Copyright
©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Psychiatry. Mar 19, 2025; 15(3): 101178
Published online Mar 19, 2025. doi: 10.5498/wjp.v15.i3.101178
Published online Mar 19, 2025. doi: 10.5498/wjp.v15.i3.101178
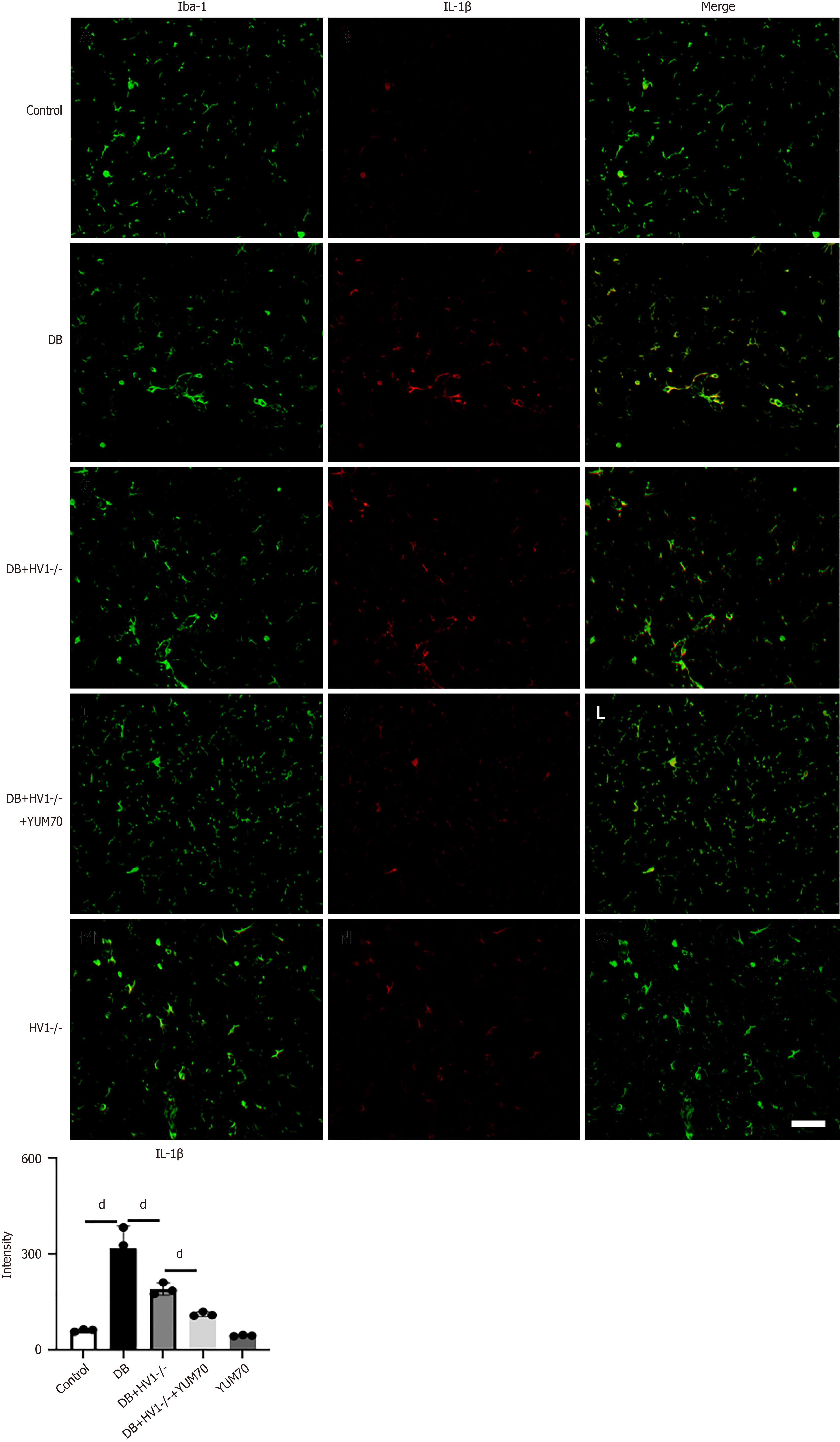
Figure 8 The voltage-gated proton channel 1 gene knockout inhibits interleukin-1β in diabetic mice by suppressing the glucose-regulated protein 78 pathway.
The microglial cells in the diabetic group exhibited elevated interleukin (IL)-1β levels compared to the control, which were restored the voltage-gated proton channel 1 (Hv1) knockout. Treatment with YUM70 enhanced the effect of Hv1 knockout, indicating that Hv1 knockout inhibits IL-1β by suppressing the glucose-regulated protein 78 pathway. dP < 0.05. The scale bar = 50 μm. Hv1: The voltage-gated proton channel 1; Iba-1: Ionized calcium-binding adaptor molecule 1; IL: Interleukin; DB: Diabetic group.
- Citation: Li CY, Zhang SJ, Xu JL, Yang Y, Zeng ZX, Ma DL. Inhibition of the microglial voltage-gated proton channel 1 channel ameliorates diabetes-associated cognitive dysfunction by regulating axon demyelination. World J Psychiatry 2025; 15(3): 101178
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2220-3206/full/v15/i3/101178.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5498/wjp.v15.i3.101178