Copyright
©The Author(s) 2015.
World J Psychiatr. Sep 22, 2015; 5(3): 260-272
Published online Sep 22, 2015. doi: 10.5498/wjp.v5.i3.260
Published online Sep 22, 2015. doi: 10.5498/wjp.v5.i3.260
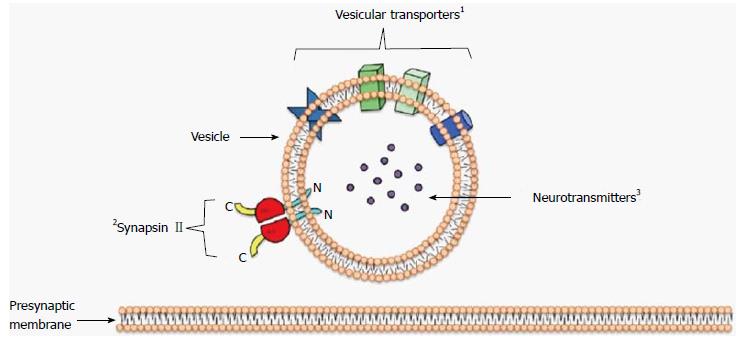
Figure 3 Illustrated depiction of a synaptic vesicle and associated pre-synaptic membrane.
This is a simplified depiction containing proteins and neurotransmitters that are most pertinent to the subject matter of this review; others have been omitted for simplicity sake (ex. Synapsin I, various transporter proteins, etc.). 1Vesicular transporters (also specific to the type and function of synapse) may include: VGLUT1, VGLUT2, VGAT and VMAT2; 2Various synapsin isoforms have been implicated in the tethering of synaptic vesicles (depending on the type of neurotransmitter and vesicular transporters associated). Synapsin isoforms include Ia-b, IIa-b, and IIa-e; 3Neurotransmitters contain within synaptic vesicle, may include: glutamate, GABA, DA, etc. VGLUT: Vesicular glutamate transporter; VGAT: Vesicular GABA transporter; VMAT2: Vesicular monoamine transporter 2; GABA: γ-aminobutyric acid.
- Citation: Molinaro L, Hui P, Tan M, Mishra RK. Role of presynaptic phosphoprotein synapsin II in schizophrenia. World J Psychiatr 2015; 5(3): 260-272
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2220-3206/full/v5/i3/260.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5498/wjp.v5.i3.260