Copyright
©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Psychiatry. Mar 19, 2025; 15(3): 100112
Published online Mar 19, 2025. doi: 10.5498/wjp.v15.i3.100112
Published online Mar 19, 2025. doi: 10.5498/wjp.v15.i3.100112
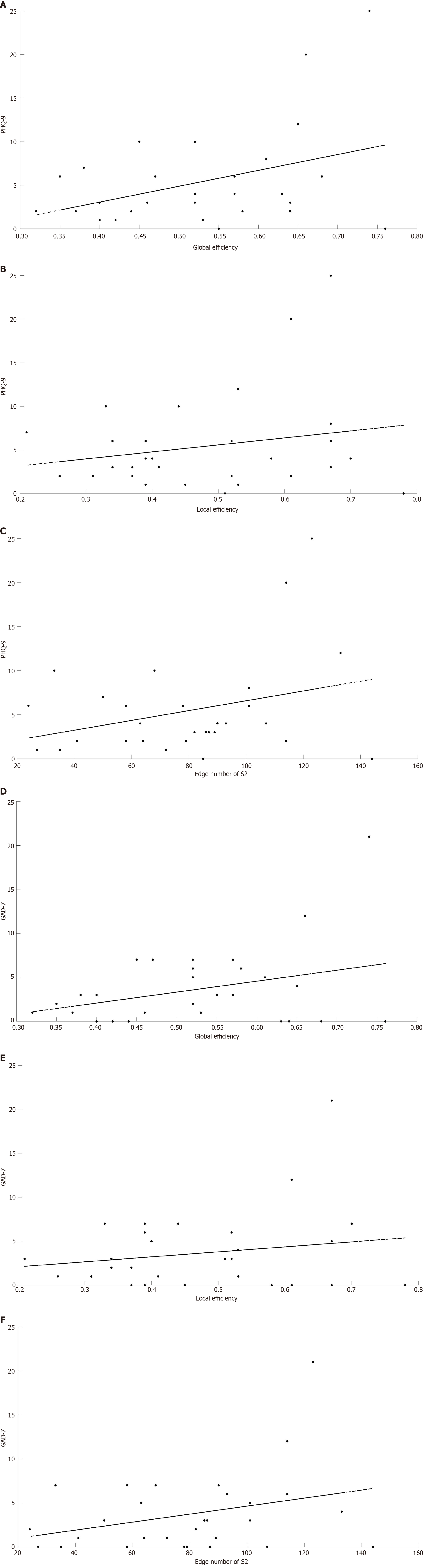
Figure 6 Scatter maps showing the correlations between the scores of Patient Health Questionnaire-9 and network measures and correlations between the scores of General Anxiety Disorder-7 and network measures.
The black dotted line indicates the Linear fitting trend. A: Correlation between Patient Health Questionnaire-9 (PHQ-9) and global efficiency; B: Correlation between PHQ-9 and local efficiency of dorsolateral prefrontal cortex; C: Correlation between PHQ-9 and Short-II (intrahemispheric connectivity between different regions of interest); D: Correlation between General Anxiety Disorder-7 (GAD-7) and global efficiency; E: Correlation between GAD-7 and local efficiency of dorsolateral prefrontal cortex; F: Correlation between GAD-7 and Short-II. All correlations were calculated at 0.5 threshold.
- Citation: Ma WJ, Yuan RC, Peng ZY, Wu Q, Al-Matary M, Yang HS, Cheng P, Zhao GJ, Lu CC, Zhang YX, Hong JK, Li WH. Mood symptoms, cognitive function, and changes of brain hemodynamics in patients with COVID-19: A functional near-infrared spectroscopy study. World J Psychiatry 2025; 15(3): 100112
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2220-3206/full/v15/i3/100112.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5498/wjp.v15.i3.100112