Copyright
©The Author(s) 2024.
World J Psychiatry. Aug 19, 2024; 14(8): 1254-1266
Published online Aug 19, 2024. doi: 10.5498/wjp.v14.i8.1254
Published online Aug 19, 2024. doi: 10.5498/wjp.v14.i8.1254
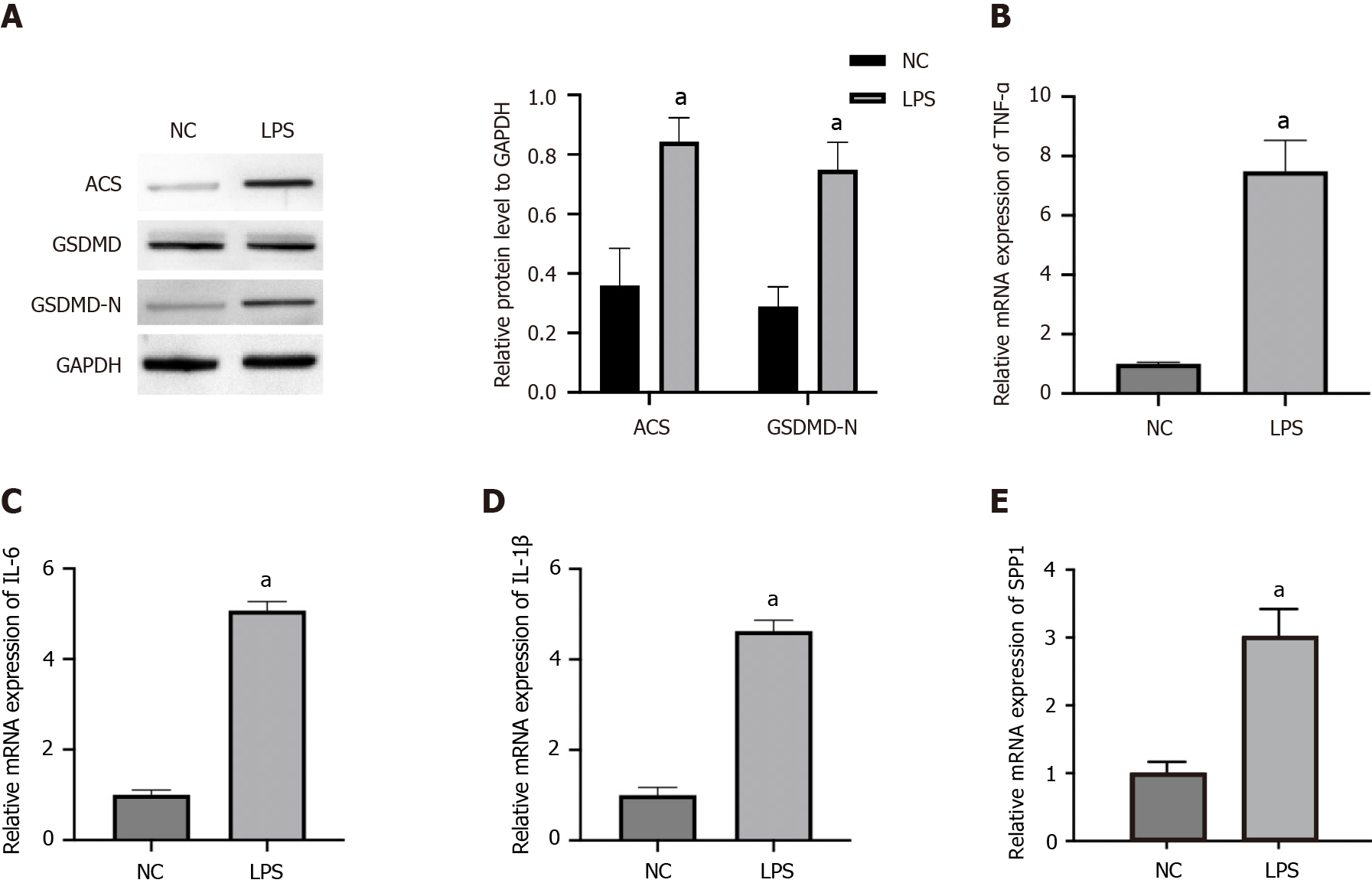
Figure 1 SPP1 and pyroptosis are activated in lipopolysaccharide-induced microglia.
A-E: The microglia were treated with lipopolysaccharide. The expression of ACS, GSDMD, and GSDMD-N was measured by western blot (A). The levels of tumor necrosis factor-α, interleukin (IL)-6, and IL-1β were detected by quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction (B-D). The expression of SPP1 was analyzed by quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction (E). aP < 0.001. LPS: Lipopolysaccharide; TNF: Tumor necrosis factor; IL: Interleukin; NC: Negative control.
- Citation: Chen LP, Gui XD, Tian WD, Kan HM, Huang JZ, Ji FH. Botulinum toxin type A-targeted SPP1 contributes to neuropathic pain by the activation of microglia pyroptosis. World J Psychiatry 2024; 14(8): 1254-1266
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2220-3206/full/v14/i8/1254.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5498/wjp.v14.i8.1254