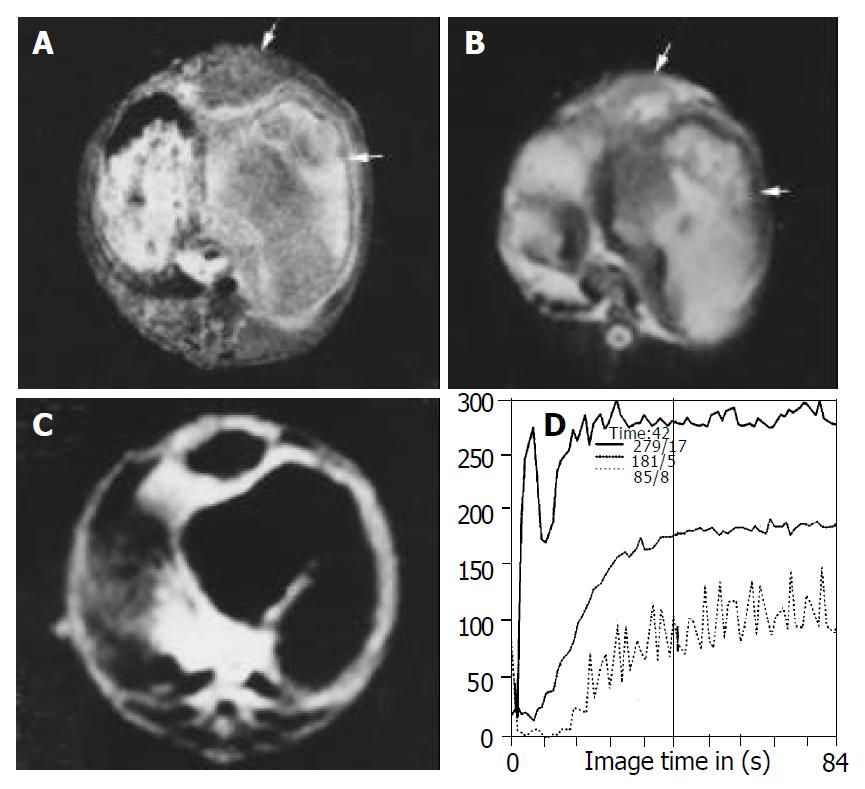
Figure 2 Images obtained after treatment in lipiodol group.
Inhomogeneous hyperintense lesions with intermediate intense rim (arrow head) can be seen on T1WI (A) and T2WI (B), indicating the necrosis of the lesion and intratumor retention of lipiodol. (C) FP T1-weighted image with gadolinium shows thinner rim enhancement and no enhancement in the center of the lesion com-pared with control group although the lesion volume is increased. (D) SS of the curve in center of the lesion is decreased compared with those of the border.
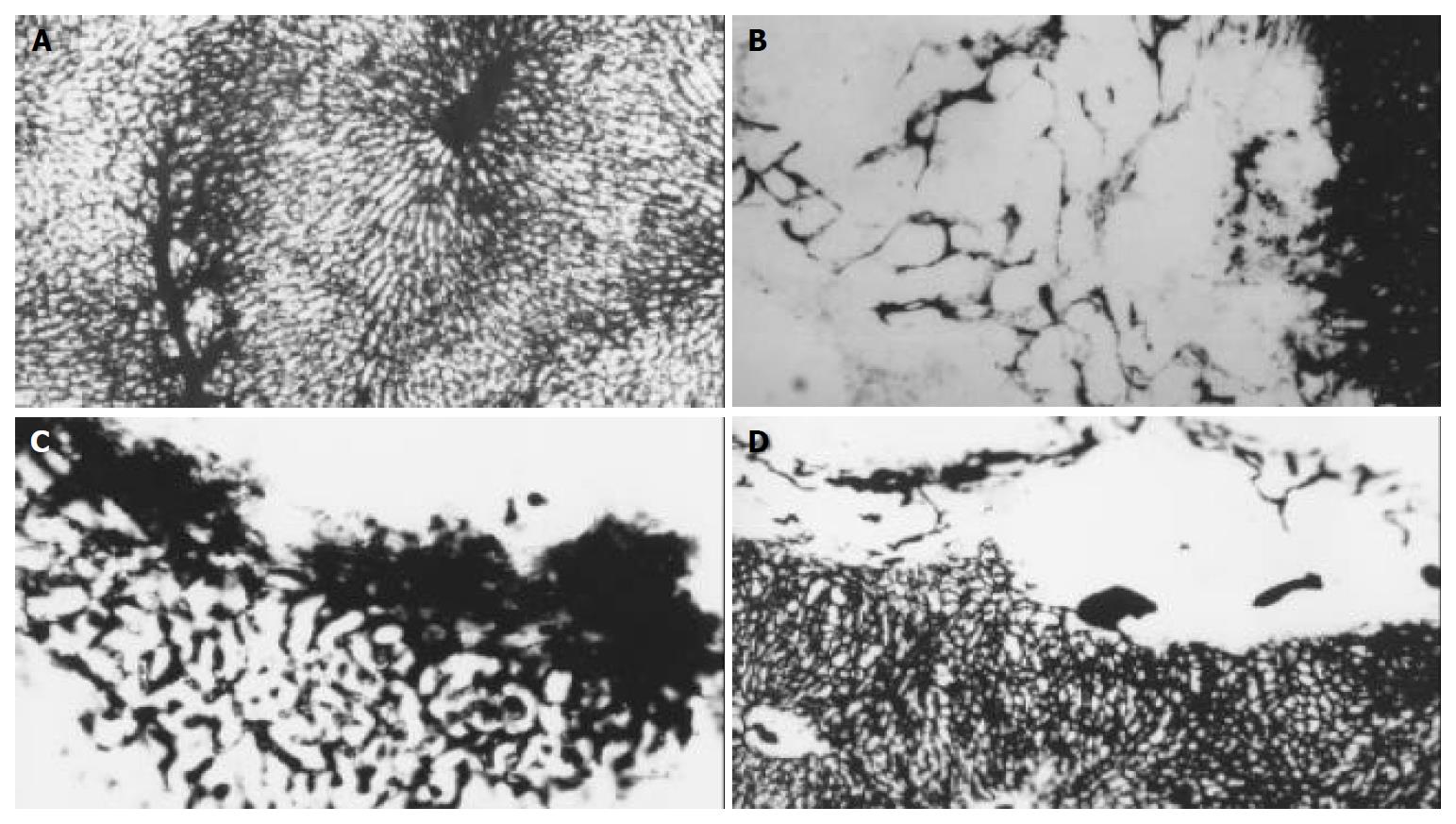
Figure 3 Micro-vessel casting with Chinese ink through ascending artery.
