Copyright
©The Author(s) 2023.
World J Clin Cases. Sep 6, 2023; 11(25): 5840-5856
Published online Sep 6, 2023. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v11.i25.5840
Published online Sep 6, 2023. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v11.i25.5840
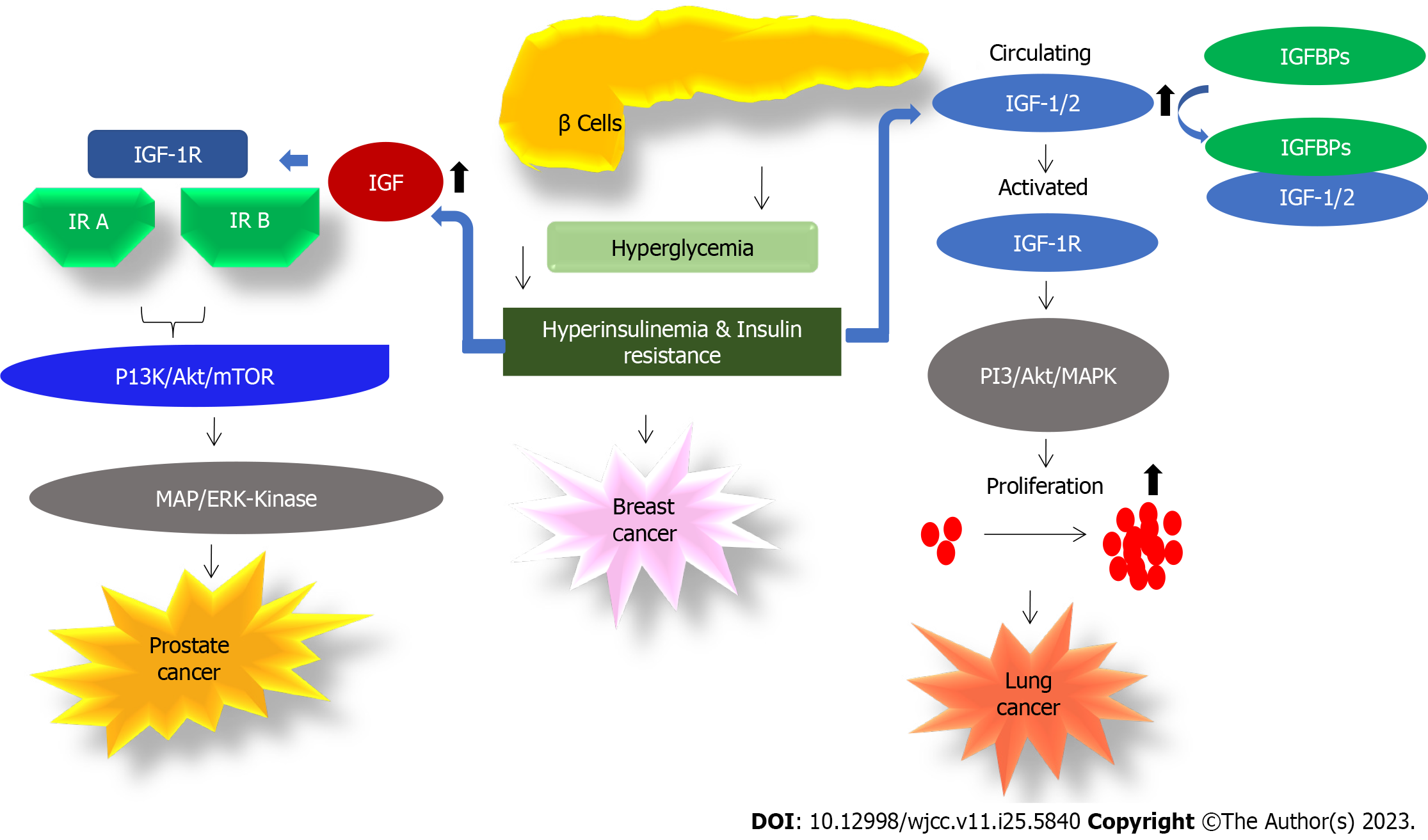
Figure 5 Molecular association of hyperinsulinemia/hyperglycaemia and cancer.
Increased insulin-like growth factor (IGF) due to hyperinsulinemia increases IGF-1R activation which in turn activates downstream signaling and causes prostate cancer[135]. Hyperinsulinemia, hyperglycemia, and insulin resistance may lead to breast cancer[129]. Increased insulin in diabetic patients increases IGF-1/IGF-2 circulating levels which interact with IGF-1R present on lung cells. Thus, the activation of the receptor and thereby activated downstream signaling increase carcinogenesis in lung cells. Most of the IGF binding proteins are known to bind circulating IGF-1/IGF-2 and thereby interrupt their interaction with IGF-1R[133,137]. IGF: Insulin-like growth factor; IGFBPs: Insulin-like growth factor binding proteins; PI3K: Phosphatidylinositol-3-kinase; mTOR: Mammalian target of rapamycin; MAP: Mitogen-activated protein; ERK: Extracellular signal-regulated kinase; MAPK: Mitogen-activated protein kinase; IR: Insulin receptor.
- Citation: Kumar S, Senapati S, Bhattacharya N, Bhattacharya A, Maurya SK, Husain H, Bhatti JS, Pandey AK. Mechanism and recent updates on insulin-related disorders. World J Clin Cases 2023; 11(25): 5840-5856
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v11/i25/5840.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v11.i25.5840