Copyright
©The Author(s) 2024.
World J Psychiatry. Feb 19, 2024; 14(2): 234-244
Published online Feb 19, 2024. doi: 10.5498/wjp.v14.i2.234
Published online Feb 19, 2024. doi: 10.5498/wjp.v14.i2.234
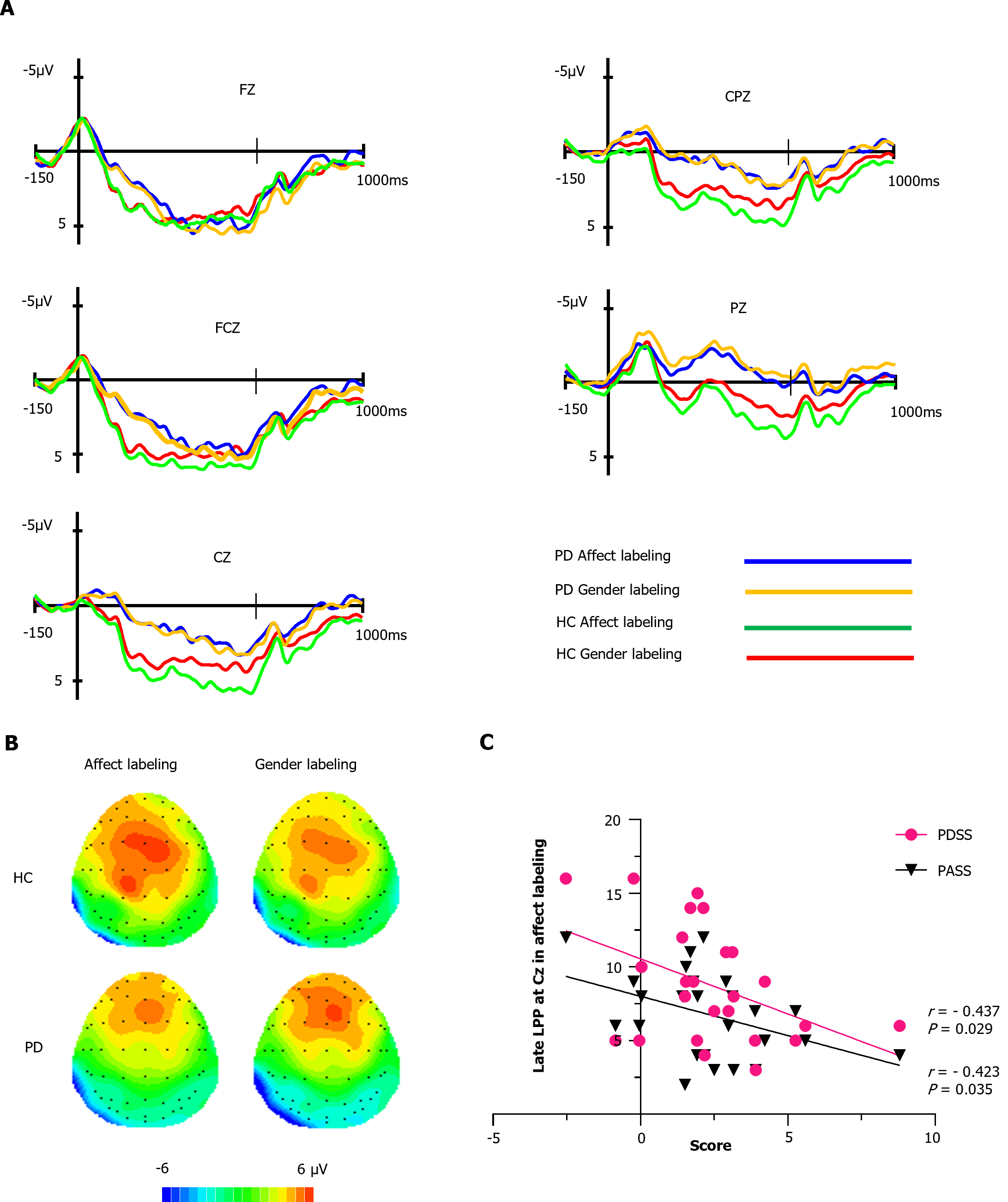
Figure 3 Late positive potential amplitude.
A: Illustrates the early late positive potential (LPP) amplitudes at each electrode site for the healthy controls (HC) and panic disorder (PD) groups under affect labeling and gender labeling conditions. Firstly, a 2 × 2 × 5 repeated measures analysis of variance (350-630 ms) revealed significant main effects of electrode (P < 0.001) and a significant group × condition interaction effect (P = 0.02). Post-hoc comparisons indicated that the HC group exhibited higher LPP amplitudes in the affect labeling condition compared to the gender labeling condition (P = 0.044), while there was no significant difference in the PD group (P > 0.05). Secondly, no significant effects of electrode, condition, group, or interactions were observed in the 630-1000 ms time window (P > 0.05 for all comparisons); B: Presents topographic maps of the two groups under the two conditions; C: Demonstrates negative correlations between LPP amplitudes at the CZ site during affect labeling and Panic Disorder Severity Scale scores as well as Panic-Associated Symptom Scale scores in PD patients (P = 0.029, P = 0.035, respectively). PD: Panic disorder; HC: Healthy control; PDSS: Panic Disorder Severity Scale; PASS: Panic-Associated Symptom Scale; Fz: Frontal midline; FCz: Frontocentral midline; Cz: Central midline; CPz: Centroparietal midline; Pz: Parietal midline.
- Citation: Wang HY, Li LZ, Chang Y, Pang XM, Zhang BW. Impaired implicit emotion regulation in patients with panic disorder: An event-related potential study on affect labeling. World J Psychiatry 2024; 14(2): 234-244
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2220-3206/full/v14/i2/234.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5498/wjp.v14.i2.234