Copyright
©The Author(s) 2022.
World J Psychiatry. Jan 19, 2022; 12(1): 77-97
Published online Jan 19, 2022. doi: 10.5498/wjp.v12.i1.77
Published online Jan 19, 2022. doi: 10.5498/wjp.v12.i1.77
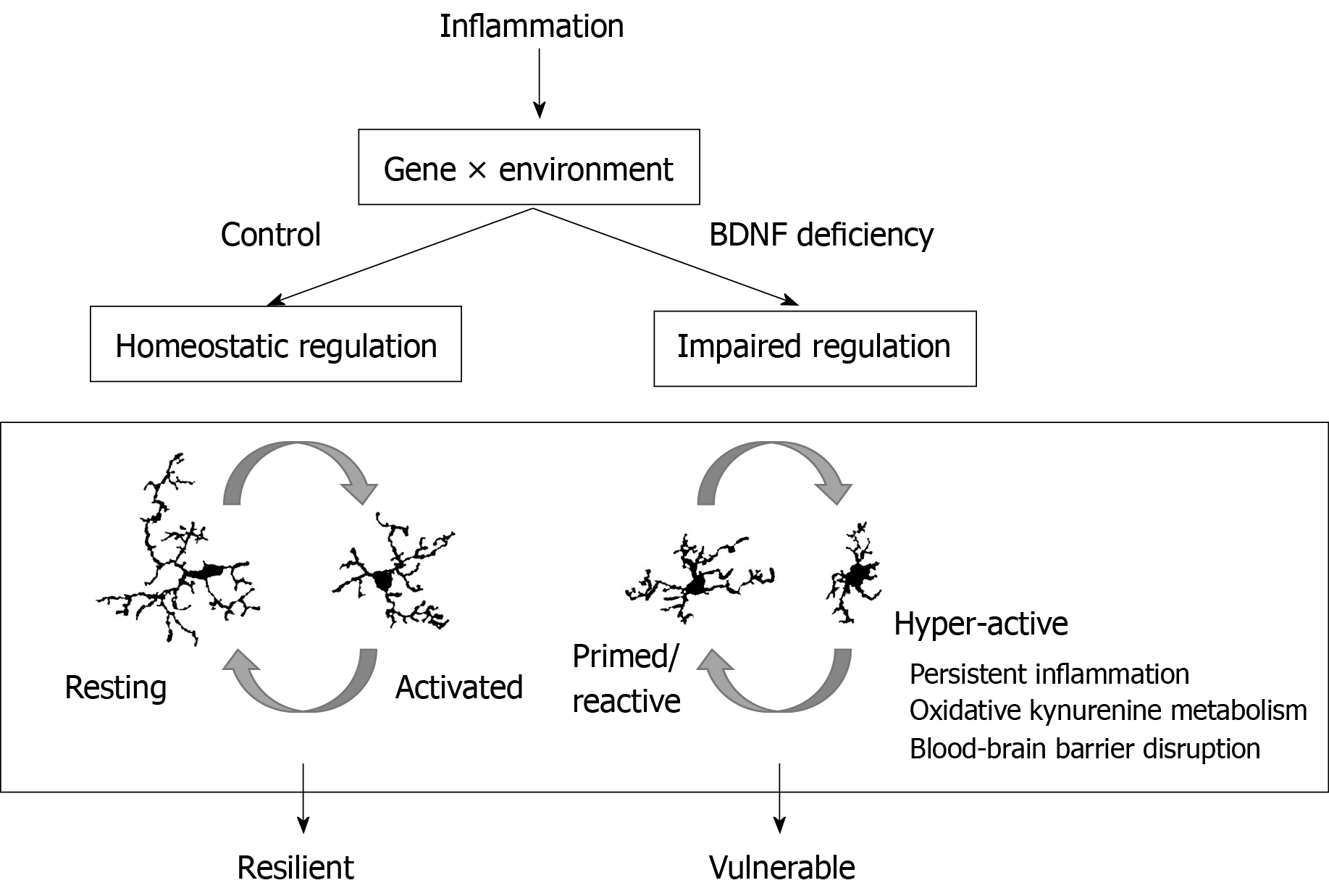
Figure 4 Brain-derived neurotrophic factor deficiency impairs resolution of microglial inflammatory phenotypes.
Brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) levels are altered by genetics and environmental circumstances. Reduced levels of BDNF impair microglia regulation after inflammation. Hyper-active microglia contribute to blood-brain barrier disruption and express higher levels of pro-inflammatory cytokines and kynurenine metabolism pathway enzymes. Individuals with hyper-active microglia are vulnerable to developing symptoms of depression after inflammatory challenge. BDNF: Brain-derived neurotrophic factor.
- Citation: Porter GA, O’Connor JC. Brain-derived neurotrophic factor and inflammation in depression: Pathogenic partners in crime? World J Psychiatry 2022; 12(1): 77-97
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2220-3206/full/v12/i1/77.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5498/wjp.v12.i1.77