Copyright
©The Author(s) 2021.
World J Psychiatr. Nov 19, 2021; 11(11): 1075-1094
Published online Nov 19, 2021. doi: 10.5498/wjp.v11.i11.1075
Published online Nov 19, 2021. doi: 10.5498/wjp.v11.i11.1075
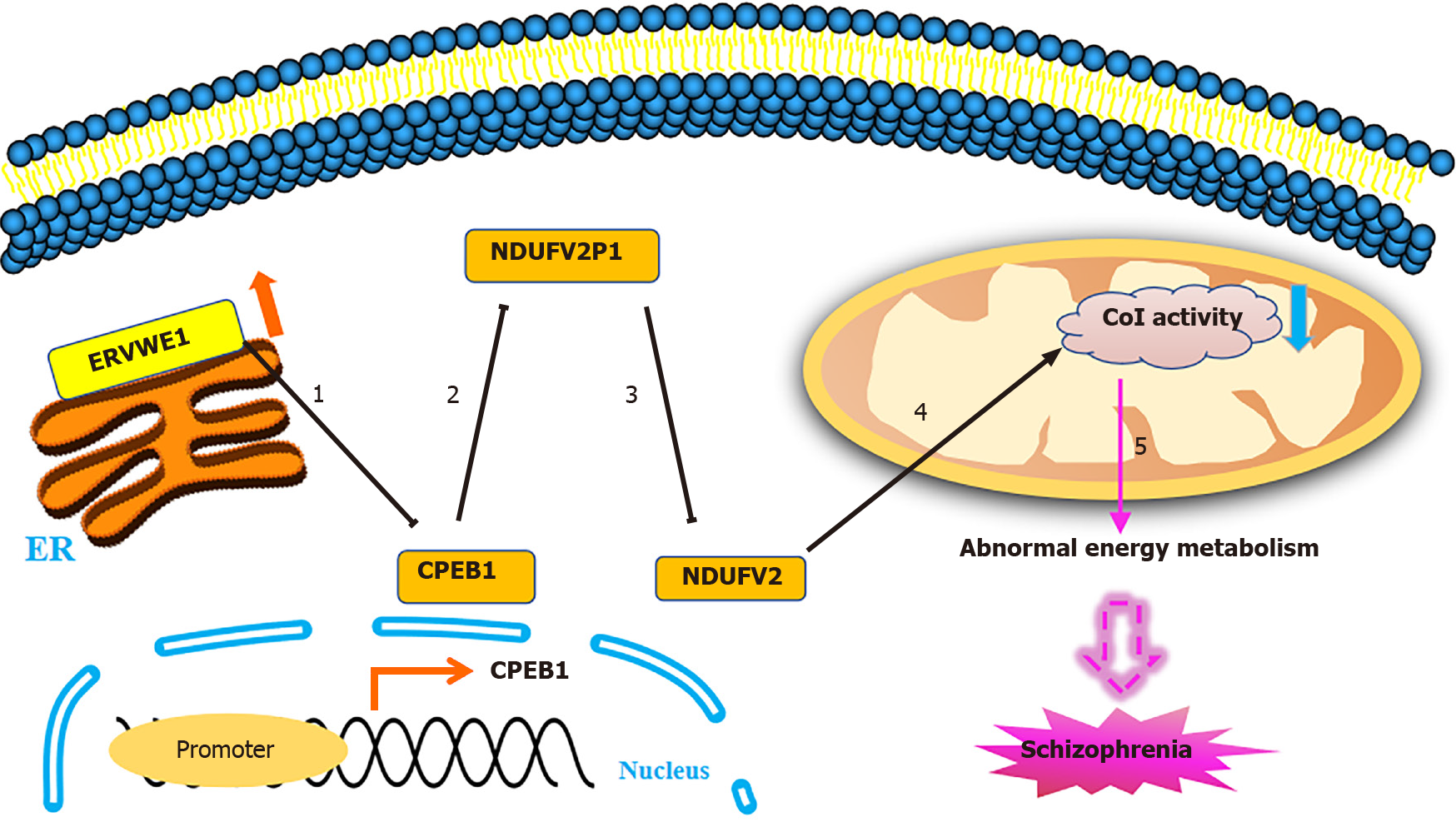
Figure 7 The proposed signaling pathways for ERVWE1 contributes to mitochondrial energy metabolism deficiency in schizophrenia.
1: ERVWE1 suppressed cytoplasmic polyadenylation element-binding protein 1 (CPEB1) mRNA and protein expression by regulating its promoter activity; 2: ERVWE1 upregulated the expression of NADH dehydrogenase ubiquinone flavoprotein 2 (NDUFV2) pseudogene (NDUFV2P1) through enhancing its promoter activity. CPEB1 downregulated NDUFV2P1 expression and functioned as a mediator of NDUFV2P1 transcript induced by ERVWE1; 3: NDUFV2P1 reduced NDUFV2 expression through inhibiting its promoter activation. Additionally, ERVWE1 decreased the mRNA and protein expression of NDUFV2 and suppressed NDUFV2 promoter through increasing NDUFV2P1 transcript. Moreover, CPEB1 was involved in regulating NDUFV2P1/NDUFV2 signaling pathway triggered by ERVWE1; 4: ERVWE1 reduced complex I activity via regulating NDUFV2 and its retrocopies expression. Decreased CPEB1 was involved in the complex I activity deficiency induced by ERVWE1; 5: Deficient complex I activity might result in mitochondrial metabolic dysregulation and contributed to the development of schizophrenia.
- Citation: Xia YR, Wei XC, Li WS, Yan QJ, Wu XL, Yao W, Li XH, Zhu F. CPEB1, a novel risk gene in recent-onset schizophrenia, contributes to mitochondrial complex I defect caused by a defective provirus ERVWE1. World J Psychiatr 2021; 11(11): 1075-1094
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2220-3206/full/v11/i11/1075.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5498/wjp.v11.i11.1075