Copyright
©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Psychiatry. Mar 19, 2025; 15(3): 101178
Published online Mar 19, 2025. doi: 10.5498/wjp.v15.i3.101178
Published online Mar 19, 2025. doi: 10.5498/wjp.v15.i3.101178
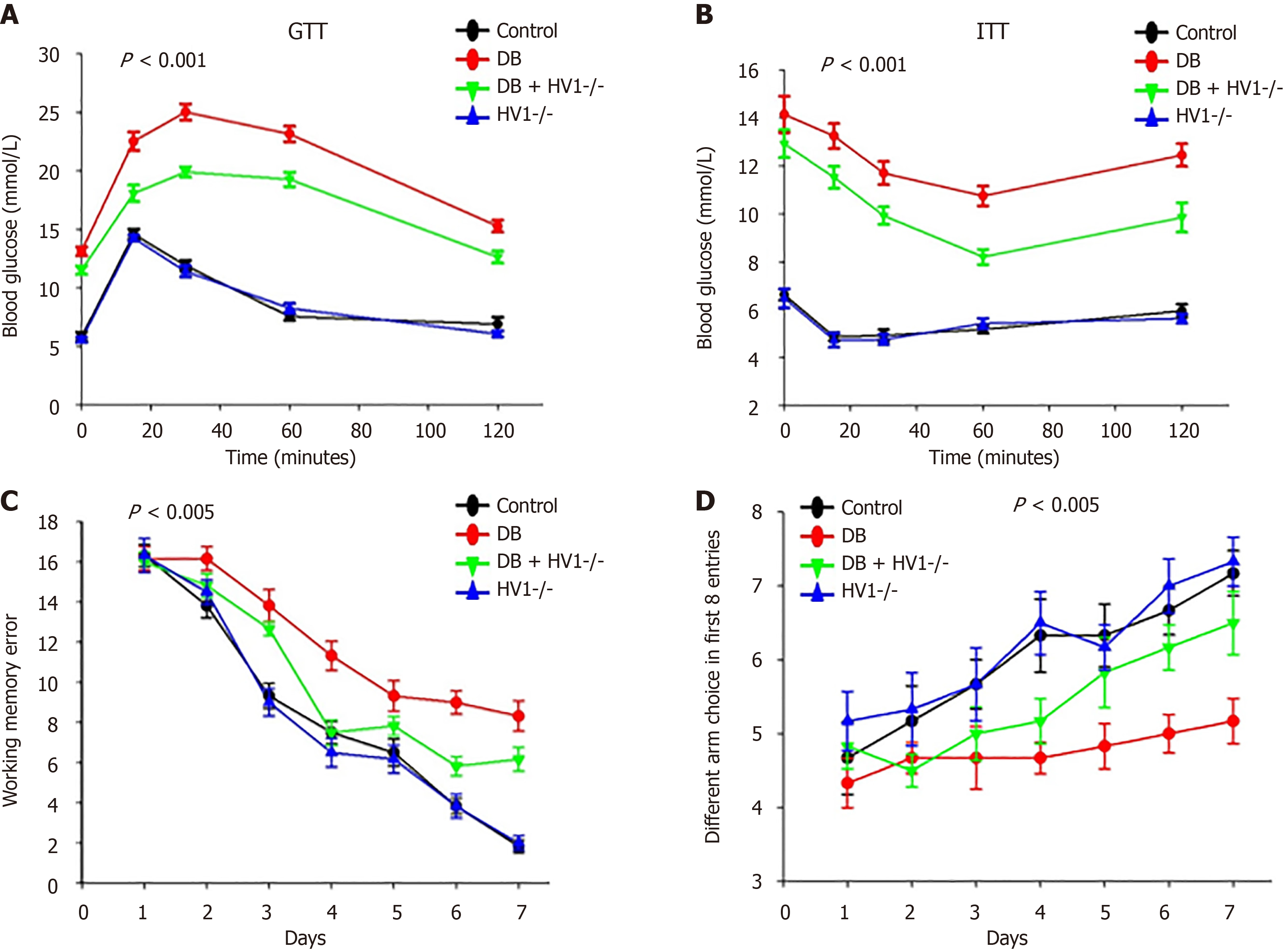
Figure 1 The voltage-gated proton channel 1 gene deletion alleviates early cognitive impairment induced by diabetes.
A: Blood glucose levels during glucose tolerance tests (n = 4 per group); B: Blood glucose levels during insulin tolerance tests (n = 4 per group); C: Working memory errors (n = 6 per group); D: In the eight-arm radial maze test, the voltage-gated proton channel 1-/- diabetic group mice made more different arm choices in the first eight entries than DB mice (n=6 per group). GTT: Glucose tolerance tests; ITT: Insulin tolerance tests; DB: Diabetic group; Hv1: The voltage-gated proton channel 1.
- Citation: Li CY, Zhang SJ, Xu JL, Yang Y, Zeng ZX, Ma DL. Inhibition of the microglial voltage-gated proton channel 1 channel ameliorates diabetes-associated cognitive dysfunction by regulating axon demyelination. World J Psychiatry 2025; 15(3): 101178
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2220-3206/full/v15/i3/101178.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5498/wjp.v15.i3.101178