Copyright
©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Psychiatry. Feb 19, 2025; 15(2): 101807
Published online Feb 19, 2025. doi: 10.5498/wjp.v15.i2.101807
Published online Feb 19, 2025. doi: 10.5498/wjp.v15.i2.101807
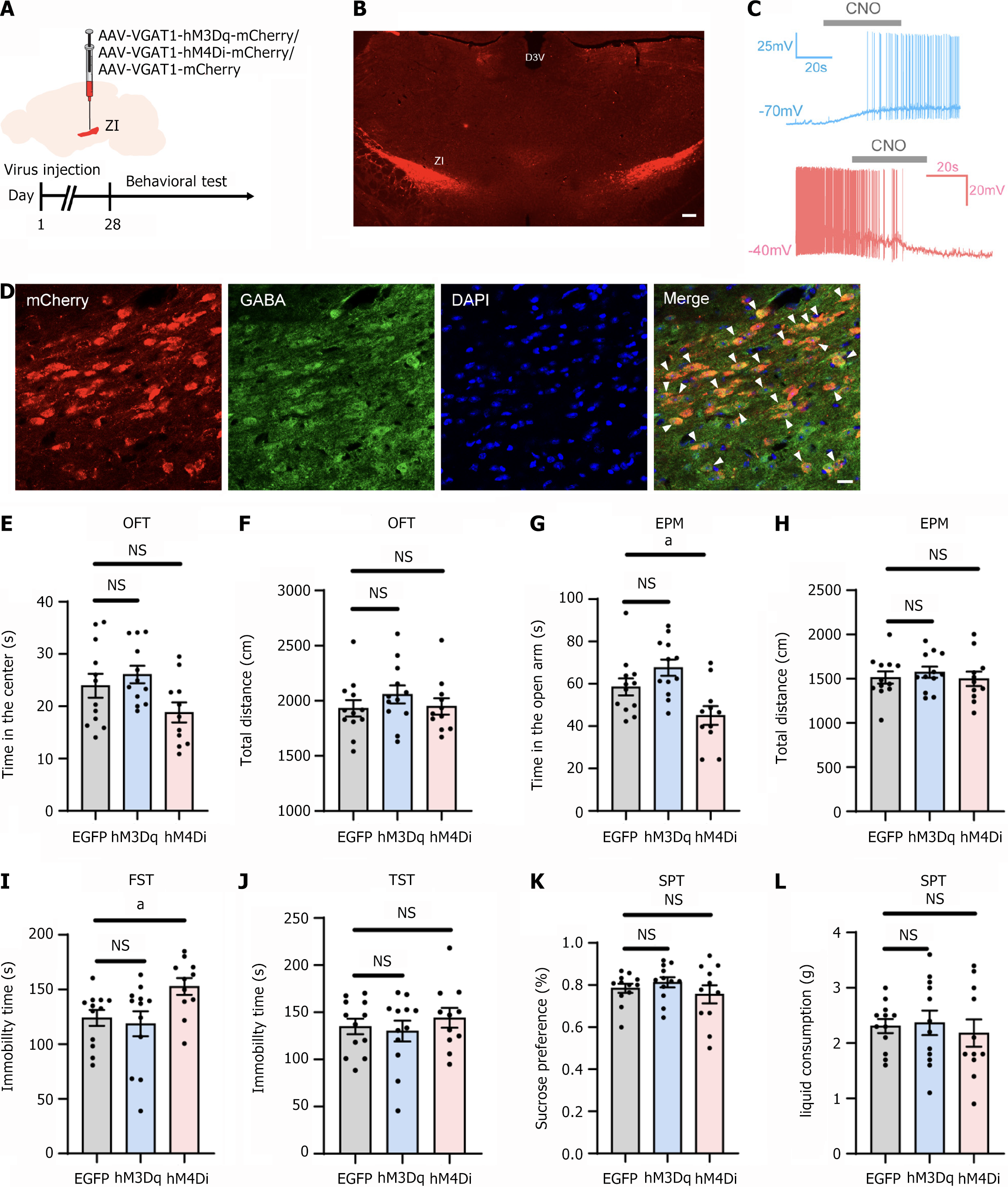
Figure 4 Effects of chemogenetic manipulation of the gamma-aminobutyric acid-ergic neurons in the zona incerta on normal mice behavior.
A: Experimental strategy and timeline for behavioral assays; B: The injection site of the virus in the zona incerta. Scale bars: 200 µm; C: Bath application of clozapine-N-oxide (10 μM) elicited neuronal discharge in neurons expressing hM3Dq-mCherry (clamped at -70 mV). It suppressed spiking in the hM4Di-mCherry group (clamped at -40 mV); D: Representative images of colocalization of neurons expressing mCherry and gamma-aminobutyric acid in the zona incerta. Blue: DAPI staining. Scale bars: 100 μm; E: Impact of chemogenetic manipulation on the time spent in the center of the open field test (OFT); F: Impact of chemogenetic manipulation on the total distance traveled in the OFT; G: Impact of chemogenetic manipulation on the time spent in the open arms of the elevated plus maze (EPM); H: Impact of chemogenetic manipulation on the total distance traveled in the EPM; I: Effect of chemogenetic manipulation on immobility time in the forced swim test; J: Effect of chemogenetic manipulation on immobility time in the tail suspension test; K and L: Effect of chemogenetic manipulation on sucrose preference and total liquid consumption in the sucrose preference test. aP < 0.05; n = 10 for the EGFP group and hM3Dq group; n = 11 for the hM4Di group; D3v: Dorsal 3rd ventricle; NS: Not significant; CNO: Clozapine-N-oxide; GABA: Gamma-aminobutyric acid; OFT: Open field test; EPM: Elevated plus maze; FST: Forced swimming test; TST: Tail suspension test; SPT: Sucrose preference test.
- Citation: Chen SH, Lan B, Zhang YY, Li GH, Qian YL, Hu MX, Tian YL, Zang WD, Cao J, Wang GH, Wang YG. Activation of zona incerta gamma-aminobutyric acid-ergic neurons alleviates depression-like and anxiety-like behaviors induced by chronic restraint stress. World J Psychiatry 2025; 15(2): 101807
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2220-3206/full/v15/i2/101807.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5498/wjp.v15.i2.101807