Copyright
©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Psychiatry. Feb 19, 2025; 15(2): 101807
Published online Feb 19, 2025. doi: 10.5498/wjp.v15.i2.101807
Published online Feb 19, 2025. doi: 10.5498/wjp.v15.i2.101807
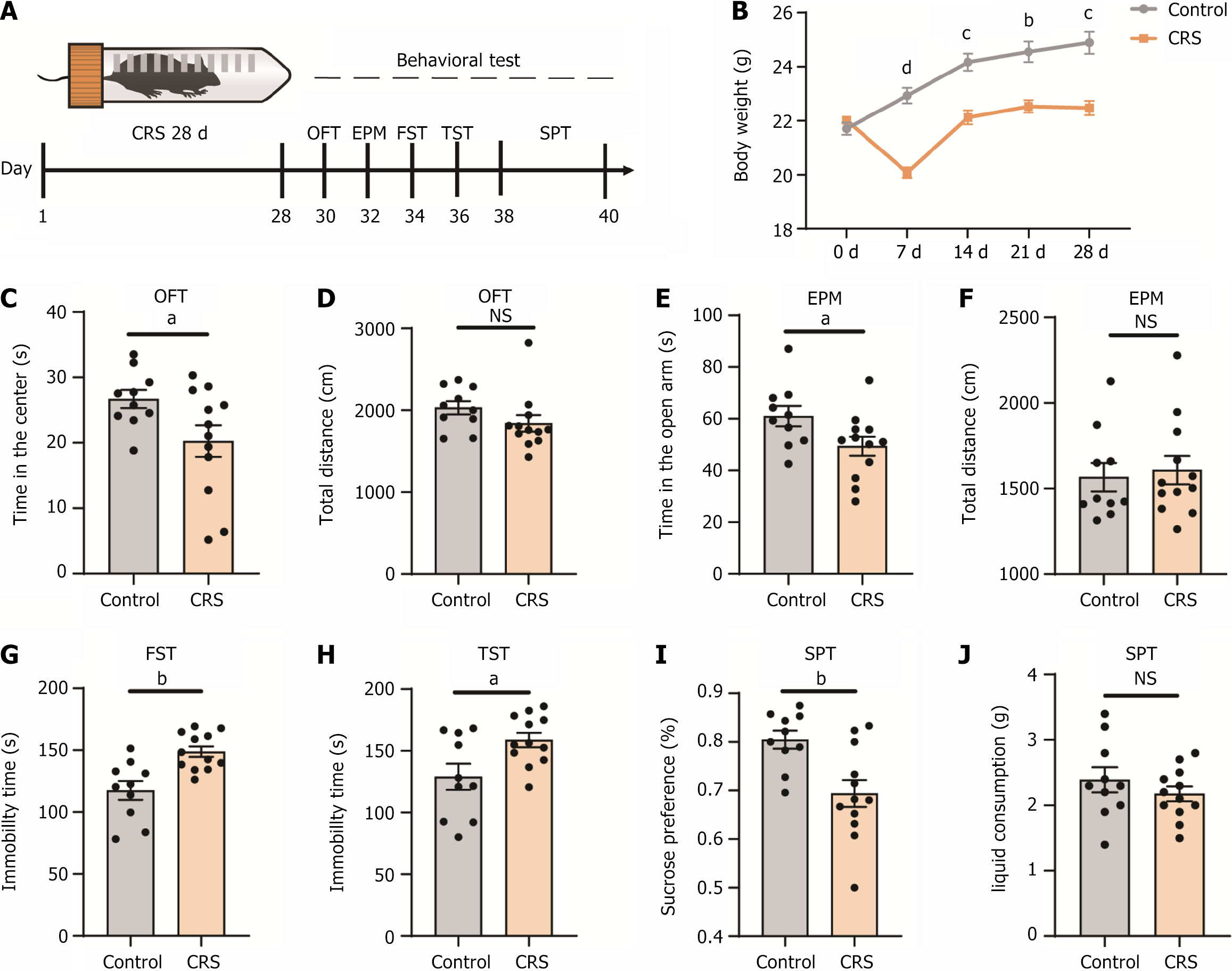
Figure 1 Chronic resistant stress induced anxiety-like and depression-like behaviors in mice.
A: Experimental strategy and timeline for behavioral assays; B: Bodyweight comparison over 4 weeks between mice in the chronic resistant stress (CRS) group and the control group; C and D: In the open field test, mice in the CRS group spent less time in the center compared to the control group. There was no change in the total distance traveled in both groups; E and F: In the elevated plus maze, mice in the CRS group spent less time in the open arms than the control group. The total distance traveled was similar between both groups; G: In the forced swim test, mice in the CRS group exhibited increased immobility time compared to the control group; H: In the tail suspension test, the mice in the CRS group showed longer immobility time compared with the control group; I and J: In the sucrose preference test, the mice in the CRS group had a significantly lower preference for sucrose than the control group. However, the total liquid consumption was the same for both groups. aP < 0.05; bP < 0.01; cP < 0.001; dP < 0.0001; n = 10 for control group; n = 12 for CRS group; NS: Not significant; CRS: Chronic resistant stress; GABA: Gamma-aminobutyric acid; OFT: Open field test; EPM: Elevated plus maze; FST: Forced swimming test; TST: Tail suspension test; SPT: Sucrose preference test.
- Citation: Chen SH, Lan B, Zhang YY, Li GH, Qian YL, Hu MX, Tian YL, Zang WD, Cao J, Wang GH, Wang YG. Activation of zona incerta gamma-aminobutyric acid-ergic neurons alleviates depression-like and anxiety-like behaviors induced by chronic restraint stress. World J Psychiatry 2025; 15(2): 101807
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2220-3206/full/v15/i2/101807.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5498/wjp.v15.i2.101807