Copyright
©The Author(s) 2024.
World J Psychiatry. Jun 19, 2024; 14(6): 767-783
Published online Jun 19, 2024. doi: 10.5498/wjp.v14.i6.767
Published online Jun 19, 2024. doi: 10.5498/wjp.v14.i6.767
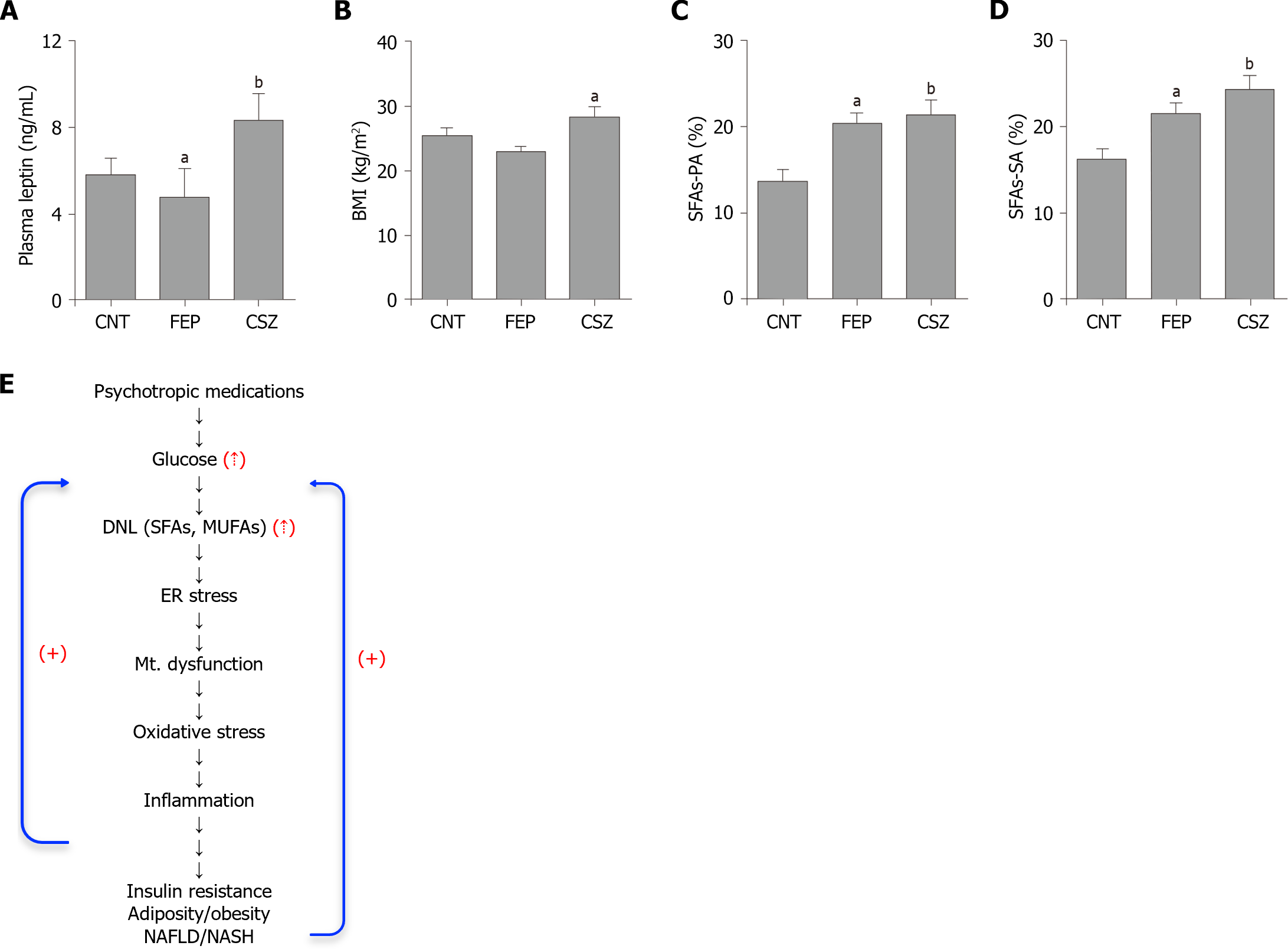
Figure 1 Influence of antipsychotic drugs on metabolic parameters.
A: Plasma leptin in control subjects, drug-naïve first-episode and antipsychotic-treated chronic schizophrenia patients; B: Body mass index; C: Saturated fatty acids (SAFs)-palmitic acid; D: SFAs-stearic acid in the same groups; E: Psychotropic medications increase stimulate SAFs and monounsaturated fatty acids levels by increasing de novo lipogenesis. SFAs can induce endoplasmic reticulum stress, mitochondrial dysfunction and development of various metabolic abnormalities including insulin resistance, adiposity/obesity, and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease/steatohepatitis. Red arrows indicate increase, and blue arrows indicate stimulatory (+) effect of oxidative stress and inflammation on de novo lipogenesis and various metabolic abnormalities. CNT: Control; FEP: First-episode; CSZ: Chronic schizophrenia; BMI: Body mass index; SFAs-PA: Saturated fatty acids-palmitic acid; SFAs-SA: Saturated fatty acids-stearic acid; SFAs: Saturated fatty acids; MUFAs: Monounsaturated fatty acids; ER: Endoplasmic reticulum; DNL: De novo lipogenesis; NAFLD: Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease; NASH: Non-alcoholic steatohepatitis; Mt: Mitochondrial. Citation for Figure A-D: Khan MM. Disrupted leptin-fatty acid biosynthesis is an early manifestation of metabolic abnormalities in schizophrenia. World J Psychiatry 2022; 12: 827-842. Copyright© The Authors 2022. Published by Baishideng publishing Group. It is open access and permits to use materials provided it’s been cited properly.
- Citation: Khan MM, Khan ZA, Khan MA. Metabolic complications of psychotropic medications in psychiatric disorders: Emerging role of de novo lipogenesis and therapeutic consideration. World J Psychiatry 2024; 14(6): 767-783
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2220-3206/full/v14/i6/767.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5498/wjp.v14.i6.767