Copyright
©The Author(s) 2024.
World J Psychiatry. Mar 19, 2024; 14(3): 421-433
Published online Mar 19, 2024. doi: 10.5498/wjp.v14.i3.421
Published online Mar 19, 2024. doi: 10.5498/wjp.v14.i3.421
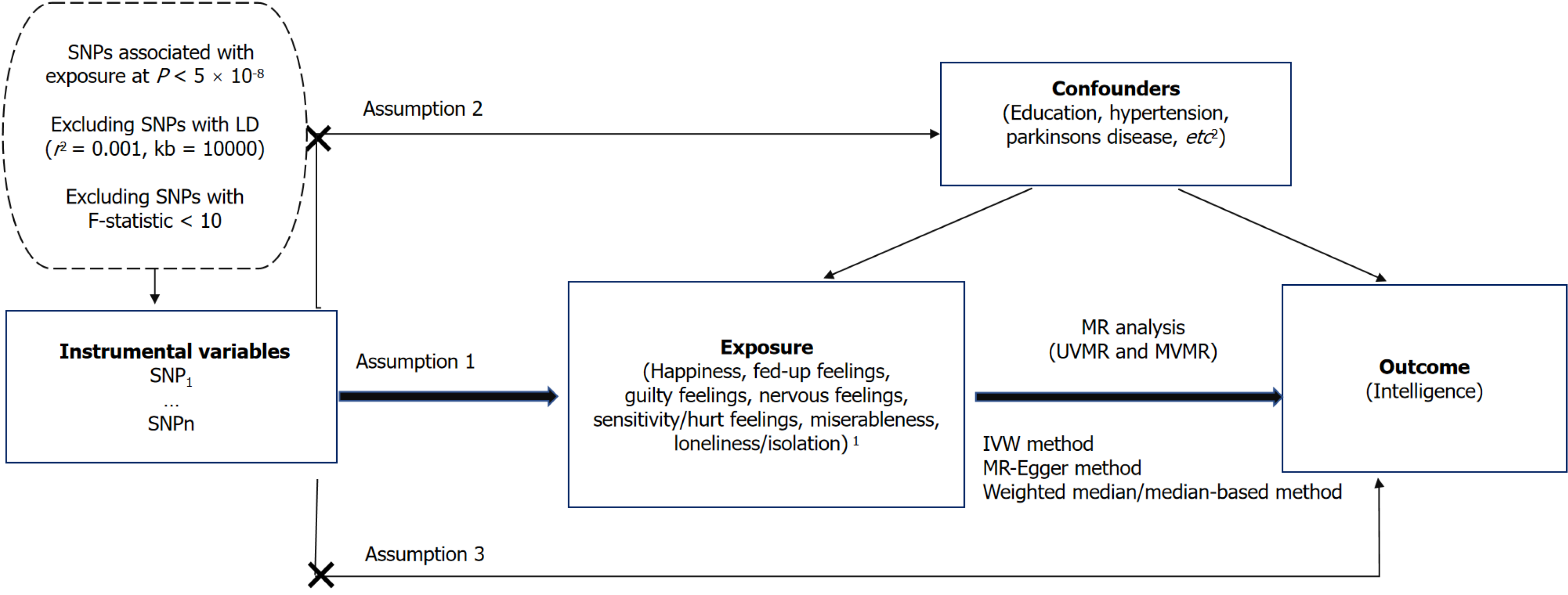
Figure 1 Study design overview.
1Worrier/anxious feelings was excluded because of potential pleiotropy. 2Hearing difficulty, diabetes, high cholesterol, body mass index, smoking, alcohol intake, coronary artery disease, progressive supranuclear palsy, neuroticism, depressive symptoms or depression, schizophrenia, multiple sclerosis, autism, bipolar disorder, progressive supranuclear palsy, epilepsy, Alzheimers disease, spinal injury. SNPs: Single-nucleotide polymorphisms; LD: Linkage disequilibrium; MR: Mendelian randomization; IVW: Inverse-variance weighted; UVMR: Univariable Mendelian randomization; MVMR: Multivariable Mendelian randomization.
- Citation: Liu J, Liu L, Hu YX, Li JH, Zou X, Zhang HY, Fan L. Causal relationship between feelings and cognitive decline: An univariable and multivariable Mendelian randomization study. World J Psychiatry 2024; 14(3): 421-433
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2220-3206/full/v14/i3/421.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5498/wjp.v14.i3.421