Copyright
©The Author(s) 2022.
World J Psychiatry. Jan 19, 2022; 12(1): 77-97
Published online Jan 19, 2022. doi: 10.5498/wjp.v12.i1.77
Published online Jan 19, 2022. doi: 10.5498/wjp.v12.i1.77
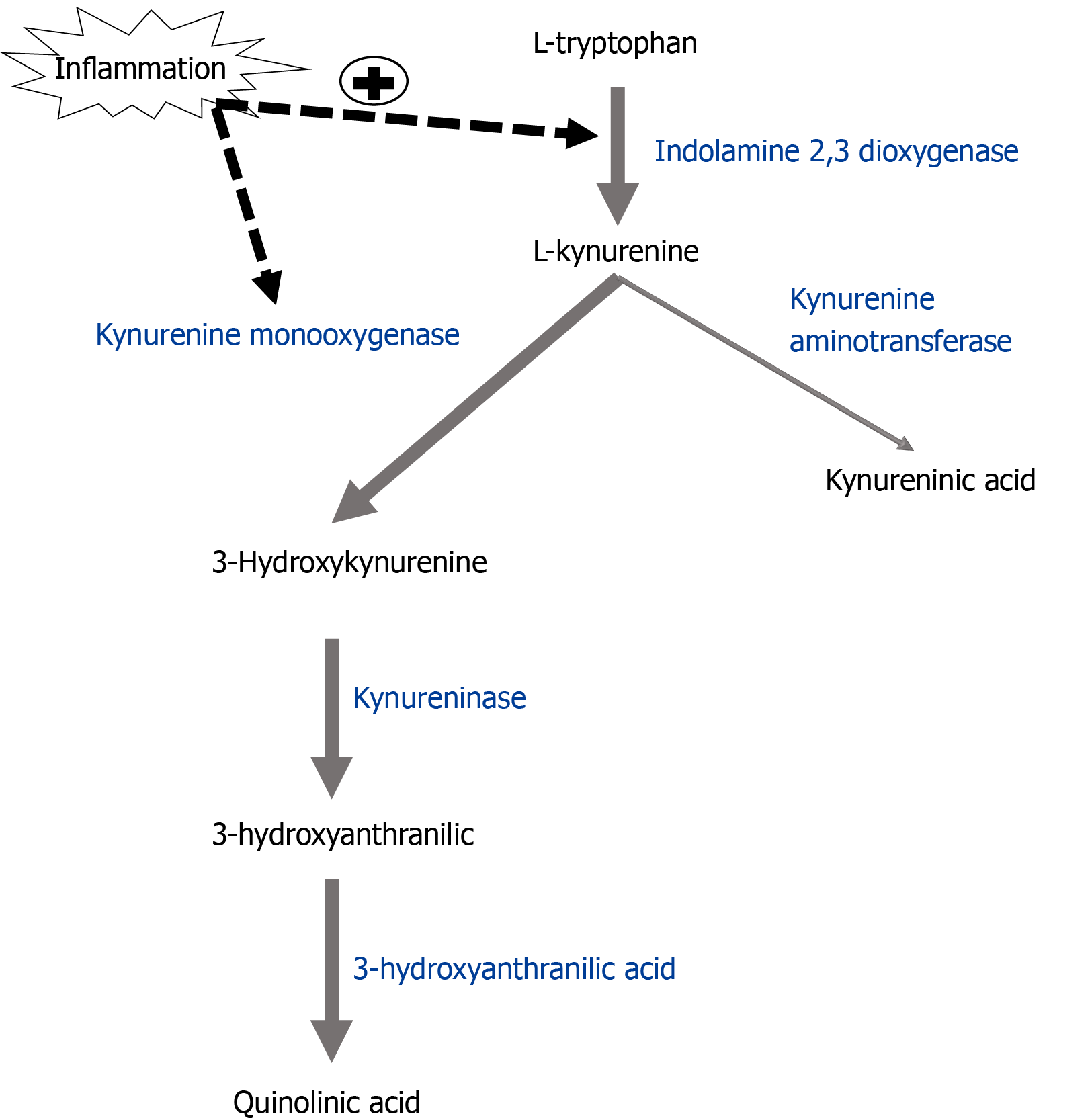
Figure 3 Inflammation shifts kynurenine metabolism pathway towards oxidative stress-associated metabolites.
The enzyme indolamine-2,3-dioxygenase (IDO) converts tryptophan to kynurenine. Kynurenine aminotransferase converts kynurenine to kynureninic acid in astrocytes while kynurenine monooxygenase (KMO) metabolizes kynurenine to 3-hyroxykynurenine (3-HK) in microglia. 3-HK is metabolized by kynureninase to 3-hydroxyanthranilic acid and 3-hydroxyanthranilic acid dioxygenase to quinolinic acid. Inflammation up-regulates the enzymes IDO and KMO, resulting in increased levels of KMO-dependent metabolites associated with oxidative stress and depression. IDO: Indolamine-2,3-dioxygenase; KAT: Kynurenine aminotransferase; KMO: Kynurenine monooxygenase; 3-HK: 3-hyroxykynurenine; KYNU: Kynureninase; HAAO: 3-hydroxyanthranilic acid dioxygenase; QA: Quinolinic acid.
- Citation: Porter GA, O’Connor JC. Brain-derived neurotrophic factor and inflammation in depression: Pathogenic partners in crime? World J Psychiatry 2022; 12(1): 77-97
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2220-3206/full/v12/i1/77.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5498/wjp.v12.i1.77