Copyright
©The Author(s) 2024.
World J Psychiatry. Jan 19, 2024; 14(1): 53-62
Published online Jan 19, 2024. doi: 10.5498/wjp.v14.i1.53
Published online Jan 19, 2024. doi: 10.5498/wjp.v14.i1.53
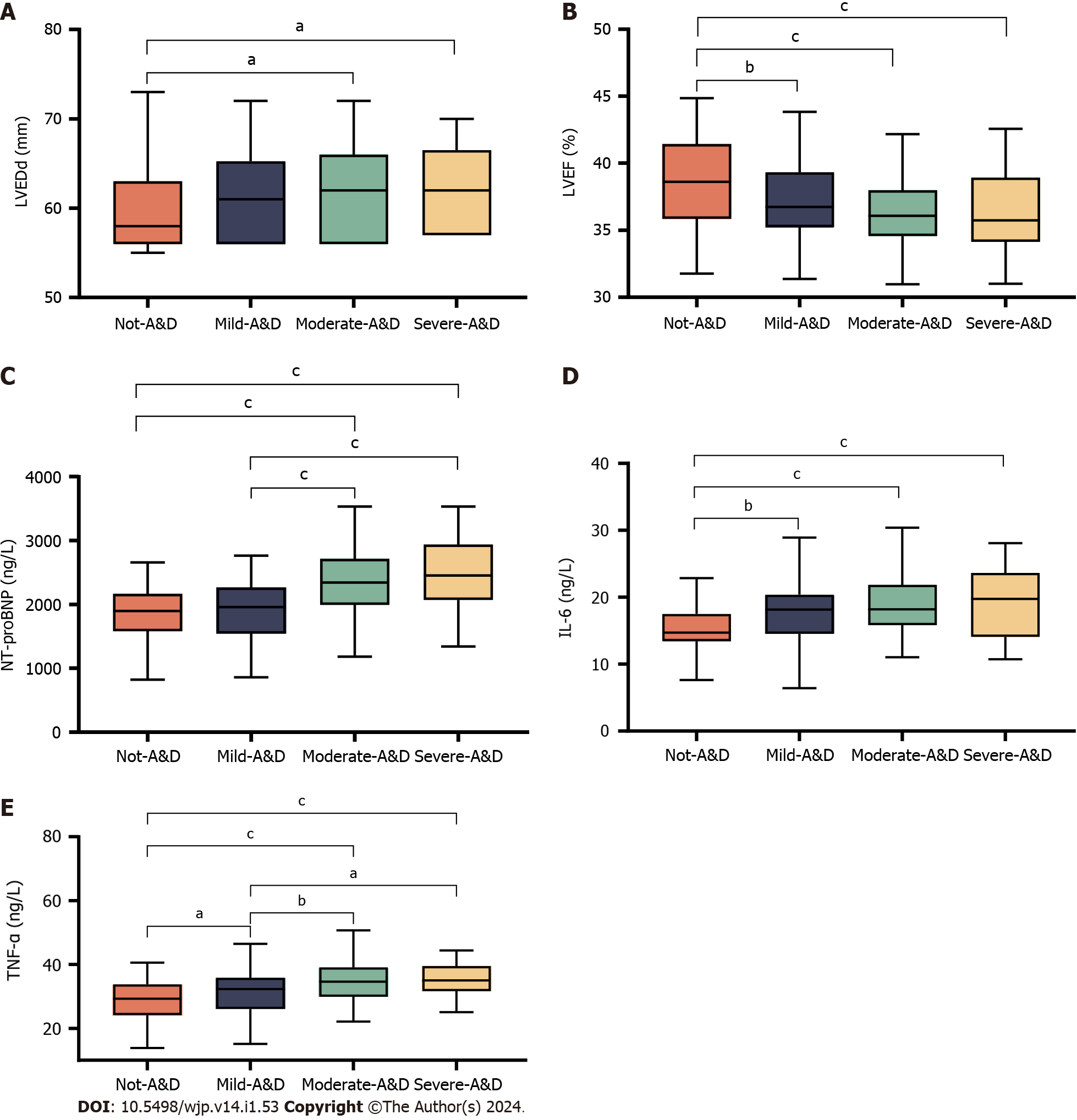
Figure 1 Post hoc multiple comparisons of significant influencing factors in patients with different levels of anxiety and depression.
A: Post hoc multiple comparisons of the left ventricular ejection fraction; B: Post hoc multiple comparisons of the left ventricular end-diastolic dimensions; C: Post hoc multiple comparisons of N-terminal pro-brain natriuretic peptide; D: Post hoc multiple comparisons of interleukin-6; E: Post hoc multiple comparisons of tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α). aP < 0.05, bP < 0.01, cP < 0.001. A&D: Anxiety and depression; No-A&D: No anxiety and depression symptoms; Mild-A&D: Mild anxiety and depression symptoms; Moderate-A&D: Moderate anxiety and depression symptoms; Severe-A&D: Severe anxiety and depression symptoms; LVEF: Left ventricular ejection fraction; LVEDd: Left ventricular end-diastolic dimensions; NT-proBNP: N-terminal pro-brain natriuretic peptide; TNF-α: Tumor necrosis factor-alpha; IL-6: Interleukin-6.
- Citation: Zhang L, Wang Q, Cui HS, Luo YY. Assessing myocardial indices and inflammatory factors to determine anxiety and depression severity in patients with chronic heart failure. World J Psychiatry 2024; 14(1): 53-62
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2220-3206/full/v14/i1/53.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5498/wjp.v14.i1.53