A: The specimens show a lobular architecture of normal liver, magnification × 100. B: In control group, hepatic artery perfusion shows networks of micro-vessels or plexuses of dilated and tortuous course around and within the tumor originated from the arterioles, some sinusoid vessels can be observed in this tumor, magnification × 100. C: The original micro-vessels of the tumor are remarkably diminished, small and dense new plexuses appear around the tumor in lipiodol group, which are correlated to intense reaction of granulation tissue, magnification × 100. D: micro-vessels are decreased in bletilla group, no new micro-vessels can be seen at all, magnification × 100.
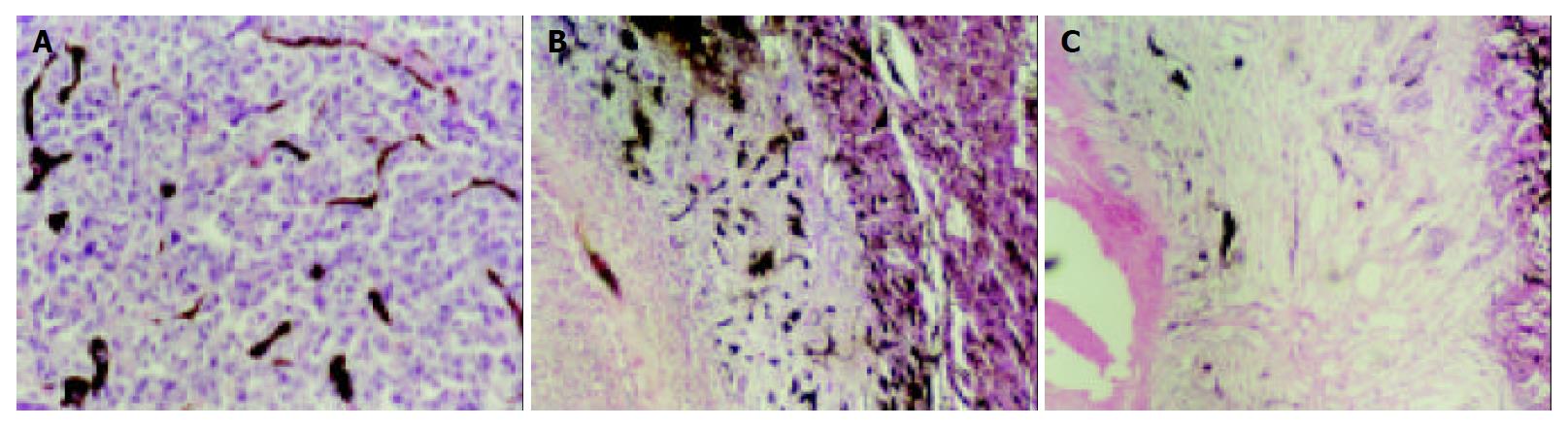
Figure 4 Histological examinations of hepatic lesion before and after treatment.
A: HE stain shows nidal arrangement of VX2 cells as well as micro-vessels filled with Chinese ink before treatment, magnification × 200. B: In lipiodol group, histological examina-tion shows coagulation necrosis at the center of lesion, very few micro-vessels can be seen within this zone, residual tumor cells are seen at the periphery of lesions, moreover, an intense reaction of granulation tissue is seen within this area, small dense vessels are scattered at border of the lesion, and congested sinusoids are seen in the periphery of the tumor, magnification × 200. C: Coagulation necrosis as well as large infarcts involving multiple adjacent lobules is seen in bletilla group, few vessels are seen at the border of the lesion, magnification × 200.
- Citation: Zhao JG, Feng GS, Kong XQ, Li X, Li MH, Cheng YS. Changes of tumor microcirculation after transcatheter arterial chemoembolization: First pass perfusion MR imaging and Chinese ink casting in a rabbit model. World J Gastroenterol 2004; 10(10): 1415-1420
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v10/i10/1415.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v10.i10.1415