Copyright
©The Author(s) 2024.
World J Psychiatry. Apr 19, 2024; 14(4): 563-581
Published online Apr 19, 2024. doi: 10.5498/wjp.v14.i4.563
Published online Apr 19, 2024. doi: 10.5498/wjp.v14.i4.563
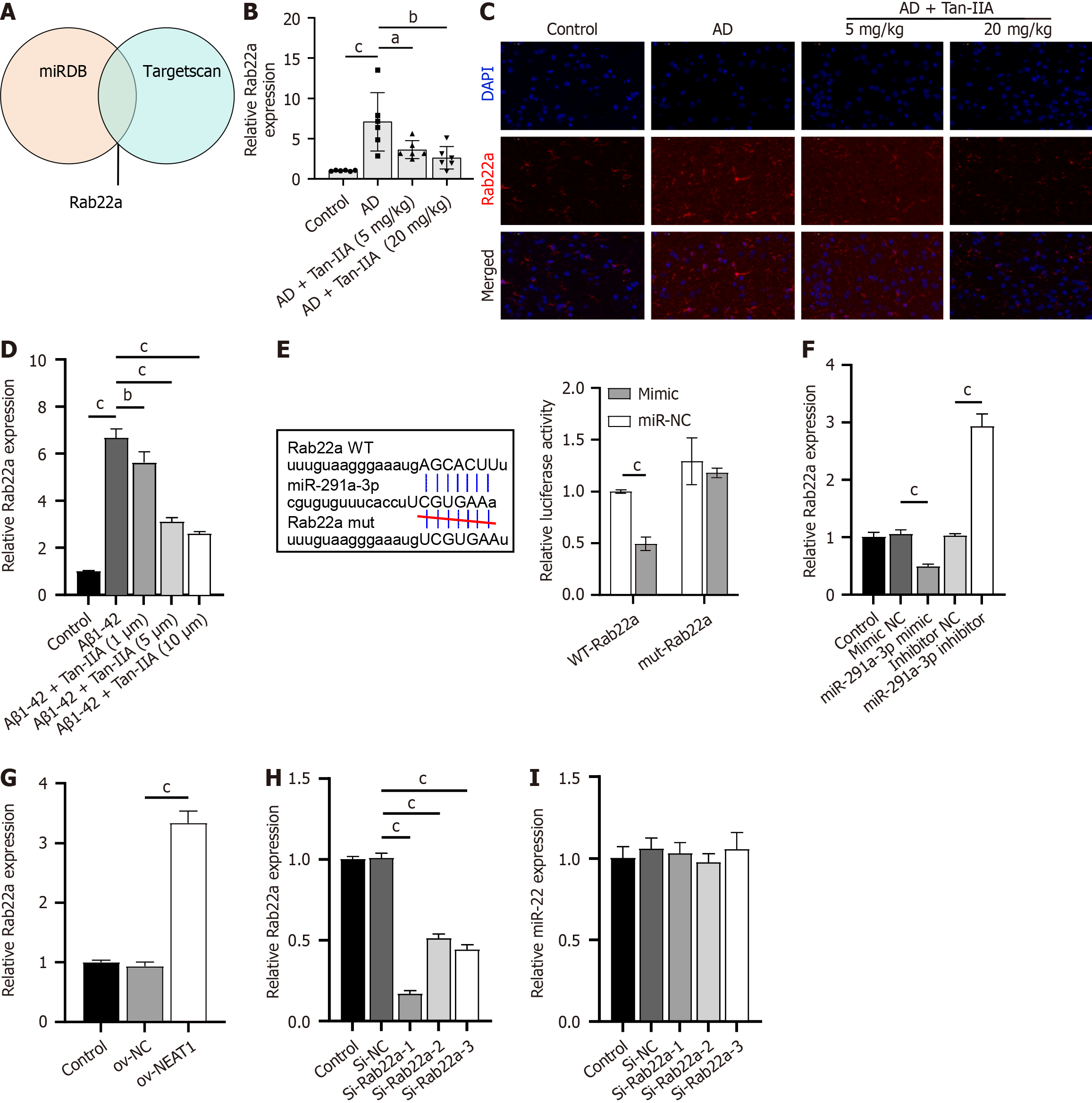
Figure 4 Rab22a as a target of miR-291a-3p, and its role in the nuclear-enriched abundant transcript 1/miR-291a-3p axis.
A: MiRDB and Targetscan database joint analysis identified Rab22a as a potential target of miR-291a-3p; B: Reverse transcription quantitative polymerase chain reaction (RT-qPCR) analysis of Rab22a expression in the Alzheimer’s disease (AD) mouse model; C: Immunofluorescence analysis of Rab22a expression in the AD mouse model; D: RT-qPCR analysis of Rab22a expression in amyloid-beta 1-42 (Aβ1-42)-induced neural stem cells (NSCs); E: Dual-luciferase assay confirming binding between Rab22a and miR-291a-3p; F and G: RT-qPCR analysis of the effect of miR-291a-3p (F) and nuclear-enriched abundant transcript 1 (G) overexpression on Rab22a expression; H: RT-qPCR validation of the inhibitory efficiency of 3 si-Rab22a on Rab22a expression in NSCs; I: RT-qPCR analysis of the effect of 3 si-Rab22a on miR-291a-3p expression. aP < 0.05, bP < 0.01, cP < 0.001. AD: Alzheimer’s disease; Aβ1-42: Amyloid-beta 1-42; Tan-IIA: Tanshinone IIA.
- Citation: Yang LX, Luo M, Li SY. Tanshinone IIA improves Alzheimer’s disease via RNA nuclear-enriched abundant transcript 1/microRNA-291a-3p/member RAS oncogene family Rab22a axis. World J Psychiatry 2024; 14(4): 563-581
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2220-3206/full/v14/i4/563.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5498/wjp.v14.i4.563