Copyright
©The Author(s) 2018.
World J Transplantation. Oct 22, 2018; 8(6): 203-219
Published online Oct 22, 2018. doi: 10.5500/wjt.v8.i6.203
Published online Oct 22, 2018. doi: 10.5500/wjt.v8.i6.203
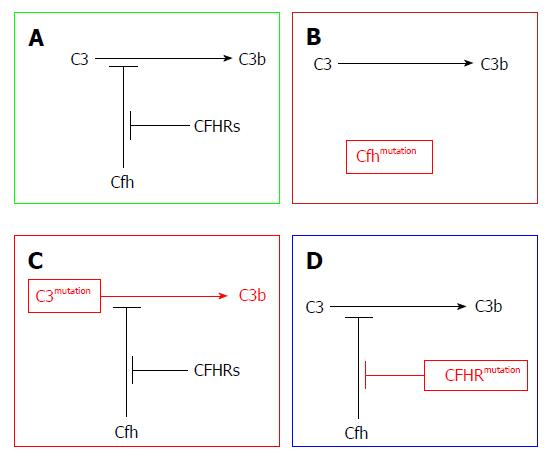
Figure 3 Disease mechanisms in C3 glomerulopathy, based on genetic defects identified in family studies.
A: Physiological regulation of C3 activation to C3b via the alternative pathway is mediated by complement factor H (CFH) (Cfh). Competitive inhibition of CFH by CFHR proteins is termed CFH deregulation; B: Homozygous deficiency or dysfunction of CFH results in excessive C3 activation; C: Hyper-functional C3 produces excessive C3 activation despite normal CFH activity; D: Abnormal CFHR proteins enhance CFH deregulation, leading to excessive C3 activation. Adapted from Barbour et al[11].
- Citation: Abbas F, El Kossi M, Kim JJ, Shaheen IS, Sharma A, Halawa A. Complement-mediated renal diseases after kidney transplantation - current diagnostic and therapeutic options in de novo and recurrent diseases. World J Transplantation 2018; 8(6): 203-219
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2220-3230/full/v8/i6/203.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5500/wjt.v8.i6.203