Copyright
©The Author(s) 2015.
World J Psychiatr. Sep 22, 2015; 5(3): 260-272
Published online Sep 22, 2015. doi: 10.5498/wjp.v5.i3.260
Published online Sep 22, 2015. doi: 10.5498/wjp.v5.i3.260
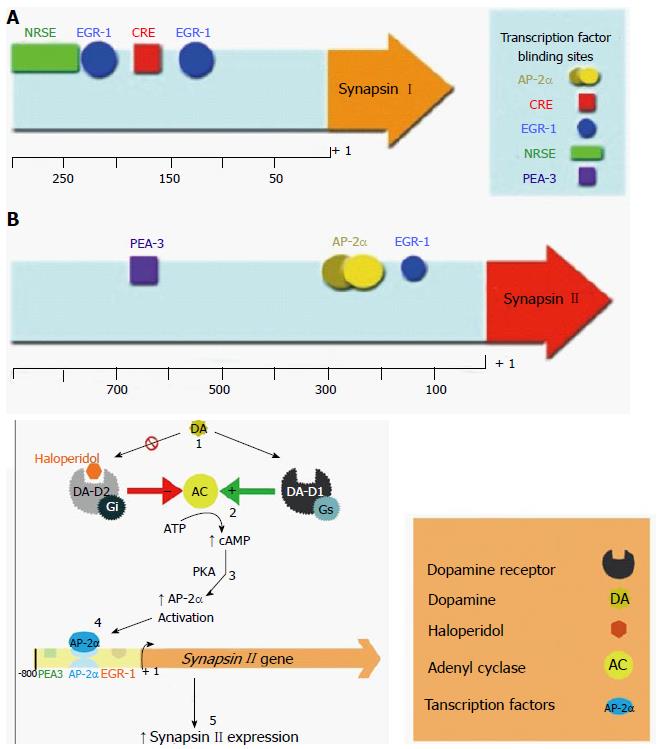
Figure 2 Illustration of the promoter regions of synapsin I and II respectively and proposed mechanism of dopaminergic regulation of synapsin II.
A: Illustration of the promoter regions of synapsin I and II respectively. Transcription factor binding sites have been indicated, showing their various positions in the promoter region; B: Proposed mechanism of dopaminergic regulation of synapsin II. Evidence: (1) Immunocytochemstry results indicate that ligand - DA Rc binding results in changes to synapsin protein levels dependant on Rc subtype; (2) Ligand binding causes changes to intercellular cAMP levels; (3) PKA inhibitors (5-24 amide trifluoroacetate salt, Rp-cAMPS) cause changes in synapsin II translation; (4) DA-D1 stimulation may cause AP-2 to bind to synapsin II promoter. Synapsin II expression levels were inhibited when cells were treated with AP-2 ADONs. Subsequent treatment with DA-D1 or -D2 agonists showed to effect on synapsin II expression; and (5) Synapsin 2 expression can be altered via upstream alteration at various points. Additional information: (1) EGR-1 levels are not affected by chronic treatment with DA-D1 or DA-D2 antagonists; (2) Antisense deoxyoligonucleotides for AP-2 reduces synapsin II expression levels; and (3) Antisense deoxyoligonucleotides for EGR-1 and PEA3 have no effect on the expression of synapsin II. EGR-1: Early growth response factor-1; PKA: Protein kinase A; cAMP: Cyclic AMP; AP-2α: Activating protein 2-alpha.
- Citation: Molinaro L, Hui P, Tan M, Mishra RK. Role of presynaptic phosphoprotein synapsin II in schizophrenia. World J Psychiatr 2015; 5(3): 260-272
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2220-3206/full/v5/i3/260.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5498/wjp.v5.i3.260