Copyright
©The Author(s) 2024.
World J Psychiatry. Mar 19, 2024; 14(3): 445-455
Published online Mar 19, 2024. doi: 10.5498/wjp.v14.i3.445
Published online Mar 19, 2024. doi: 10.5498/wjp.v14.i3.445
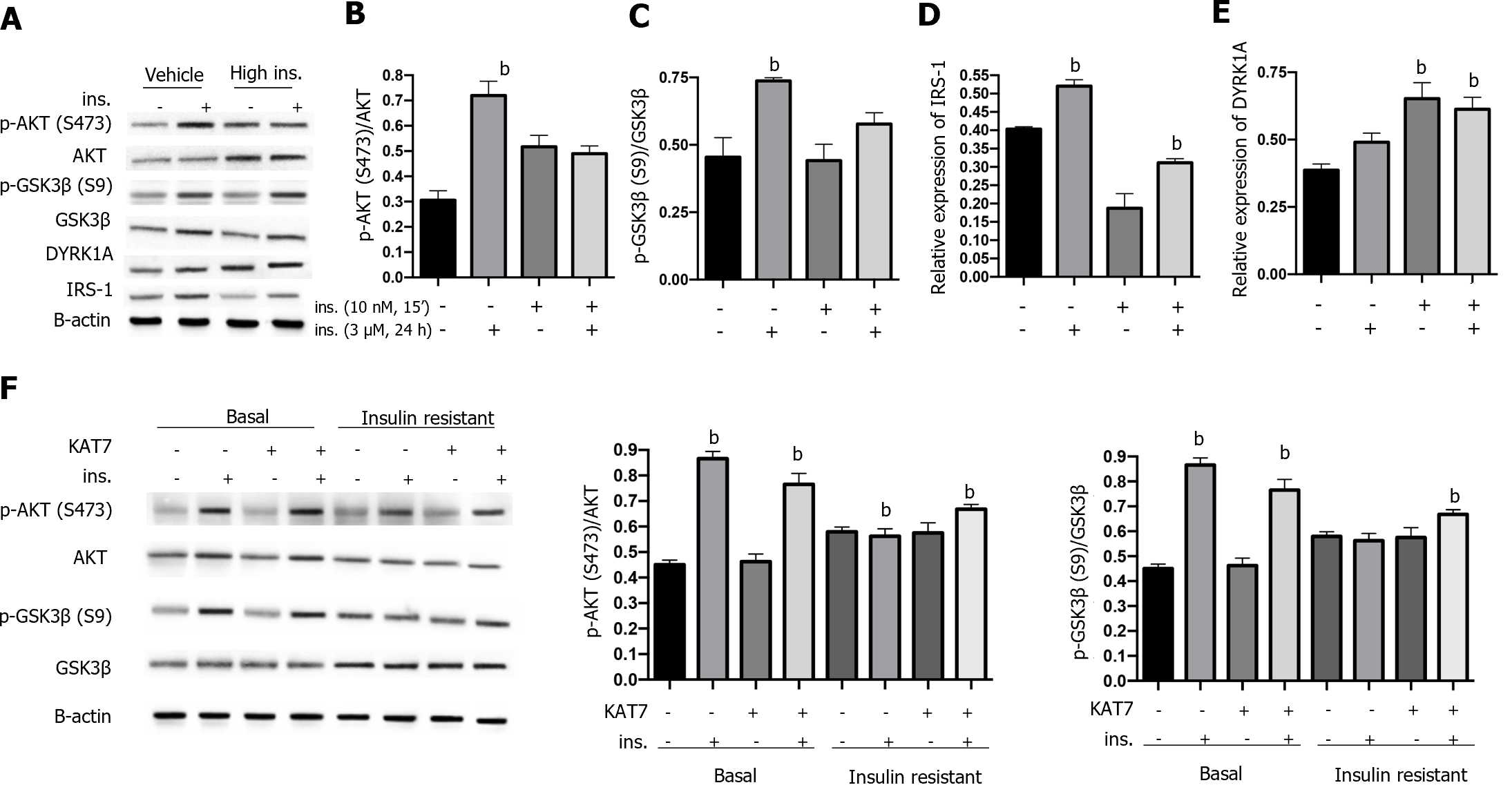
Figure 4 KAT7 ameliorates chronic high insulin-induced insulin resistance.
A: The protein levels of p-AKT, total AKT, p-GSK3β, total GSK3β, dual-specificity tyrosine phosphorylation-regulated kinase-1A (DYRK1A), and IRS-1 in neurons were assessed via western blotting; B: Histogram to quantify protein expression of pAKT in A; C: Histogram to quantify relative protein expression of p-GSK3β in A; D: Histogram to quantify relative protein expression of IRS-1 in A; E: Histogram to quantify relative protein expression of DYRK1A in A. Vehicle, no pre-stimulation with insulin; High ins, pre-stimulation with insulin (3 μM) for 24 h + indicated restimulation with insulin (10 nM, 15 min); F: Neurons treated the same as in A to establish insulin resistance, along with or without KAT7 overexpression. The protein levels of p-AKT, total AKT, p-GSK3β, and total GSK3β in neurons were assessed via western blotting. Histogram to quantify protein expression. bP < 0.01. DYRK1A: Dual-specificity tyrosine phosphorylation-regulated kinase-1A.
- Citation: Lu QS, Ma L, Jiang WJ, Wang XB, Lu M. KAT7/HMGN1 signaling epigenetically induces tyrosine phosphorylation-regulated kinase 1A expression to ameliorate insulin resistance in Alzheimer’s disease. World J Psychiatry 2024; 14(3): 445-455
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2220-3206/full/v14/i3/445.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5498/wjp.v14.i3.445