Copyright
©The Author(s) 2021.
World J Virol. Sep 25, 2021; 10(5): 256-263
Published online Sep 25, 2021. doi: 10.5501/wjv.v10.i5.256
Published online Sep 25, 2021. doi: 10.5501/wjv.v10.i5.256
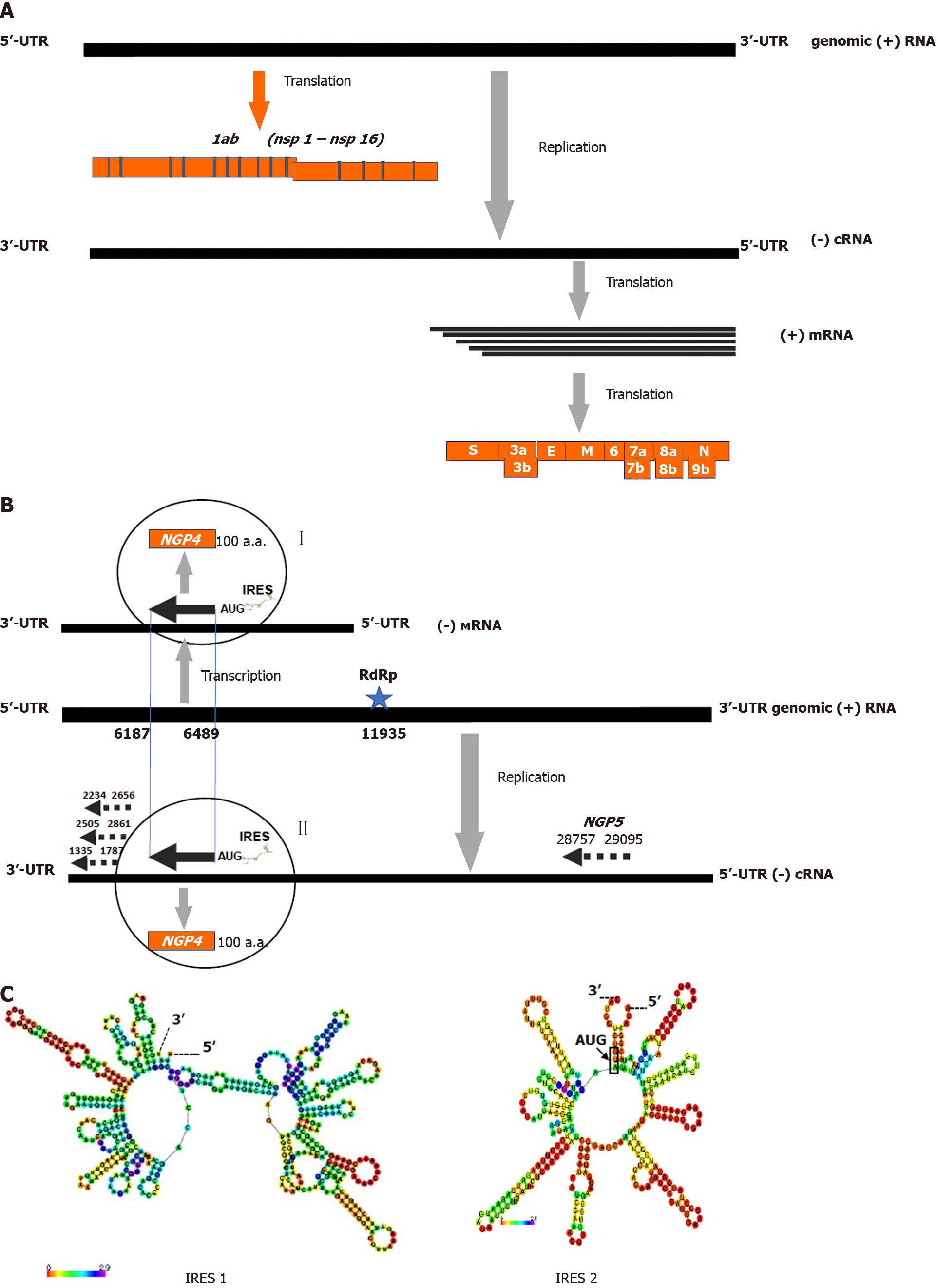
Figure 2 Positive sense genome strategy and translation cassette unit at the 3’ end of the negative sense complimentary RNA of coronavirus severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 genome.
A: Replication scheme of the RNA genome of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) coronavirus (ac.n. MT890462.1). UTR means untranslated RNA region; B: A 3’ end area of the subgenomic (-)cRNA complimentary to the virus genome 5’ end (+)vRNA of SARS-CoV-2 (ac.n. MT635445.1) is displayed. Five ORF containing cassette for NGP1-NGP5 beginning either with classical AUG (NGP4) or noncanonical CUG (NGP1-3, NGP5) codons are shown by arrows. Nucleotides counting from the 5’ end of (+)vRNA are shown for each ORFs. Phases of the translation frame (fr) are estimated regarding the frame of NGP4 (fr.0) as follows: NGP1and 2 (fr. +1), NGP3 (fr.0). Poly A tract (11935-11940 nt) functioning as a viral RNA dependent RNA polymerase binding site is shown by star; C: IRES-like structures enriched with 16 and 10 canonical “hair-pins” RNA elements in the regions 8100-8599 nt (IRES 1) and 6488-6792 nt (IRES 2), respectively, were predicted by the IRESpred program[22]. The IRES-like structures 1 and 2 have significant free energy value as low as -99,4 and -73,8 kkal/mol, respectively. The data were partially presented in[15]. These partial elements were used here with the Publisher’s permission.
- Citation: Zhirnov O. Ambisense polarity of genome RNA of orthomyxoviruses and coronaviruses. World J Virol 2021; 10(5): 256-263
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2220-3249/full/v10/i5/256.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5501/wjv.v10.i5.256