Copyright
©The Author(s) 2022.
World J Psychiatry. Feb 19, 2022; 12(2): 308-322
Published online Feb 19, 2022. doi: 10.5498/wjp.v12.i2.308
Published online Feb 19, 2022. doi: 10.5498/wjp.v12.i2.308
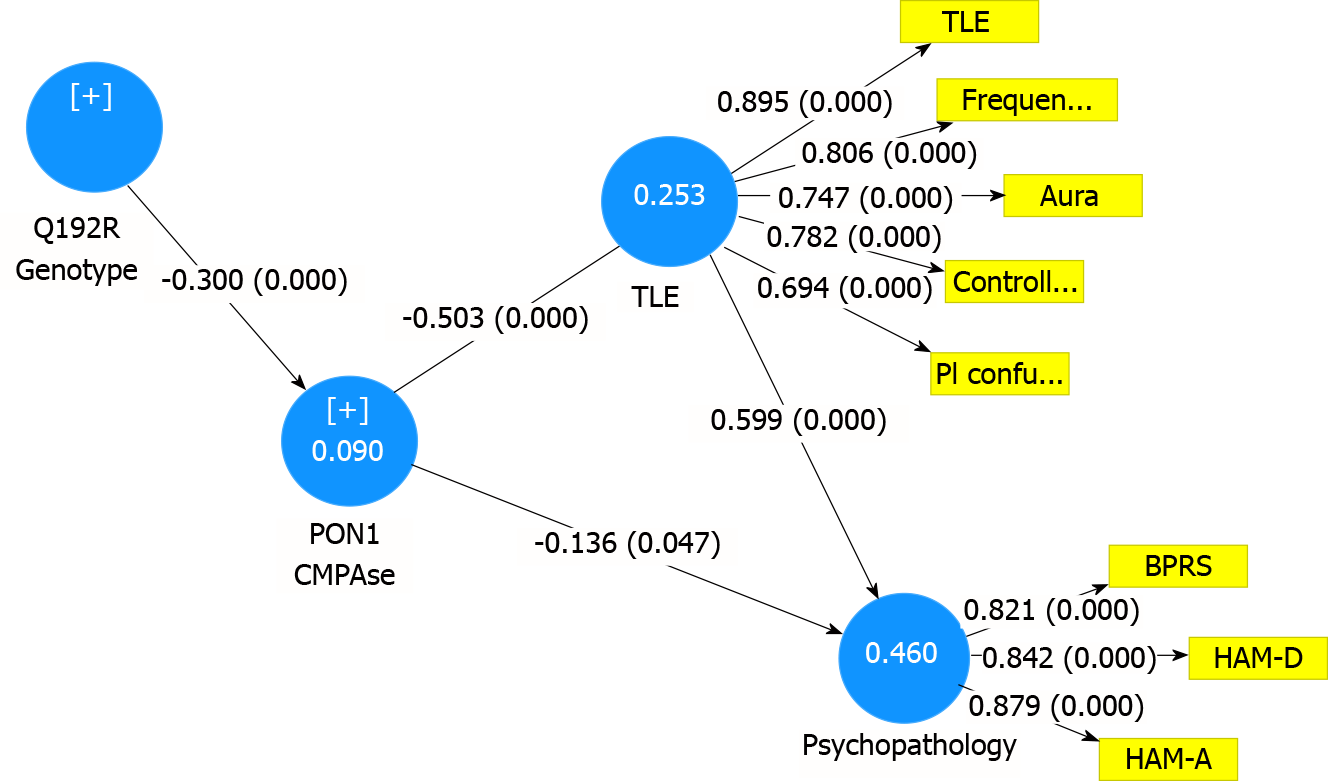
Figure 3 Results of partial least squares path analysis with a latent vector extracted from three psychopathology dimensions as outcome variable and a latent vector extracted from temporal lobe epilepsy features, paraoxonase 1 activity and the Q19R paraoxonase 1 genotype (additive model) as input variables.
Shown are path coefficient with P value (between brackets). Frequency: Seizure frequency; Aura: Aura present or not; Controlled: Seizure free and fairly and poorly controlled seizures; PI confusion: History of post-ictal confusion; BPRS: Brief Psychiatric Rating Scale; HAM-D/HAM-A: Hamilton Depression and Anxiety Rating Scale scores; TLE: Temporal lobe epilepsy; CMPAase: 4-(chloromethyl)phenyl acetate hydrolysis.
- Citation: Michelin AP, Maes MHJ, Supasitthumrong T, Limotai C, Matsumoto AK, de Oliveira Semeão L, de Lima Pedrão JV, Moreira EG, Kanchanatawan B, Barbosa DS. Reduced paraoxonase 1 activities may explain the comorbidities between temporal lobe epilepsy and depression, anxiety and psychosis. World J Psychiatry 2022; 12(2): 308-322
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2220-3206/full/v12/i2/308.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5498/wjp.v12.i2.308